Abstract
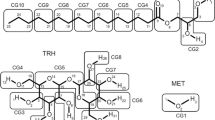
Fully atomistic molecular dynamics simulation studies of thermotropic bilayers were performed using a set of glycosides namely n-octyl-β-D-glucopyranoside (β-C8Glc), n-octyl-α-D-glucopyranoside (α-C8Glc), n-octyl-β-D-galactopyranoside (β-C8Gal), and n-octyl-α-D-galactopyranoside (α-C8Gal) to investigate the stereochemical relationship of the epimeric/anomeric quartet liner glycolipids with the same octyl chain group. The results showed that, the anomeric stereochemistry or the axial/equatorial orientation of C1–O1 (α/β) is an important factor controlling the area and d-spacing of glycolipid bilayer systems in the thermotropic phase. The head group tilt angle and the chain ordering properties are affected by the anomeric effect. In addition, the LC phase of β-C8Gal, is tilting less compared to those in the fluid Lα. The stereochemistry of the C4-epimeric (axial/equatorial) and anomeric (α/β) centers simultaneously influence the inter-molecular hydrogen bond. Thus, the trend in the values of the hydrogen bond for these glycosides is β-C8Gal > α-C8Glc > β-C8Glc > α-C8Gal. The four bilayer systems showed anomalous diffusion behavior with an observed trend for the diffusion coefficients; and this trend is β-C8Gal > β-C8Glc > α-C8Gal > α-C8Glc. The “bent” configuration of the α-anomer results in an increase of the hydrophobic area, chain vibration and chain disorganization. Since thermal energy is dispensed more entropically for the chain region, the overall molecular diffusion decreases.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shallenberger RS (1982) Sugar chemistry. AVI, Westport
Hashim R, Sugimura A, Minamikawa H, Heidelberg T (2012) Nature-like synthetic alkyl branched-chain glycolipids: a review on chemical structure and self-assembly properties. Liq Cryst 39(1):1–17
Seddon JM, Ces O, Templer RH, Mannock DA, McElhaney RN (2003) Structure and phase behaviour of synthetic glycolipids. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst 402(1):77–84
Vill V, Hashim R (2002) Carbohydrate liquid crystals: structure-property relationship of thermotropic and lyotropic glycolipids. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 7(5):395–409
Barón M (2001) Definitions of basic terms relating to low-molar-mass and polymer liquid crystals. Pure Appl Chem 73(5):845–895
Lawrence MJ (1994) Surfactant systems: their use in drug delivery. Chem Soc Rev 23(6):417–424
Sakya P, Seddon JM, Vill V (1997) Thermotropic and lyotropic phase behaviour of monoalkyl glycosides. Liq Cryst 23(3):409–424
Balzer D, Luders H (2000) Nonionic surfactants: Alkyl polyglucosides. Dekker, New York
Abel S, Dupradeau F-Y, Raman EP, MacKerell AD Jr, Marchi M (2011) Molecular simulations of dodecyl-β-maltoside micelles in water: Influence of the headgroup conformation and force field parameters. J Phys Chem B 115(3):487–499
Hashim R, Mirzadeh SM, Heidelberg T, Minamikawa H, Yoshiaki T, Sugimura A (2011) A reevaluation of the epimeric and anomeric relationship of glucosides and galactosides in thermotropic liquid crystal self-assemblies. Carbohydr Res 346:2948–2956
Boyd BJ, Drummond CJ, Krodkiewska I, Grieser F (2000) How chain length, headgroup polymerization, and anomeric configuration govern the thermotropic and lyotropic liquid crystalline phase behavior and the air-water interfacial adsorption of glucose-based surfactants. Langmuir 16(19):7359–7367
Luzzati V (1968) X-ray diffraction studies of lipid-water systems. In: Chapman D (ed) Biological membranes, vol 1. Academic, London, pp 71–123
Chong TT, Heidelberg T, Hashim R, Gary S (2007) Computer modelling and simulations of thermotropic and lyotropic alkyl glycoside bilayers. Liq Cryst 34(3):267–281
Ane'zo C, de Vries AH, Holltje H-D, Tieleman DP, Marrink S-J (2003) Methodological issues in lipid bilayer simulations. J Phys Chem B 107(35):9424–9433
Pedersen A, Henkelman G, Schiøtz J, Jónsson H (2009) Long time scale simulation of a grain boundaryin copper. New J Phys. doi:10.1088/1367-2630/11/7/073034
Kocherbitov V, Söderman O (2003) Phase diagram and physicochemical properties of the n-octyl α-D-glucoside/water system. Phys Chem Chem Phys 5(23):5262–5270
Ericsson CA, Ericsson LC, Kocherbitov V, Söderman O, Ulvenlund S (2005) Thermotropic phase behaviour of long-chain alkylmaltosides. Phys Chem Chem Phys 7(15):2970–2977
Elder M, Hitchcock P, Mason R, Shipley G (1977) A refinement analysis of the crystallography of the phospholipid, 1, 2-dilauroyl-DL-phosphatidylethanolamine, and some remarks on lipid-lipid and lipid-protein interactions. Proc R Soc Lond A Mat 354(1677):157–170
Hitchcock PB, Mason R, Thomas KM, Shipley GG (1974) Structural chemistry of 1, 2 dilauroyl-DL-phosphatidylethanolamine: molecular conformation and intermolecular packing of phospholipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 71(8):3036–3040
Pearson RH, Pascher I (1979) The molecular structure of lecithin dihydrate. Nature 281:499–501
Damodaran KV, Merz KM Jr, Gaber BP (1992) Structure and dynamics of the ilauroylphosphatidylethanolamine lipid bilayer. Biochemistry 31(33):7656–7664
van Meel JA, Arnold A, Frenkel D, Portegies Zwart SF, Belleman RG (2008) Harvesting graphics power for MD simulations. Mol Simul 34(3):259–266
Case DA, Darden TA, Cheatham TEI, Simmerling CL, Wang J, Duke RE, Luo R, Walker RC, Zhang W, Merz KM, Roberts BP, Wang B, Hayik S, Roitberg A, Seabra G, Kolossvai I, Wong KF, Paesani F, Vanicek J, Liu J, Wu X, Brozell SR, Steinbrecher T, Gohlke H, Cai Q, Ye X, Wang J, Hsieh M-J, Cui G, Roe DR, Mathews DH, Seetin MG, Sagui C, Babin V, Luchko T, Gusarov S, Kovalenko A, Kollman PA (2012) AMBER 12. University of California, San Francisco
Götz AW, Williamson MJ, Xu D, Poole D, Le Grand S, Walker RC (2012) Routine microsecond molecular dynamics simulations with AMBER on GPUs. 1. Generalized Born. J Chem Theory Comput 8(5):1542–1555
Kirschner KN, Yongye AB, Tschampel SM, González‐Outeiriño J, Daniels CR, Foley BL, Woods RJ (2008) GLYCAM06: a generalizable biomolecular force field. Carbohydrates. J Comput Chem 29(4):622–655
Manickam Achari V, Nguan HS, Heidelberg T, Bryce RA, Hashim R (2012) Molecular dynamics study of anhydrous lamellar structures of synthetic glycolipids: effects of chain branching and disaccharide headgroup. J Phys Chem B 106(38):11626–11634
Chong TT, Hashim R, Bryce RA (2006) Molecular dynamics simulation of monoalkyl glycoside micelles in aqueous solution: influence of carbohydrate headgroup stereochemistry. J Phys Chem B 110(10):4978–4984. doi:10.1021/jp056851g
Vishnyakov A, Widmalm G, Kowalewski J, Laaksonen A (1999) Molecular dynamics simulation of the α-D-Man p-(1 → 3)-β-D-Glc p-OMe disaccharide in water and water/DMSO solution. J Am Chem Soc 121(23):5403–5412
HyperChem(TM) (2003) Hypercube, Inc., Gainesville, FL
Martínez L, Andrade R, Birgin EG, Martínez JM (2009) Packmol: A package for building initial configurations for molecular dynamics simulations. J Comput Chem 30(13):2157–2164
Hornak V, Abel R, Okur A, Strockbine B, Roitberg A, Simmerling C (2006) Comparison of multiple Amber force fields and development of improved protein backbone parameters. Proteins Struct Funct Bioinform 65(3):712–725
Case DA, Pearlman DA, Caldwell JW, Cheatham III TE, Wang J, Ross WS, Simmerling C, Darden T, Merz KM, Stanton RV (2002) University of California, San Francisco
Gong Z, Zhao Y, Xiao Y (2010) RNA stability under different combinations of Amber force fields and solvation models. J Biomol Struct Dyn 28(3):431–441
Spasic A, Serafini J, Mathews DH (2012) The Amber ff99 force field predicts relative free energychanges for RNA helix formation. J Chem Theory Comput 8(7):2497–2505
Andrea TA, Swope WC, Andersen HC (1983) The role of long ranged forces in determining the structure and properties of liquid water. J Chem Phys 79:4576
Berendsen HJC, Postma JPM, van Gunsteren WF, DiNola A, Haak JR (1984) Molecular dynamics with coupling to an external bath. J Chem Phys 81(8):3684–3690
Feller SE, Zhang Y, Pastor RW, Brooks BR (1995) Constant pressure molecular dynamics simulation: The Langevin piston method. J Chem Phys 103(11):4613–4621
Darden T, York D, Pedersen L (1993) Particle mesh Ewald: An N⋅ log (N) method for Ewald sums in large systems. J Chem Phys 98:10089
Essmann U, Perera L, Berkowitz ML, Darden T, Lee H, Pedersen LG (1995) A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J Chem Phys 103(19):8577–8593
Miyamoto S, Kollman PA (1992) SETTLE: an analytical version of the SHAKE and RATTLE algorithm for rigid water models. J Comput Chem 13(8):952–962
Abou-Zied OK, Al-Lawatia N, Elstner M, Steinbrecher TB (2013) The binding of hydroxyquinoline probes to human serum albumin-combining molecular modeling and FRET spectroscopy to understand flexible ligand binding. J Phys Chem B117(4):1062–1074
Petrache HI, Tu K, Nagle JF (1999) Analysis of simulated NMR order parameters for lipid bilayer structure determination. Biophys J 76(5):2479–2487
Shinoda W, Namiki N, Okazaki S (1997) Molecular dynamics study of a lipid bilayer: convergence, structure, and long-time dynamics. J Chem Phys 106:5731
Shinoda W, Mikami M, Baba T, Hato M (2003) Molecular dynamics study on the effect of chain branching on the physical properties of lipid bilayers: structural stability. J Phys Chem B 107(50):14030–14035
Losonczi JA, Andrec M, Fischer MW, Prestegard JH (1999) Order matrix analysis of residual dipolar couplings using singular value decomposition. J Magn Reson 138(2):334–342
van der Ploeg P, Berendsen HJC (1982) Molecular dynamics simulation of a bilayer membrane. J Chem Phys 76(6):3271–3276
Róg T, Vattulainen I, Bunker A, Karttunen M (2007) Glycolipid membranes through atomistic simulations: effect of glucose and galactose head groups on lipid bilayer properties. J Phys Chem B 111(34):10146–10154
van Buuren AR, Berendsen HJC (1994) Molecular dynamics simulations of carbohydrate-based surfactants in surfactant/water/oil systems. Langmuir 10(6):1703–1713
Nagle JF, Tristram-Nagle S (2000) Lipid bilayer structure. Curr Opin Struct Biol 10(4):474–480
Nguan HS, Heidelberg T, Hashim R, Tiddy GJT (2010) Quantitative analysis of the packing of alkyl glycosides: a comparison of linear and branched alkyl chains. Liq Cryst 37(9):1205–1213
Auvray X, Petipas C, Dupuy C, Louvet S, Anthore R, Rico-Lattes I, Lattes A (2001) Small-angle X-ray diffraction study of the thermotropic and lyotropic phases of five alkyl cyclic and acyclic disaccharides: Influence of the linkage between the hydrophilic and hydrophobic moieties. Eur Phys J E 4(4):489–504
Dorset DL (1990) Anomeric exchange and the structure of n-alkyl D-glucopyranosides. A study of binary phase behavior. Carbohydr Res 206(2):193–205
Nilsson F, Söderman O, Johansson I (1996) Physical-chemical properties of the n-octyl β-D-glucoside/water system. A phase diagram, self-diffusion NMR, and SAXS study. Langmuir 12(4):902–908
Kocherbitov V, Söderman O, Wadsö L (2002) Phase diagram and thermodynamics of the n-octyl β-D-glucoside/water system. J Phys Chem B 106(11):2910–2917
Seddon JM, Cevc G (1993) Lipid Polymorphism: Structure and Stability of Lyotropic Mesophases of Phospholipids. In: Cevc G (ed) Phospholipids Handbook. CRC, New York, pp 403–454
Ericsson CA, Ericsson LC, Ulvenlund S (2005) Solid-state phase behaviour of dodecylglycosides. Carbohydr Res 340(8):1529–1537
Jimenez-Barbero J, Junquera E, Martin-Pastor M, Sharma S, Vicent C, Penades S (1995) Molecular recognition of carbohydrates using a synthetic receptor. A model system to understand the stereoselectivity of a carbohydrate-carbohydrate interaction in water. J Am Chem Soc 117(45):11198–11204
Balasubramanian D, Raman B, Sundari CS (1993) Polysaccharides as amphiphiles. J Am Chem Soc 115(1):74–77
Pascher I (1976) Molecular arrangements in sphingolipids. Conformation and hydrogen bonding of ceramide and their implication on membrane stability and permeability. Biochim Biophys Acta 455(2):433–451
Kotena ZM, Behjatmanesh-Ardakani R, Hashim R, Achari VM (2013) Hydrogen bonds in galactopyranoside and glucopyranoside: a density functional theory study. J Mol Model 19(2):589–599
Mouritsen OG, Jørgensen K (1994) Dynamical order and disorder in lipid bilayers. Chem Phys Lipids 73(1):3–25
Marčelja S (1974) Chain ordering in liquid crystals: II. Structure of bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 367(2):165–176
Seelig J (1977) Deuterium magnetic resonance: theory and application to lipid membranes. Q Rev Biophys 10(3):353–418
Damodaran K, Merz KM Jr (1994) A comparison of DMPC-and DLPE-based lipid bilayers. Biophys J 66(4):1076–1087
Muddana HS, Gullapalli RR, Manias E, Butler PJ (2011) Atomistic simulation of lipid and DiI dynamics in membrane bilayers under tension. Phys Chem Chem Phys 13(4):1368–1378
Jeon JH, Monne HMS, Javanainen M, Metzler R (2012) Anomalous diffusion of phospholipids and cholesterols in a lipid bilayer and its origins. Phys Rev Lett 109(18):188103
Guigas G, Weiss M (2008) Sampling the cell with anomalous diffusion - the discovery of slowness. Biophys J 94(1):90–94
Lomholt MA, Zaid IM, Metzler R (2007) Subdiffusion and weak ergodicity breaking in the presence of a reactive boundary. Phys Rev Lett 98(20):200603
Bronstein I, Israel Y, Kepten E, Mai S, Shav-Tal Y, Barkai E, Garini Y (2009) Transient anomalous diffusion of telomeres in the nucleus of mammalian cells. Phys Rev Lett 103(1):018102
Shinoda W, Mikami M, Baba T, Hato M (2004) Dynamics of a highly branched lipid bilayer: a molecular dynamics study. Chem Phys Lett 390(1):35–40
Baba T, Minamikawa H, Hato M, Handa T (2001) Hydration and molecular motions in synthetic phytanyl-chained glycolipid vesicle membranes. Biophys J 81(6):3377–3386
Wu J, Berland KM (2008) Propagators and time-dependent diffusion coefficients for anomalous diffusion. Biophys J 95(4):2049–2052
Acknowledgments
The grants from the University of Malaya RG072-09AFR and the Ministry of Higher Education UM.C/625/1/HIR/MOHE/05 supported this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 48 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmadi, S., Manickam Achari, V., Nguan, H. et al. Atomistic simulation studies of the α/β-glucoside and galactoside in anhydrous bilayers: effect of the anomeric and epimeric configurations. J Mol Model 20, 2165 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-014-2165-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00894-014-2165-0