Abstract
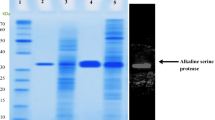
A novel extracellular serine protease designated Pernisine was purified to homogeneity and characterized from the archaeon Aeropyrum pernix K1. The molecular mass, estimated by SDS-PAGE analysis and by gel filtration chromatography, was about 34 kDa suggesting that the enzyme is monomeric. Pernisine was active in a broad range of pH (5.0–12.0) and temperature (60–120 °C) with maximal activity at 90 °C and between pH 8.0 and 9.0. In the presence of 1 mM CaCl2 the activity, as a function of the temperature, reached a maximum at 90 °C but at 120 °C the enzyme retained almost 80% of its maximal activity. Activity inhibition studies suggest that the enzyme is a serine metalloprotease and biochemical data indicate that Pernisine is a subtilisin-like enzyme. The protease gene, identified from the sequenced genome of A. pernix, was amplified from total genomic DNA by PCR technique to construct the expression plasmid pGEX-Pernisine. The Pernisine, lacking the leader sequence, was expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 strain as a fusion protein with glutathione-S-transferase. The biochemical properties of the recombinant enzyme were found to be similar to those of the native enzyme.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham LD, Breuil C (1996) Isolation and characterization of a subtilisin-like serine proteinase secreted by the sap-staining fungus Ophiostoma piceae. Enzyme Microbiol Technol 18:133–144
Adams MW, Kelly RM (1998) Finding and using hyperthermophilic enzymes. Trends Biotechnol 16:329–332
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Barthomeuf C, Pourrat H, Pourrat A (1989) Properties of a new alkaline proteinase from Aspergillus niger. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 37:1333–1336
Blochl E, Rachel R, Burggraf S, Hafenbrandl D, Jannasch HW, Stetter KO (1997) Pyrolobus fumarii, gen. and sp. nov. represents a novel group of Archaea, extending the upper temperature limit for life to 113°C. Extremophiles 1:14–21
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Chavez Croocker P, Sako Y, Uchida A (1999) Purification and characterization of an intracellular heat-stable proteinase (pernilase) from the marine hyperthermophilic archaeon Aeropyrum pernix K1. Extremophiles 3:3–9
Chavira R Jr, Burnett TJ, Hageman JH (1984) Assaying proteinases with azocoll. Anal Biochem 136:446–450
Cowan DA, Smolenski KA, Daniel RM, Morgan HW (1987) An extremely thermostable intracellular proteinase from a strain of the archaebacterium Desulfurococcus growing at 88°C. Biochem J 247:121–133
Debette J (1991) Isolation and characterization of an extracellular proteinase produced by a soil strain of Xanthomonas maltophila. Curr Microbiol 22:85–90
Donaghy JA, Mckay AM (1993) Production and properties of an alkaline protease by Aureobasidium pullulans. J Appl Bacteriol 74:662–666
Douglas SE (1994) DNA Strider. A Macintosh program for handling protein and nucleic acid sequences. Methods Mol Biol 25:181–194
Eggen R, Geerling A, Watts J, Wos WM de (1990) Characterization of pyrolysin, a hyperthermoactive serine protease from the archaebacterium Pyrococcus furiosus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 71:17–20
Frosco M, Chase T, Macmillan JD (1992) Purification and properties of the elastase from Aspergillus fumigatus. Infect Immun 60:728–734
Fusek M, Lin XL, Tang J (1990) Enzymic properties of thermopsin. J Biol Chem 265:1496–1501
Hanzawa S, Hoaki T, Jannasch HW, Maruyama T (1996) An extremely thermostable serine protease from a hyperthermophilic archaeon, Desulfurococcus strain SY, isolated from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent. J Mar Biotechnol 4:121–126
Horikoshi K (1997) A new microbial world: extremophiles. Extremophiles 1:1
Jain SC, Shinde U, Li Y, Inouye M, Berman HM (1998) The crystal structure of an autoprocessed Ser221Cys-subtilisin E-propeptide complex at 2.0 A resolution. J Mol Biol 284:137–144
Jannasch HW, Wirsen CO, Molyneaux SJ, Langworth TA (1988) Extremely thermophilic fermentative archaebacteria of the genus Desulfurococcus from deep-sea hydrothermal vents. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:1203–1209
Kamekura M, Seno Y, Dyall-Smith M (1996) Halolysin R4, a serine proteinase from the halophilic archaeon Haloferax mediterranei; gene cloning, expression and structural studies. Biochim Biophys Acta 1294:159–167
Kannan Y, Koga Y, Inoue Y, Haruki M, Takagi M, Imanaka T, Morikawa M, Kanaya S (2001) Active subtilisin-like protease from a hyperthermophilic archaeon in a form with a putative prosequence. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:2445–2452
Kawarabayasi Y, Hino Y, Horikawa H, Yamazaki S, Haikawa Y, Jin-no K, Takahashi M, Sekine M, Baba S, Ankai A, Kosugi H, Hosoyama A, Fukui S, Nagai Y, Nishijima K, Nakazawa H, Takamiya M, Masuda S, Funahashi T, Tanaka T, Kudoh Y, Yamazaki J, Kushida N, Oguchi A, Kikuchi H (1999) Complete genome sequence of an aerobic hyper-thermophilic crenarchaeon, Aeropyrum pernix K1. DNA Res 6:83–101
Klingeberg M, Hashwa F, Antranikian G (1991) Properties of extremely thermostable proteases from anaerobic hyperthermophilic bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 34:715–719
Klingeberg M, Galuusky B, Sjoholm C, Kasche V, Antranikian G (1995) Purification and properties of highly thermostable SDS resistant and stereospecific proteinase from the extreme thermophilic archaeon Thermococcus stetteri. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3098–3104
Kolattukudy PE, Lee JD, Rogers LM, Zimmerman P, Ceselski S, Fox B, Stein B, Copelan EA (1993) Evidence for possible involvement of an elastolytic serine protease in aspergillosis. Infect Immun 61:2357–2368
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lee MA, Liu Y (2000) Sequencing and characterization of a novel serine metalloprotease from Burkholderia pseudomallei. FEMS Microbiol Lett 192:67–72
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL, Randell JR (1951) Protein measurements with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Manonmani HK, Joseph R (1993) Purification and properties of an extracellular proteinase of Trichoderma koningii. Enzyme Microbiol Technol 15:624–628
Mayr J, Lupas A, Kellermann J, Echerskorn C, Baumeistar W, Peters J (1996) A hyperthermostable protease of the subtilisin family bound to the surface layer of the archaeon Staphylothermus marinus. Curr Biol 6:739–749
Matsuzawa H, Tokugawa K, Hamaoki M, Mizoguchi M, Taguchi H, Terada I, Kwon ST, Ohta T (1988) Purification and characterization of aqualysin I (a thermophilic alkaline serine protease) produced by Thermus aquaticus YT-1. Eur J Biochem 171:441–447
Murao S, Ohkuni K, Nagao M, Hirayama K, Fukuhara K, Oha K, Oyama H, Shin T (1993) Purification and characterization of kumamolysin, a novel thermostable pepstatin-insensitive carboxyl proteinase from Bacillus novosp. MN-32. J Biol Chem 268:349–355
Peek K, Daniel MR, Monk, C, Parker L, Coolbear T (1992) Purification and characterization of a thermostable proteinase isolated from Thermus sp. strain Rt41A. Eur J Biochem 207:1035–1044
Reichard U, Buttner S, Eiffert H, Staib F, Ruchel R (1990) Purification and characterization of an extracellular serine proteinase from Aspergillus fumigatus and its detection in tissue. J Med Microbiol 33:243–251
Robb FT, Clark DS (1999) Adaptation of proteins from hyperthermophiles to high pressure and high temperature. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 1:101–105
Sako Y, Nomura N, Uchida A, Ishida Y, Morii H, Koga Y, Hoaki T, Maruyama TL (1996) Aeropyrum pernix gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel aerobic hyperthermophilic archaeon growing at temperatures up to 100 degrees C. Int J Syst Bacteriol 46:1070–1077
Sako Y, Croocker PC, Ishida Y (1997) An extremely heat-stable extracellular proteinase (aeropyrolysin) from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Aeropyrum pernix K1. FEBS Lett 415:329–334
Schechter I, Berger A (1967) On the size of the active site in proteases. I. Papain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 27:157–162
Schmidt BF, Woodhouse L, Adams RM, Ward T, Mainzer SE, Lad PJ (1995) Alkalophilic Bacillus sp. strain LG12 has a series of serine protease genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:4490–4493
Siezen RJ, Leunissen JA (1997) Subtilases: the superfamily of subtilisin-like serine proteases. Protein Sci 6:501–523
Siezen RJ, Leunissen WM, Dijkstra BW (1991) Homology modelling and protein engineering strategy of subtilases, the family of subtilisin-like serine proteinase. Protein Eng 4:719–737
Snowden LJ, Blumentals II, Kelly RM (1992) Regulation of intracellular proteolysis in the hyperthermophilic archaebacterium Pyrococcus furiosus. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:1134–1141
Suzuki M, Taguchi S, Yamada S, Kojima S, Miura KI, Momose H (1997) A novel member of the subtilisin-like protease family from Streptomyces albogriseolus. J Bacteriol 179:430–438
Vieille C, Zeikus GJ (2001) Hyperthermophilic enzymes: sources, uses and molecular mechanism for thermostability. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 65:1–43
Volkl P, Markiewicz P, Stetter KO, Miller JH (1994) The sequence of a subtilisin-type protease (aerolysin) from the hyperthermophilic archaeum Pyrobaculum aerophilum reveals sites important to thermostability. Protein Sci 3:1329–1340
Voorhorst WGB, Eggen RIL, Geerling ACM, Platteeuw C, Siezen RJ, Wos WM de (1996) Isolation and characterization of the hyperthermostable serine protease, pyrolysin, and its gene from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus. J Biol Chem 271:20426–20431
Vos WM de, Voorhorst WG, Dijkgraaf M, Kluskens LD, Van der Oost J, Siezen RJ (2001) Purification, characterization, and molecular modeling of pyrolysin and other extracellular thermostable serine proteases from hyperthermophilic microorganisms. Methods Enzymol 330:383–393
Wells JA, Estell DA (1988) Subtilisin: an enzyme designed to be engineered. Trends Biochem Sci 13:271–297
Wells JA, Powers DB, Bott RR, Gray TP, Estell DA (1987) Designing substrate specificity by protein engineering of electrostatic interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 84:1219–1223
Wright CS, Alden RA, Kraut J (1969) Structure of subtilisin BPN′ at 2.5 angstrom resolution. Nature 221:235–242
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the U E grant number BIO 4-98-6065.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by G. Antranikian
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Catara, G., Ruggiero, G., La Cara, F. et al. A novel extracellular subtilisin-like protease from the hyperthermophile Aeropyrum pernix K1: biochemical properties, cloning, and expression. Extremophiles 7, 391–399 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-003-0337-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-003-0337-4