Abstract
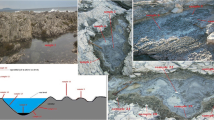
Only recently, a novel anoxic hypersaline (thalassic) basin in the eastern Mediterranean was discovered at a depth of 3,258 m. The halite-saturated brine of this polyextreme basin revealed one of the highest salt concentrations ever reported for such an environment (salinity of 348‰). Using a eukaryote-specific probe and fluorescence in situ hybridization, we counted 0.6 × 104 protists per liter of anoxic brine. SSU rRNA sequence analyses, based on amplification of environmental cDNA identified fungi as the most diverse taxonomic group of eukaryotes in the brine, making deep-sea brines sources of unknown fungal diversity and hotspots for the discovery of novel metabolic pathways and for secondary metabolites. The second most diverse phylotypes are ciliates and stramenopiles (each 20%). The occurrence of closely related ciliate sequences exclusively in other Mediterranean brine basins suggests specific adaptations of the respective organisms to such habitats. Betadiversity-analyses confirm that microeukaryote communities in the brine and the interface are notably different. Several distinct morphotypes in brine samples suggest that the rRNA sequences detected in Thetis brine can be linked to indigenous polyextremophile protists. This contradicts previous assumptions that such extremely high salt concentrations are anathema to eukaryotic life. The upper salinity limits for eukaryotic life remain unidentified.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander E, Stock A, Breiner HW, Behnke A, Bunge J, Yakimov MM, Stoeck T (2009) Microbial eukaryotes in the hypersaline anoxic L’Atalante deep-sea basin. Environ Microbiol 11:360–381
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang JH, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Bass D, Howe A, Brown N, Barton H, Demidova M, Michelle H, Li L, Sanders H, Watkinson SC, Willcock S, Richards TA (2007) Yeast forms dominate fungal diversity in the deep oceans. Proc Royal Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci 274:3069–3077
Burgaud G, Le Calvez T, Arzur D, Vandenkoornhuyse P, Barbier G (2009) Diversity of culturable marine filamentous fungi from deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Environ Microbiol 11:1588–1600
Butschinsky P (1897) Die Protozooenfauna der Salzsee-Limane bei Odessa. Zool Anz 20:194–197
Cantrell SA, Casillas-Martinez L, Molina M (2006) Characterization of fungi from hypersaline environments of solar salterns using morphological and molecular techniques. Mycol Res 110:962–970
Caron DA, Gast RJ (2008) The diversity of free-living protists seen and unseen, cultured and uncultured. In: Zengler K (ed) Accessing uncultivated microorganisms. From the environment to organisms and genomes and back. ASM Press, Washington, pp 67–93
Caron DA, Countway PD, Savai P, Gast RJ, Schnetzer A, Moorthi SD, Dennett MR, Moran DM, Jones AC (2009) Defining DNA-based operational taxonomic units for microbial-eukaryote ecology. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:5797–5808
Castresana J (2000) Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol Biol Evol 17:540–552
Chao A, Shen TJ (2003–2005) Program SPADE (species prediction and diversity estimates). http://chao.stat.nthu.edu.tw
Chao A, Chazdon RL, Colwell RK, Shen TJ (2005) A new statistical approach for assessing similarity of species composition with incidence and abundance data. Ecol Lett 8:148–159
Clarke KJ, Finlay BJ, Esteban G, Guhl BE, Embley TM (1993) Cyclidium porcatum n. sp: a free-living anaerobic scuticociliate containing a stable complex of hydrogenosomes, eubacteria and archaeobacteria. Eur J Protistol 29:262–270
Colwell RK (2009) EstimateS: statistical estimation of species richness and shared species from samples. Version 8.2. User’s Guide and application
Cox CS (1993) Roles of water molecules in bacteria and viruses. Orig Life Evol Biosph 23:29–36
D’Elia T, Veerapaneni R, Theraisnathan V, Rogers SO (2009) Isolation of fungi from Lake Vostok accretion ice. Mycologia 101:751–763
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792–1797
Edgcomb VP, Kysela DT, Teske A, de Vera Gomez A, Sogin ML (2002) Benthic eukaryotic diversity in the Guaymas Basin hydrothermal vent environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:7658–7662
Edgcomb V, Orsi W, Leslin C, Epstein S, Bunge J, Jeon S, Yakimov MM, Behnke A, Stoeck T (2009) Protistan community patterns within the brine and halocline of deep hypersaline anoxic basins in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Extremophiles 13:151–167
Edgcomb VP, Beaudoin D, Gast R, Biddle JF, Teske A (2011) Marine subsurface eukaryotes: the fungal majority. Environ Microbiol 13:172–183
Elloumi J, Carrias J-F, Ayadi H, Sime-Ngando T, Boukhris M, Bouain A (2006) Composition and distribution of planktonic ciliates from ponds of different salinity in the solar saltwork of Sfax, Tunisia. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 67:21–29
Enz G (1879) Über einige Infusorien des Salzteiches zu Szamosfalva. Termes Füzetek 3:1–40
Epstein S, López-García P (2007) “Missing” protists: a molecular prospective. Biodivers Conserv 17:261–276
Esteban GF, Finlay BJ (2003) Cryptic freshwater ciliates in a hypersaline lagoon. Protist 154:411–418
Fenchel T, Bernard C (1996) Behavioural responses in oxygen gradients of ciliates from microbial mats. Eur J Protistol 32:55–63
Finlay BJ, Esteban GF, Brown S, Fenchel T, Hoef-Emden K (2006) Multiple cosmopolitan ecotypes within a microbial eukaryote morphospecies. Protist 157:377–390
Florentin R (1899) Etudes sur la faune des mares salées de Lorraine. Ann Sci Nat Zool 10:209–350
Galtier N, Gouy M, Gautier C (1996) SEAVIEW and PHYLO_WIN: two graphic tools for sequence alignment and molecular phylogeny. Comput Appl Biosci 12:543–548
Giovannoni SJ, DeLong EF, Olsen GJ, Pace NR (1988) Phylogenetic group-specific oligodeoxynucleotide probes for identification of single microbial cells. J Bacteriol 170:720–726
Gomez F, Moreira D, Benzerara K, López-García P (2011) Solenicola setigera is the first characterized member of the abundant and cosmopolitan uncultured marine stramenopile group MAST-3. Environ Microbiol 13(1):193–202
Guillou L, Viprey M, Chambouvet A, Welsh RM, Kirkham AR, Massana R, Scanlan DJ, Worden AZ (2008) Widespread occurrence and genetic diversity of marine parasitoids belonging to Syndiniales (Alveolata). Environ Microbiol 10:3349–3365
Gunde-Cimerman N, Zalar P, de Hoog S, Plemenitaš A (2000) Hypersaline waters in salterns—natural ecological niches for halophilic black yeasts. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 32:235–240
Gunde-Cimerman N, Ramos J, Plemenitaš A (2009) Halotolerant and halophilic fungi. Mycol Res 113:1231–1241
Henneguy F (1890) Sur un Infusoire heterotriche, Fabrea salina. Ann d’Micrographie 3:118–135
Horton TR, Bruns TD (2001) The molecular revolution in ectomycorrhizal ecology: peeking into the black-box. Mol Ecol 10:1855–1871
Iwataki M, Kawami H, Matsuoka K (2007) Cochlodinium fulvescens sp. nov. (Gymnodiniales, Dinophyceae), a new chain-forming unarmored dinoflagellate from Asian coasts. Phycol Res 55:231–239
Jebaraj CS, Raghukumar C, Behnke A, Stoeck T (2010) Fungal diversity in oxygen-depleted regions of the Arabian Sea revealed by targeted environmental sequencing combined with cultivation. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 71:399–412
Kunte HJ, Trüper H, Stan-Lotter H (2002) Halophilic microorganisms. In: Horneck G, Baumstark-Khan C (eds) Astrobiology: the quest for the conditions of life. Springer, Berlin, pp 185–200
La Cono V, Smedile F, Bortoluzzi G, Arcadi E, Maimone G, Messina E, Borghini M, Olliveri E, Mazzola S, L’Haridon S, Toffin L, Genovese L, Ferrer M, Giuliano L, Golyshin PN, Yakimov MM (2011) Unveiling microbial life in new deep-sea hypersaline Lake Thetis. Part I: prokaryotes and environmental settings. Environ Microbiol 13(8):2250–2268
Lahav R, Fareleira P, Nejidat A, Abeliovich A (2002) The identification and characterization of osmotolerant yeast isolates from chemical wastewater evaporation ponds. Microb Ecol 43:388–396
Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley, New York, pp 115–148
Le Calvez T, Burgaud G, Mahe S, Barbier G, Vandenkoornhuyse P (2009) Fungal diversity in deep-sea hydrothermal ecosystems. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:6415–6421
Liu H, Probert I, Uitz J, Claustre H, Aris-Brosou S, Frada M, Not F, de Vargas C (2009) Extreme diversity in noncalcifying haptophytes explains a major pigment paradox in open oceans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:12803–12808
Lozupone C, Knight R (2008) Species divergence and the measurement of microbial diversity. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32:557–578
Ma Y, Galinski EA, Grant WD, Oren A, Ventosa A (2010) Halophiles 2010: life in saline environments. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:6971–6981
MacGregor BJ, Moser DP, Baker BJ, Alm EW, Maurer M, Nealson KH, Stahl DA (2001) Seasonal and spatial variability in Lake Michigan sediment small-subunit rRNA concentrations. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:3908–3922
Massana R, Guillou L, Díez B, Pedrós-Alió C (2002) Unveiling the organisms behind novel eukaryotic ribosomal DNA sequences from the ocean. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:4554–4558
Medlin L, Elwood HJ, Stickel S, Sogin ML (1988) The characterization of enzymatically amplified eukaryotic 16S-like rRNA-coding regions. Gene 71:491–499
Mills HJ, Martinez RJ, Story S, Sobecky PA (2005) Characterization of microbial community structure in Gulf of Mexico gas hydrates: comparative analysis of DNA- and RNA-derived clone libraries. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:3235–3247
Nagahama T, Hamamoto M, Nakase T, Takami H, Horikoshi K (2001) Distribution and identification of red yeasts in deep-sea environments around the northwest Pacific Ocean. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 80:101–110
Nebel M, Pfabel C, Stock A, Dunthorn M, Stoeck T (2010) Delimiting operational taxonomic units for assessing ciliate environmental diversity using small-subunit rRNA gene sequences. Environ Microbiol Rep 3:154–158
Oren A (2005) A hundred years of Dunaliella research: 1905–2005. Saline Syst 1:2
Park JS, Simpson AG (2010) Characterization of halotolerant Bicosoecida and Placididea (Stramenopila) that are distinct from marine forms, and the phylogenetic pattern of salinity preference in heterotrophic stramenopiles. Environ Microbiol 12:1173–1184
Park JS, Kim H, Choi DH, Cho BC (2003) Active flagellates grazing on prokaryotes in high salinity waters of a solar saltern. Aquat Microb Ecol 33:173–179
Park JS, Cho BC, Simpson AG (2006) Halocafeteria seosinensis gen. et sp. nov. (Bicosoecida), a halophilic bacterivorous nanoflagellate isolated from a solar saltern. Extremophiles 10:493–504
Park JS, Simpson AG, Lee WJ, Cho BC (2007) Ultrastructure and phylogenetic placement within Heterolobosea of the previously unclassified, extremely halophilic heterotrophic flagellate Pleurostomum flabellatum (Ruinen 1938). Protist 158:397–413
Patterson DJ, Simpson AG (1996) Heterotrophic flagellates from coastal marine and hypersaline sediments in Western Australia. Eur J Protistol 32:423–448
Pedrós-Alió C (2004) Trophic ecology of solar salterns. In: Ventosa A (ed) Halophilic microorganisms. Springer, Berlin, pp 33–48
Pedrós-Alió C, Calderón-Paz JI, MacLean MH, Medina G, Marrasé C, Gasol JM, Guixa-Boixereu N (2000) The microbial food web along salinity gradients. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 32:143–155
Pernthaler J, Glöckner FO, Schönhuber W, Amann R (2001) Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) with rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes. In: Paul JH (ed) Methods in microbiology. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 207–226
Post FJ, Borowitzka LJ, Borowitzka MA, Mackay B, Moulton T (1983) The protozoa of a western Australian hypersaline lagoon. Hydrobiologia 105:95–113
Prokopowich CD, Gregory TR, Crease TJ (2003) The correlation between rDNA copy number and genome size in eukaryotes. Genome 46:48–50
Ruinen J (1938a) Notizen über Ciliaten aus konzentrierten Salzgewässern. Zool Meded 20:243–256
Ruinen J (1938b) Notizen über Salzflagellaten II. Über die Verbreitung der Salzflagellaten. Arch Protistenk 90:210–258
Skovgaard A, Legrand C (2005) Observation of live specimens of Pseudotontonia cornuta (Ciliophora: Oligotrichida) reveals new distinctive characters. J Mar Biol Ass UK 85:783–786
Stamatakis A, Hoover P, Rougemont J (2008) A fast bootstrapping algorithm for the RAxML web-servers. Syst Biol 57:758–771
Stoeck T, Zuendorf A, Breiner HW, Behnke A (2007) A molecular approach to identify active microbes in environmental eukaryote clone libraries. Microbiol Ecol 53:328–339
Stoecker DK, Gustafson DE, Merrell JR, Black MMD, Baier CT (1997) Excystment and growth of chrysophytes and dinoflagellates at low temperatures and high salinities in Antarctic sea-ice. J Phycol 33:585–595
Tucolesco J (1962) Etudes Protozoologiques sur les eaux Roumaines. I. Espèces nouvelles d’Infusoires de la mer Noire et des bassins salés paramarins. Arch Protistenk 106:1–36
Vaupotič T, Gunde-Cimerman N, Plemenitaš A (2007) Novel 3′-phosphoadenosine-5′-phosphatases from extremely halotolerant Hortaea werneckii reveal insight into molecular determinants of salt tolerance of black yeasts. Fungal Genet Biol 44:1109–1122
Vengosh A, Starinsky A (1993) Relics of evaporated sea water in deep basins of the eastern Mediterranean. Mar Geol 1:15–19
Voronin LV (2010) The fungi of small acid lakes. Inland Water Biol 3:254–259
Wilbert N (1995) Benthic ciliates of salt lakes. Acta Protozool 34:271–288
Zhadanova NN, Zakharchenko V, Vember VV, Nakonechnaya LT (2000) Fungi from Chernobyl: mycobiota of the inner regions of the containment structures of the damaged nuclear reactor. Mycol Res 104:1421–1426
Zhu F, Massana R, Not F, Marie D, Vaulot D (2005) Mapping of picoeucaryotes in marine ecosystems with quantitative PCR of the 18S rRNA gene. FEMS Microb Ecol 52:79–92
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by CNR in the frame of EU Project FP7-KBBE-2009-2B-226977 MAMBA. Further financial support comes from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) awarded to TS. We thank Captain Emanuele Gentile and all crew of RV Urania for their valuable professionalism and support during the cruises. We thank Natascha Brecht for help during sampling on the cruise.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. Oren.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stock, A., Breiner, HW., Pachiadaki, M. et al. Microbial eukaryote life in the new hypersaline deep-sea basin Thetis. Extremophiles 16, 21–34 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-011-0401-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-011-0401-4