Summary.
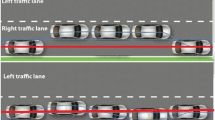
500 ml of a glucose based "energy" drink versus a control without the active ingredients (caffeine, taurine, glucuronolactone) were given double blind to 11 sleepy participants driving an interactive real-car driving simulator. Lane drifting and a secondary task (reaction time) were measured for two hours post-treatment. The energy drink significantly improved both indices, particularly for the first hour.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received January 2, 2000 / Accepted February 1, 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horne, J., Reyner, L. Beneficial effects of an "energy drink" given to sleepy drivers. Amino Acids 20, 83–89 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007260170068
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007260170068