Abstract
Objectives
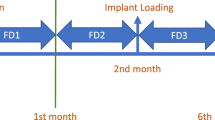
There is no consensus on the relationship between fractal dimension and trabecular bone complexity. Our aims were to examine the changes in fractal dimension (FD) from peri-implant alveolar bone on digital panoramic radiographs 6 and 12 months after prosthodontic loading and to compare these with baseline values calculated just after loading.
Material and methods
Three panoramic radiographs taken from 76 implant patients taken (1) after prosthodontic loading (3 months ± 2 weeks after insertion = baseline), (2) 6 months ± 2 weeks after loading, and (3) 12 months ±2 weeks after loading were considered for the study. Panoramic images were obtained using storage phosphor plates of the Digora PCT system and saved into a computer. Three regions of interest from mesial, distal, and apical areas were selected for each implant on three consecutive panoramic images. Statistical analysis of the data was performed using two-way repeated measures ANOVA, independent t test and paired t test, and pairwise comparisons (P < 0.05).
Results
Mean FD values at baseline were 1.202, 1.224, and 1.199 for apical, mesial, and distal areas. The FD values were calculated as 1.121, 1.113, and 1.128 at the 6th month. The differences between values calculated at baseline and the 6th month were statistically significant for all aspects, indicating a significant decrease in FD 6 months after prosthodontic loading (P < 0.05). FD values calculated at the 12th month were 1.121, 1.110, and 1.121 for apical, mesial, and distal aspects, respectively, with no significant differences from corresponding values obtained at the 6th month (P > 0.05).
Conclusions
FD values of trabecular bone around implants 6 months after prosthodontic loading are significantly lower than the baseline values. However, no significant decrease or increase was observed at 12 months, which revealed comparable results with peri-implant alveolar bone at 6 months.
Clinical relevance
Trabecular bone around successful dental implants exhibits lower fractal dimension values 6 months after prosthodontic loading and displays stable bony microstructure at 12 months of follow-up.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Geraets WG, van der Stelt PF (2000) Fractal properties of bone. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 29:144–153
Fazzalari NL, Parkinson IH (1996) Fractal dimension and architecture of trabecular bone. J Pathol 178:100–105
Ruttimann UE, Webber RL, Hazelrig JB (1992) Fractal dimension from radiographs of peridental alveolar bone. A possible diagnostic indicator of osteoporosis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 74:98–110
Bollen AM, Taguchi A, Hujoel PP, Hollender LG (2001) Fractal dimension on dental radiographs. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 30:270–275
Parkinson IH, Fazzalari NL (2000) Methodological principles for fractal analysis of trabecular bone. J Microsc 198:134–142
Tosoni GM, Lurie AG, Cowan AE, Burleson JA (2006) Pixel intensity and fractal analyses: detecting osteoporosis in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women by using digital panoramic images. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 102:235–241
Benhamou CL, Lespessailles E, Jacquet G, Harba R, Jennane R, Loussot T et al (1994) Fractal organization of trabecular bone images on calcaneus radiographs. J Bone Miner Res 9:1909–1918
Pothuaud L, Benhamou CL, Porion P, Lespessailles E, Harba R, Levitz P (2000) Fractal dimension of trabecular bone projection texture is related to three-dimensional microarchitecture. J Bone Miner Res 15:691–699
Jolley L, Majumdar S, Kapila S (2006) Technical factors in fractal analysis of periapical radiographs. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 35:393–397
Shrout MK, Potter BJ, Hildebolt CF (1997) The effect of image variations on fractal dimension calculations. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 84:96–100
Law AN, Bollen AM, Chen SK (1996) Detecting osteoporosis using dental radiographs: a comparison of four methods. J Am Dent Assoc 127:1734–1742
Prouteau S, Ducher G, Nanyan P, Lemineur G, Benhamou L, Courteix D (2004) Fractal analysis of bone texture: a screening tool for stress fracture risk? Eur J Clin Invest 34:137–142
Shrout MK, Roberson B, Potter BJ, Mailhot JM, Hildebolt CF (1998) A comparison of 2 patient populations using fractal analysis. J Periodontol 69:9–13
Southard TE, Southard KA, Jakobsen JR, Hillis SL, Najim CA (1996) Fractal dimension in radiographic analysis of alveolar process bone. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 89:569–576
Southard TE, Southard KA, Krizan KE, Hillis SL, Haller JW, Keller J, Vannier MW (2000) Mandibular bone density and fractal dimension in rabbits with induced osteoporosis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 89:244–249
Updike SX, Nowzari H (2008) Fractal analysis of dental radiographs to detect periodontitis-induced trabecular changes. J Periodontal Res 43:658–664
Yaşar F, Akgünlü F (2006) The differences in panoramic mandibular indices and fractal dimension between patients with and without spinal osteoporosis. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 35:1–9
Caligiuri P, Giger ML, Favus M (1994) Multifractal radiographic analysis of osteoporosis. Med Phys 21:503–508
Webber RL, Underhill TE, Horton RA, Dixon RL, Pope TL Jr (1993) Predicting osseous changes in ankle fractures. A fractal-based radiographic analysis. IEEE Eng Med Biol 12:103–110
Chen SK, Oviir T, Lin CH, Leu LJ, Cho BH, Hollender L (2005) Digital imaging analysis with mathematical morphology and fractal dimension for evaluation of periapical lesions following endodontic treatment. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 100:467–472
Heo MS, Park KS, Lee SS, Choi SC, Koak JY, Heo SJ, Han CH, Kim JD (2002) Fractal analysis of mandibular bony healing after orthognathic surgery. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 94:763–767
González-Martín O, Lee EA, Veltri M (2012) CBCT fractal dimension changes at the apex of immediate implants placed using undersized drilling. Clin Oral Implants Res 23:954–957
Sansare K, Singh D, Karjodkar F (2012) Changes in the fractal dimension on pre- and post-implant panoramic radiographs. Oral Radiol 28:15–23
Veltri M, Balleri P, Ferrari M (2007) Damping factor for monitoring the bone interface at dental implants. Clin Oral Implants Res 18:738–742
Wilding RJC, Slabbert JCG, Kathree H, Owen CP, Crombie K, Delport P (1995) The use of fractal analysis to reveal remodelling in human alveolar bone following the placement of dental implants. Arch Oral Biol 40:61–72
Lynch JA, Hawkes DJ, Buckland-Wright JC (1991) Analysis of texture in macroradiographs of osteoarthritic knees using the fractal signature. Phys Med Biol 36:709–722
Wagle N, Do NN, Yu J, Borke JL (2005) Fractal analysis of the PDL-bone interface and implications for orthodontic tooth movement. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 127:655–661
Yaşar F, Akgünlü F (2005) Fractal dimension and lacunarity analysis of dental radiographs. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 34:261–267
Huiskes R (2000) If bone is the answer, then what is the question. J Anat 197:145–156
Van der Linden JC, Days JS, Verhaar JAN, Weinans H (2004) Altered tissue properties induce changes in cancellous bone architecture in aging and disease. J Biomech 37:367–374
White SC, Rudolph DJ (1999) Alterations of the trabecular pattern of the jaws in patients with osteoporosis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 88:628–635
Geraets WG, Van der Stelt PF, Netelenbos CJ, Elders PJ (1990) A new method for automatic recognition of the radiographic trabecular pattern. J Bone Miner Res 5:227–233
Corpas LS, Jacobs R, QuirynenM HY, Naert I, Duyck J (2011) Peri-implant bone tissue assessment by comparing the outcome of intra-oral radiograph and cone beam computed tomography analyses to the histological standard. Clin Oral Implants Res 22:492–499
Veltri M, Ferrari M, Balleri P (2011) Correlation of radiographic fractal analysis with implant insertion torque in a rabbit trabecular bone model. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 26:108–114
Lee DH, Ku Y, Rhyu IC, Hong JU, Lee CW, Heo MS, Huh KH (2010) A clinical study of alveolar bone quality using the fractal dimension and the implant stability quotient. J Periodontal Implant Sci 40:19–24
Demirbaş AK, Ergün S, Güneri P, Aktener BO, Boyacioğlu H (2008) Mandibular bone changes in sickle cell anemia: fractal analysis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 106:41–48
Yu YY, Chen H, Lin CH, Chen CM, Oviir T, Chen SK, Hollender L (2009) Fractal dimension analysis of periapical reactive bone in response to root canal treatment. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 107:283–288
Southard TE, Southard KA, Lee A (2001) Alveolar process fractal dimension and postcranial bone density. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 91:486–491
Nair MK, Seyedain A, Webber RL, Nair UP, Piesco NP, Agarwal S, Mooney MP, Gröndahl HG (2001) Fractal analyses of osseous healing using tuned aperture computed tomography images. Eur Radiol 11:1510–1515
Wojtowicz A, Chaberek S, Pirino A, Montella A, Bandiera P, Kinsner A, Ostrowski K (2001) The trabecular structure of developing human mandible. Clin Orthod Res 4:161–171
Ergün S, Saraçoglu A, Güneri P, Ozpinar B (2009) Application of fractal analysis in hyperparathyroidism. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 38:281–288
Yi WJ, Heo MS, Lee SS, Choi SC, Huh KH, Lee SP (2007) Direct measurement of trabecular bone anisotropy using directional fractal dimension and principal axes of inertia. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 104:110–116
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeytinoğlu, M., İlhan, B., Dündar, N. et al. Fractal analysis for the assessment of trabecular peri-implant alveolar bone using panoramic radiographs. Clin Oral Invest 19, 519–524 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-014-1245-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-014-1245-y