Abstract
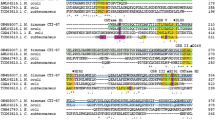
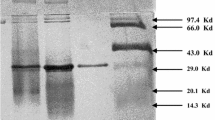
A cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase (CGTase, EC 2.4.1.19) was successfully isolated and characterized from the halophilic archaeon Haloferax mediterranei. The enzyme is a monomer with a molecular mass of 77 kDa and optimum activity at 55°C, pH 7.5 and 1.5 M NaCl. The enzyme displayed many activities related to the degradation and transformation of starch. Cyclization was found to be the predominant activity, yielding a mixture of cyclodextrins, mainly α-CD, followed by hydrolysis and to a lesser extent coupling and disproportionation activities. Gene encoding H. mediterranei CGTase was cloned and heterologously overexpressed. Sequence analysis revealed an open reading frame of 2142 bp that encodes a protein of 713 amino acids. The amino acid sequence displayed high homology with those belonging to the α-amylase family. The CGTase is secreted to the extracellular medium by the Tat pathway. Upstream of the CGTase gene, four maltose ABC transporter genes have been sequenced (malE, malF, malG, malK). The expression of the CGTase gene yielded a fully active CGTase with similar kinetic behavior to the wild-type enzyme. The H. mediterranei CGTase is the first halophilic archaeal CGTase characterized, sequenced and expressed.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcalde M, Plou FJ, Pérez-Boada M, García-Arellano H, Valdés I, Méndez E, Ballesteros A (2003) Chemical modification of carboxylic residues in a cyclodextrin glucanotransferase and its implication in the hydrolysis/transglycosylation ratio of the α-amylase family. J Mol Cat B Enzym 26:57–67
Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K (1995) Short protocols in molecular biology. Wiley, USA
Bonete MJ, Pire C, Llorca FI, Camacho ML (1996) Glucose dehydrogenase from the halophilic Archaeon Haloferax mediterranei: enzyme purification, characterisation and N-terminal sequence. FEBS Lett 383:227–229
Bonete MJ, Camacho M, Martinez-Espinosa RM, Esclapez J, Bautista V, Pire C, Zafrilla B, Díaz S, Pérez-Pomares F, Llorca F (2007) In the light of the haloarchaea metabolism. In: Méndez-Vilas A (ed) Communicating current research and educational topics and trends in applied microbiology. Formatex, Badajoz, Spain, pp 170–183
Bourne Y, Henrissat B (2001) Glycoside hydrolases and glycosyltransferases: families and functional modules. Curr Opin Struct Biol 11:593–600
Bowers KJ, Wiegel J (2011) Temperature and pH optima of extremely halophilic archaea: a mini-review. Extremophiles 15:119–128
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brenneis M, Hering O, Lange C, Soppa J (2007) Experimental characterization of Cis-acting elements important for translation and transcription in halophilic Archaea. PLoS Genet 3:2450–2467
Cantarel BL, Coutinho PM, Rancurel C, Bernard T, Lombard V, Henrissat B (2009) The Carbohydrate-Active EnZymes database (CAZy): an expert resource for glycogenomics. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D233–D238
Dym O, Mevarech M, Sussman JL (1995) Structural feature that stabilize halophilic malate dehydrogenase from an Archaebacterium. Science 267:1344–1346
Eichler J (2001) Biotechnological uses of archaeal extremozymes. Biotechnol Adv 19:261–278
Esclapez J, Britton KL, Baker PJ, Fisher M, Pire C, Ferrer J, Bonete MJ, Rice DW (2005) Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of binary and ternary complexes of Haloferax mediterranei glucose dehydrogenase. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 61(pt 8):743–746
Henrissat B (1991) A classification of glycosyl hydrolases based on amino-acid sequence similarities. Biochem J 280:309–316
Hirai H, Toshima N, Uenoyama S (1981) Inclusion complex formation of cyclodextrin with large dye molecule. Polym J 13:607–610
Hutcheon GW, Vasisht N, Bolhuis A (2005) Characterisation of a highly stable α-amylase from the halophilic archaeon Haloarcula hispanica. Extremophiles 9:487–495
Janeček S, Svensson B, MacGregor EA (2003) Relation between domain evolution, specificity, and taxonomy of the α-amylase family members containing a C-terminal starch-binding domain. Eur J Biochem 270:635–645
Kato T, Horikoshi K (1984) Colorimetric determination of γ-cyclodextrin. Anal Chem 56:1738–1740
Lanyi JK (1974) Salt-dependent properties of proteins from extremely halophilic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev 38:272–290
Lee MH, Yang SJ, Kim JW, Lee HS, Park HN (2007) Characterization of a thermostable cyclodextrin glucanotransferase from Pyrococcus furiosus DSM3638. Extremophiles 11:537–541
Lezcano M, Al-Soufi W, Novo M, Rodríguez-Nuñez E, Velázquez-Tato J (2002) Complexation of several benzimidazole-type fungicides with α- and β-cyclodextrins. J Agric Food Chem 50:108–112
MacGregor EA, Janeček S, Svensson B (2001) Relationship of sequence and structure to specificity in the α amylase family of enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1546:1–20
Machovič M, Janeček S (2006) Starch-binding domains in the post-genome era. Cell Mol Life Sci 63:2710–2724
Madern D, Ebel C, Zaccai G (2000) Halophilic adaptation of enzymes. Extremophiles 4:91–98
Martínez-Espinosa RM, Marhuenda-Egea FC, Bonete MJ (2001) Purification and characterisation of a possible assimilatory nitrite reductase from the halophile archaeon Haloferax mediterranei. FEMS Microbiol Lett 196:113–118
Martins RF, Hatti-Kaul R (2002) A new cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase from an alkaliphilic Bacillus agaradhaerens isolate: purification and characterisation. Enzyme Microb Technol 30:116–124
Mevarech M, Frolow F, Gloss LM (2000) Halophilic enzymes: proteins with a grain of salt. Biophys Chem 86:155–164
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Nakamura A, Haga K, Yamane K (1994a) Four aromatic residues in the active center of cyclodextrin glucanotransferase from alkalophilic Bacillus sp. 1011: effects of replacements on substrate binding and cyclization characteristics. Biochemistry 33:9929–9936
Nakamura A, Haga K, Yamane K (1994b) The transglycosilation reaction of cyclodextrin glucanotransferase is operated by a ping-pong mechanism. FEBS Lett 337(1):66–70
Numanoglu U, Sen T, Tarimici N, Kartak M, Koo OM, Onyuksel H (2007) Use of cyclodextrins as a cosmetic delivery system for fragrance materials: linalool and benzyl acetate. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech 8:E85
Oren A (2002) Diversity of halophilic microorganisms: environments, phylogeny, physiology and applications. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 28:56–63
Palmer JR, Daniels CJ (1995) In vivo definition of an archaeal promoter. J Bacteriol 177:1844–1849
Penninga D, Strokopytov B, Rozeboom HJ, Lawson CL, Dijkstra BW, Bergsma J, Dijkhuizen L (1995) Site-directed mutations in tyrosine 195 of cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase from Bacillus circulans strain 251 affect activity and product specificity. Biochemistry 34:3368–3376
Pérez-Pomares F, Bautista V, Ferrer J, Pire C, Marhuenda-Egea F, Bonete MJ (2003) α-Amylase activity from the halophilic archaeon Haloferax mediterranei. Extremophiles 7:299–306
Pire C (1998) NAD(P)+-glucosa deshidrogenasa de Haloferax mediterranei. Propiedades moleculares, mecanismo cinético y clonaje. Tesis Doctoral, Facultad de Ciencias, Universidad de Alicante
Pire C, Esclapez J, Ferrer J, Bonete MJ (2001) Heterologous overexpression of glucose dehydrogenase from the halophilic archaeon Haloferax mediterranei, an enzyme of the medium chain dehydrogenase/reductase family. FEMS Microbiol Lett 200:221–227
Qi Q, Zimmermann W (2005) Cyclodextrin glucanotransferase: from gene to applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66:475–485
Rashid N, Cornista J, Ezaki S, Fukui T, Atomi H, Imanaka T (2002) Characterization of an archaeal cyclodextrin glucanotransferase with a novel C-terminal domain. J Bacteriol 184:777–784
Rodríguez-Valera F, Ruiz-Barraquero F, Ramos-Cormenzana A (1980) Behaviour of mixed populations of halophilic bacteria in continuous cultures. Can J Microbiol 26:1259–1263
Rose RW, Bruser T, Kissinger JC, Pohlschröder M (2002) Adaptation of protein secretion to extremely high-salt conditions by extensive use of the twin-arginine translocation pathway. Mol Microbiol 45:943–950
Singh M, Sharma R, Banerjee UC (2002) Biotechnological applications of cyclodextrins. Biotechnol Adv 20:341–359
Soppa J (1999) Transcription initiation in Archaea: facts, factors, and future aspects. Mol Microbiol 31:1295–1305
Stam MR, Danchin EG, Rancurel C, Coutinho PM, Henrissat B (2006) Dividing the large glycoside hydrolase family 13 into subfamilies: towards improved functional annotations of α-amylase-related proteins. Protein Eng Des Sel 19:555–562
Svensson B, Jespersen H, Sierks MR, MacGregor EA (1989) Sequence homology between putative raw-starch binding domains from different starch-degrading enzymes. Biochem J 264:309–311
Szente L, Szejtli J (2004) Cyclodextrins as food ingredients. Trends Food Sci Technol 15:137–142
van de Manakker F, Vermonden T, van Nostrum CF, Hennink WE (2009) Cyclodextrin-based polymeric materials: synthesis, properties, and pharmaceutical/biomedical applications. Biomacromolecules 10:3157–3175
van der Maarel MJ, van der Veen B, Uitdehaag JC, Leemhuis H, Dijkhuizen L (2002) Properties and applications of starch-converting enzymes of the α-amylase family. J Biotechnol 94:137–155
van der Veen BA, van Alebeek GJ, Uitdehaag JC, Dijkstra BW, Dijkhuizen L (2000) The three transglycosylation reactions catalyzed by cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase from Bacillus circulans (strain 251) proceed via different kinetic mechanisms. Eur J Biochem 267:658–665
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by research projects (BIO2005-08991-C02-01, BIO2008-00082) from Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación from Spain and FEDER funds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by F. Robb.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bautista, V., Esclapez, J., Pérez-Pomares, F. et al. Cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase: a key enzyme in the assimilation of starch by the halophilic archaeon Haloferax mediterranei . Extremophiles 16, 147–159 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-011-0414-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-011-0414-z