Abstract
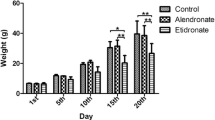
Bisphosphonates have been known to suppress osteoclast activity, survival, and recruitment. In this study, we tested effects of BPs on expression of two critical genes for osteoclastogenesis, M-CSF, and OPG in the process of osteoblast differentiation from hMSC. (1) The cells were cultured in osteogenic induction medium together with 0 (control group) and 10–8 M alendronate, pamidronate for up 2 and 3 weeks (for real-time PCR) and 3 and 4 weeks (for ELISA). (2) The real-time PCR protocol for M-CSF, OPG, and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) consist of 40 cycles. (3) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): the amounts of M-CSF and OPG in the culture medium were determined using commercially available ELISA kits for M-CSF and OPG. Treatment of differentiating cells with alendronate or pamidronate, nitrogen-containing BPs increase the expression of OPG, which suppresses osteoclastogenesis, whereas it decreases the expression of M-CSF, which enhances preosteoclast formation. These results suggest a new mechanism by which BPs inhibit osteoclastogenesis. Results support hypothesis that progressive accumulation of bisphosphonate in jaws causes imbalance in osteogenesis and bone absorption and collateral osteoclast–osteoblast interaction. Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of jaw (BPONJ) is one of the most serious complications of bisphosphonate (BP) therapy. However, the mechanism behind the this process of BPONJ is still unclear and there are so many hypotheses. Among many hypotheses, we focused on osteoclast–osteoblast interaction in this study. The findings of this study show new light on the present BPONJ occurrence theory based on the osteoclastic activity of BPs. Also, a more advanced and developed theory for BRONJ occurrence may be obtained by combining the osteoclast inhibition mechanism and the effects on osteoblastic differentiation by BPs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen MR, Burr DB (2009) The pathogenesis of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: so many hypotheses, so few data. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67:61–70. doi:10.1016/j.joms.2009.01.007
Kyrgidis A, Vahtsevanos K (2009) “Fatigue” having a role in the pathogenesis of osteonecrosis of the jaws. Clin Oral Investig 13 :479–480; author reply 483–474. doi:10.1007/s00784-009-0319-8
Hoefert S, Schmitz I, Tannapfel A, Eufinger H (2009) Importance of microcracks in etiology of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: a possible pathogenetic model of symptomatic and non-symptomatic osteonecrosis of the jaw based on scanning electron microscopy findings. Clin Oral Investig 14:271–284. doi:10.1007/s00784-009-0300-6
Marx RE, Sawatari Y, Fortin M, Broumand V (2005) Bisphosphonate-induced exposed bone (osteonecrosis/osteopetrosis) of the jaws: risk factors, recognition, prevention, and treatment. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 63:1567–1575. doi:10.1016/j.joms.2005.07.010
Bertoldo F, Santini D, Lo Cascio V (2007) Bisphosphonates and osteomyelitis of the jaw: a pathogenic puzzle. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 4:711–721. doi:10.1038/ncponc1000
Ziebart T, Pabst A, Klein MO, Kammerer P, Gauss L, Brullmann D, Al-Nawas B, Walter C (2011) Bisphosphonates: restrictions for vasculogenesis and angiogenesis: inhibition of cell function of endothelial progenitor cells and mature endothelial cells in vitro. Clin Oral Investig 15:105–111. doi:10.1007/s00784-009-0365-2
Pabst AM, Ziebart T, Koch FP, Taylor KY, Al-Nawas B, Walter C (2011) The influence of bisphosphonates on viability, migration, and apoptosis of human oral keratinocytes-in vitro study. Clin Oral Investig. doi:10.1007/s00784-010-0507-6
Simon MJ, Niehoff P, Kimmig B, Wiltfang J, Acil Y (2010) Expression profile and synthesis of different collagen types I, II, III, and V of human gingival fibroblasts, osteoblasts, and SaOS-2 cells after bisphosphonate treatment. Clin Oral Investig 14:51–58. doi:10.1007/s00784-009-0312-2
Benford HL, McGowan NW, Helfrich MH, Nuttall ME, Rogers MJ (2001) Visualization of bisphosphonate-induced caspase-3 activity in apoptotic osteoclasts in vitro. Bone 28:465–473
Rogers MJ, Chilton KM, Coxon FP, Lawry J, Smith MO, Suri S, Russell RG (1996) Bisphosphonates induce apoptosis in mouse macrophage-like cells in vitro by a nitric oxide-independent mechanism. J Bone Miner Res 11:1482–1491
Boonekamp PM, van der Wee-Pals LJ, van Wijk-van Lennep MM, Thesing CW, Bijvoet OL (1986) Two modes of action of bisphosphonates on osteoclastic resorption of mineralized matrix. Bone Miner 1:27–39
Rodan GA, Reszka AA (2002) Bisphosphonate mechanism of action. Curr Mol Med 2:571–577
Sato M, Grasser W, Endo N, Akins R, Simmons H, Thompson DD, Golub E, Rodan GA (1991) Bisphosphonate action. Alendronate localization in rat bone and effects on osteoclast ultrastructure. J Clin Invest 88:2095–2105. doi:10.1172/JCI115539
Kim TW, Yoshida Y, Yokoya K, Sasaki T (1999) An ultrastructural study of the effects of bisphosphonate administration on osteoclastic bone resorption during relapse of experimentally moved rat molars. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 115:645–653
Luckman SP, Hughes DE, Coxon FP, Graham R, Russell G, Rogers MJ (1998) Nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates inhibit the mevalonate pathway and prevent post-translational prenylation of GTP-binding proteins, including Ras. J Bone Miner Res 13:581–589. doi:10.1359/jbmr.1998.13.4.581
Fisher JE, Rogers MJ, Halasy JM, Luckman SP, Hughes DE, Masarachia PJ, Wesolowski G, Russell RG, Rodan GA, Reszka AA (1999) Alendronate mechanism of action: geranylgeraniol, an intermediate in the mevalonate pathway, prevents inhibition of osteoclast formation, bone resorption, and kinase activation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:133–138
Coxon FP, Helfrich MH, Van't Hof R, Sebti S, Ralston SH, Hamilton A, Rogers MJ (2000) Protein geranylgeranylation is required for osteoclast formation, function, and survival: inhibition by bisphosphonates and GGTI-298. J Bone Miner Res 15:1467–1476. doi:10.1359/jbmr.2000.15.8.1467
Khosla S, Burr D, Cauley J, Dempster DW, Ebeling PR, Felsenberg D, Gagel RF, Gilsanz V, Guise T, Koka S, McCauley LK, McGowan J, McKee MD, Mohla S, Pendrys DG, Raisz LG, Ruggiero SL, Shafer DM, Shum L, Silverman SL, Van Poznak CH, Watts N, Woo SB, Shane E (2007) Bisphosphonate-associated osteonecrosis of the jaw: report of a task force of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. J Bone Miner Res 22:1479–1491. doi:10.1359/jbmr.0707ONJ
Aubin JE, Triffitt JT (2002) Mesenchymal stem cells and the osteoblast lineage. In Principles of Bone Biology, 2nd edn. Academic, New York, NY
Lagasse E, Weissman IL (1997) Enforced expression of Bcl-2 in monocytes rescues macrophages and partially reverses osteopetrosis in op/op mice. Cell 89:1021–1031
Bai S, Kopan R, Zou W, Hilton MJ, Ong CT, Long F, Ross FP, Teitelbaum SL (2008) NOTCH1 regulates osteoclastogenesis directly in osteoclast precursors and indirectly via osteoblast lineage cells. J Biol Chem 283:6509–6518. doi:10.1074/jbc.M707000200
Risbud MV, Shapiro IM, Guttapalli A, Di Martino A, Danielson KG, Beiner JM, Hillibrand A, Albert TJ, Anderson DG, Vaccaro AR (2006) Osteogenic potential of adult human stem cells of the lumbar vertebral body and the iliac crest. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 31 :83–89. doi:00007632-200601010-00019
Rustemeyer J, Bremerich A (2009) Bisphosphonate-associated osteonecrosis of the jaw: what do we currently know? A survey of knowledge given in the recent literature. Clin Oral Investig 14:59–64. doi:10.1007/s00784-009-0294-0
Walter C, Klein MO, Pabst A, Al-Nawas B, Duschner H, Ziebart T (2010) Influence of bisphosphonates on endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and osteogenic cells. Clin Oral Investig 14(1):35–41. doi:10.1007/s00784-009-0266-4
Koch FP, Merkel C, Ziebart T, Smeets R, Walter C, Al-Nawas B (2010) Influence of bisphosphonates on the osteoblast RANKL and OPG gene expression in vitro. Clin Oral Investig. doi:10.1007/s00784-010-0477-8
Stanley Er Fau-Berg KL, Berg Kl Fau-Einstein DB, Einstein Db Fau-Lee PS, Lee Ps Fau-Pixley FJ, Pixley Fj Fau-Wang Y, Wang Y Fau-Yeung YG, Yeung YG (1997) Biology and action of colony-stimulating factor-1. Mol Reprod Dev 46:4–10
Boyce BF, Xing L (2008) Functions of RANKL/RANK/OPG in bone modeling and remodeling. Arch Biochem Biophys 473:139–146
Rogers MJ (2003) New insights into the molecular mechanisms of action of bisphosphonates. Curr Pharm Des 9:2643–2658
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by Kyung Hee University (Grant No. 20091412).
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohe, JY., Kwon, YD. & Lee, HW. Bisphosphonates modulate the expression of OPG and M-CSF in hMSC-derived osteoblasts. Clin Oral Invest 16, 1153–1159 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-011-0614-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-011-0614-z