Abstract
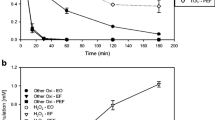
The electrochemical degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride (TeC) was comparatively investigated in artificial urine and chloride-containing media using a one-compartment filter-press flow cell composed of a Ti/Ru0.3Ti0.7O2 dimensionally stable anode. The effect of the current density (10–40 mA cm−2) on the removal levels attained for TeC and total organic carbon (TOC) (in both media), as well as for urea and creatinine in artificial urine medium, was assessed. The TeC removal rate in the artificial urine medium was much lower than in chloride-containing medium, probably due to the higher consumption of the electrogenerated active chlorine species by the urea and creatinine in the artificial urine medium. Moreover, the obtained removal levels for the urea and creatinine were negligible at current densities lower than 30 mA cm−2. As TOC abatement was also very small, it is possible that TeC oxidation leads to intermediate compounds. Thus, if current densities less than 20 mA cm−2 are applied, TeC can be selectively removed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nogrady T, Weaver DF (2005) Medicinal chemistry: a molecular and biochemical approach, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press Inc., New York
Korolkovas A, Burckhalter JH (1982) Química farmacêutica. Guanabara Dois S.A, Rio de Janeiro
Sarmah AK, Meyer MT, Boxall ABA (2006) A global perspective on the use, sales, exposure pathways, occurrence, fate and effects of veterinary antibiotics (VAs) in the environment. Chemosphere 65:725–759
Mitema ES, Kikuvi GM, Wegener HC, Stohr K (2001) An assessment of antimicrobial consumption in food producing animals in Kenya. J Vet Pharmacol Ther 24:385–390
Charest MG, Lerner CD, Brubaker JD, Siegel DR, Myers AG (2005) A convergent enantioselective route to structurally diverse 6-deoxytetracycline antibiotics. Science 308:395–398
Nelson ML, Levy SB (2011) The history of the tetracyclines. Ann NY Acad Sci 124:17–32
Cunha BA, Garabedian-Buffalo SM (1990) Tetracyclines in urology: current concepts. Urology 36:548–556
Witte W (1998) Medical consequences of antibiotic use in agriculture. Science 279:996–997
Betteridge T, Merlino J, Natoli J, Cheong EY, Gottlieb T, Stokes HW (2013) Plasmids and bacterial strains mediating multidrug-resistant hospital-acquired infections are coresidents of the hospital environment. Microb Drug Resist 19:104–109
Du L, Liu W (2012) Occurrence, fate, and ecotoxicity of antibiotics in agro-ecosystems. A review. Agron Sustain Dev 32:309–327
Brigante M, Schulz PC (2012) Adsorption of the antibiotic minocycline on cerium(IV) oxide: effect of pH, ionic strength and temperature. Micropor Mesopor Mater 156:138–144
Huet AC, Charlier C, Singh G, Godefroy SB, Leivo J, Vehniäinen M, Nielen MW, Weigel S, Delahaut P (2008) Development of an optical surface plasmon resonance biosensor assay for (fluoro)quinolones in egg, fish, and poultry meat. Anal Chim Acta 623:195–203
Allison JRD (1985) Antibiotic residues in milk. Brit Vet J 141:9–16
Wen X, Jia Y, Li J (2010) Enzymatic degradation of tetracycline and oxytetracycline by crude manganese peroxidase prepared from Phanerochaete chrysosporium. J Hazar Mater 177:924–928
Prado N, Ochoa J, Amrane A (2009) Biodegradation by activated sludge and toxicity of tetracycline into a semi-industrial membrane bioreactor. Bioresour Technol 100:3769–3774
Liu S, X-r Z, H-y S, R-p L, Y-f F, Y-p H (2013) The degradation of tetracycline in a photo-electro-Fenton system. Chem Eng J 231:441–448
Homem V, Alves A, Santos L (2013) Microwave-assisted Fenton’s oxidation of amoxicillin. Chem Eng J 220:35–44
El-Ghenymy A, Oturan N, Oturan MA, Garrido JA, Cabot PL, Centellas F, Rodríguez RM, Brillas E (2013) Comparative electro-Fenton and UVA photoelectro-Fenton degradation of the antibiotic sulfanilamide using a stirred BDD/air-diffusion tank reactor. Chem Eng J 234:115–123
Orbeci C, Untea I, Nechifor G, Segneanu AE, Craciun ME (2014) Effect of a modified photo-Fenton procedure on the oxidative degradation of antibiotics in aqueous solutions. Sep Purif Technol 122:290–296
Rajeshwar K, Ibanez JG, Swain GM (1994) Electrochemistry and the environment. J Appl Electrochem 24:1077–1091
Comninellis C (1994) Electrocatalysis in the electrochemical conversion/combustion of organic pollutants for waste water treatment. Electrochim Acta 39:1857–1862
Wu J, Zhang H, Oturan N, Wang Y, Chen L, Oturan MA (2012) Application of response surface methodology to the removal of the antibiotic tetracycline by electrochemical process using carbon-felt cathode and DSA (Ti/RuO2–IrO2) anode. Chemosphere 87:614–620
Zhang H, Liu F, Wu X, Zhang J, Zhang D (2009) Degradation of tetracycline in aqueous medium by electrochemical method. Asia‐Pac J Chem Eng 4:568–573
Turro E, Giannis A, Cossu R, Gidarakos E, Mantzavinos D, Katsaounis A (2012) Reprint of: electrochemical oxidation of stabilized landfill leachate on DSA electrodes. J Hazar Mater 207–208:73–78
Scialdone O, Randazzo S, Galia A, Silvestri G (2009) Electrochemical oxidation of organics in water: role of operative parameters in the absence and in the presence of NaCl. Water Res 43:2260–2272
Rodríguez FA, Rivero EP, Lartundo-Rojas L, González I (2014) Preparation and characterization of Sb2O5-doped Ti/RuO2-ZrO2 for dye decolorization by means of active chlorine. J Solid State Electrochem 18:3153–3162
Malpass GRP, Miwa DW, Santos RL, Vieira EM, Motheo AJ (2012) Unexpected toxicity decrease during photoelectrochemical degradation of atrazine with NaCl. Environ Chem Lett 10:177–182
Fornazari ALT, Malpass GRP, Miwa DW, Motheo AJ (2012) Application of electrochemical degradation of wastewater composed of mixtures of phenol-formaldehyde. Water Air Soil Poll 223:4895–4904
Kitazono Y, Ihara I, Yoshida G, Toyoda K, Umetsu K (2012) Selective degradation of tetracycline antibiotics present in raw milk by electrochemical method. J Hazar Mater 243:112–116
Laube N, Mohr B, Hesse A (2001) Laser-probe-based investigation of the evolution of particle size distributions of calcium oxalate particles formed in artificial urines. J Cryst Growth 233:367–374
Malpass GRP, Miwa DW, Mortari DA, Machado SAS, Motheo AJ (2007) Decolorization of real textile waste using electrochemical techniques: effect of the chloride concentration. Water Res 41:2969–2977
Malpass GRP, Miwa DW, Machado SAS, Motheo AJ (2008) Decolourisation of real textile waste using electrochemical techniques: effect of electrode composition. J Hazar Mater 156:170–177
Gomes L, Miwa DW, Malpass GRP, Motheo AJ (2011) Electrochemical degradation of the dye reactive orange 16 using electrochemical flow-cell. J Braz Chem Soc 22:1299–1306
Falcó PC, Genaro LAT, Lloret SM, Gomez FB, Cabeza AS, Legua CM (2001) Creatinine determination in urine samples by batchwise kinetic procedure and flow injection analysis using the Jaffé reaction: chemometric study. Talanta 55:1079–1089
Knorst MT, Neubert R, Wohlrab W (1997) Analytical methods for measuring urea in pharmaceutical formulations. J Pharm Biomed Anal 15:1627–1632
Rossi A, Alves VA, Da Silva LA, Oliveira MA, Assis DOS, Santos FA, De Miranda RRS (2009) Electrooxidation and inhibition of the antibacterial activity of oxytetracycline hydrochloride using a RuO2 electrode. J Appl Electrochem 39:329–337
Cheng CY, Kelsall GH (2007) Models of Hypochlorite production in electrochemical reactors with plate and porous anodes. J Appl Electrochem 37:1203–1217
Cañizares P, García-Gómez J, De Marcos IF, Rodrigo MA, Lobato J (2006) Measurement of mass-transfer coefficient by an electrochemical technique. J Chem Educ 83:1204–1207
Deborde M, von Gunten U (2008) Reactions of chlorine with inorganic and organic compounds during water treatment-kinetics and mechanisms: a critical review. Water Res 42:13–51
Wang P, He Y-L, Huang C-H (2011) Reactions of tetracycline antibiotics with chlorine dioxide and free chlorine. Water Res 45:1838–1846
Rocha J, Solano A, Fernandes N, Silva D, Peralta-Hernandez J, Martínez-Huitle CA (2012) Electrochemical degradation of Remazol Red BR and Novacron Blue C-D dyes using diamond electrode. Electrocatalysis 3:1–12
Brigante M, Schulz PC (2011) Remotion of the antibiotic tetracycline by titania and titania–silica composed materials. J Hazar Mater 192:1597–1608
Gu C, Karthikeyan KG, Sibley SD, Pedersen JA (2007) Complexation of the antibiotic tetracycline with humic acid. Chemosphere 66:1494–1501
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Brazilian research funding agencies, the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), and the Federal Agency for the Support and Improvement of Higher Education (CAPES) for the financial support. Saima Gul thanks the TWAS-CNPq Fellowship Programme for Postgraduate Research grant. De Nora do Brazil is also gratefully acknowledged for supplying the DSA® samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parra, K.N., Gul, S., Aquino, J.M. et al. Electrochemical degradation of tetracycline in artificial urine medium. J Solid State Electrochem 20, 1001–1009 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-015-2833-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-015-2833-8