Abstract
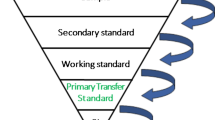
A complete metrological traceability system for measurement results of chemical analysis was set up. Core components are pure substances (national standards) characterised at the highest metrological level, primary solutions prepared from these pure substances and secondary solutions deduced from the primary solutions and intended for sale. The relative uncertainty of the element mass fraction of the primary substances and solutions is < 0.01 and < 0.05%, respectively. For the certification of transfer solutions and for stability testing, a precision measurement method for element contents has been developed by means of optical emission spectrometry (ICP OES) by which uncertainties between 0.1 and 0.05% can be achieved. The dissemination to field laboratories is effected with the aid of a calibration laboratory of the German Calibration Service (DKD) which certifies the element content of the secondary solutions with an uncertainty ≤ 0.3%. Calibration with these solutions enables the user to establish traceability of his measurement results to the International System of Units (SI). Currently, the system comprises Cu, Fe, Bi, Ga, Si, Na, K, Sn, W, and Pb.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
DIN EN ISO/IEC 17025 General requirements for the competence of calibration and testing laboratories (1999) ISO, Geneva
EU Water Framework Directive: Directive 2000/60/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council establishing a framework for the Community action in the field of water policy (2000) Amtsblatt: L 327
King B (1997) Metrologia 34:77–82
Labarraque G, Rivier C, Marschal A (1999) In: Proceedings of the 9th International Metrology Congress, Bordeaux, France, October 1999
Mutual Recognition Arrangement, Available at http://www.bipm.fr/en/convention/mra
Matschat R, Czerwensky M, Pattberg S, Heinrich H-J, Tutschku S (2002) Mat Trans (JIM) 43:90–97
Matschat R, Kipphardt H (2003) Erzmetall 56:179–189
Matschat R, Czerwensky M, Pattberg S, Heinrich H-J (2002) Phys Stat Solidi A 189:107–122
Kipphardt H, Dudzus T, Meier K, Recknagel S, Hedrich M, Matschat R (2002) Mat Trans (JIM) 43:98–100
Guide to the Expression of Uncertainty in Measurement (1993) ISO, Geneva
Salit ML, Turk GC (1998) Anal Chem 70:3184–3190
BIPM Key Comparison Database, Available at http://kcdb.bipm.org/
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Federal Ministry of Economics and Labour (BMWA) for granting financial support to this project. Furthermore, the scientific discussion with colleagues from the JEPPIM (Joint European Programme for Primary Isotopic Measurements, a programme co-ordinated by the Institute for Reference Materials and Measurements) is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kipphardt, H., Matschat, R., Rienitz, O. et al. Traceability system for elemental analysis. Accred Qual Assur 10, 633–639 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00769-005-0084-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00769-005-0084-6