Abstract
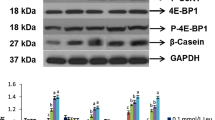
Alpha-ketoglutarate (AKG), a key intermediate in the Krebs cycle, has been reported to promote protein synthesis through activating mechanistic targeting of rapamycin (mTOR) in enterocytes. The study tested the hypothesis that AKG may enhance growth and milk protein synthesis in porcine mammary epithelial cells (PMECs). PMECs were cultured for 96 h in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s-F12 Ham medium (DMEM-F12) containing prolactin (2 µg/ml) and AKG (0 or 1.5 mM). At the end of 96-h culture, the abundance of apoptosis-related proteins (caspase-3, caspase-9), milk-specific proteins (α-lactalbumin and β-casein), mTOR signaling proteins (mTOR, p-mTOR, PERK, p-PERK, eIF2a, P70S6K and p-P70S6K), and endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS)-associated proteins (BiP and CHOP) in PMEC were determined. Addition of AKG dose-dependently enhanced cell viability in the absence or presence of prolactin, with optimal concentrations of AKG being at 1.0 and 1.5 mM, respectively. In the presence of prolactin, addition of 1.5 mM AKG: (1) decreased (P < 0.05) the abundance of caspase-3 and caspase-9 by 21 and 39 %; (2) enhanced (P < 0.05) the phosphorylation of p-mTOR and p-P70S6K by 39 and 89 %, respectively; (3) increased (P < 0.05) the production of β-casein and α-lactalbumin by 16 and 20 %, respectively; (4) attenuated (P < 0.05) the expression of CHOP by 34 % but promoted (P < 0.05) the expression of BiP by 46 %; (5) increased (P < 0.05) the secretion of lactose by 15 %, when compared to the 0 mM AKG group. Rapamycin (50 nM; an inhibitor of mTOR) attenuated (P < 0.05) the stimulatory effect of AKG on mTOR signaling and syntheses of milk protein and lactose, while relieving (P < 0.05) an inhibitory effect of AKG on expression of proteins related to ERS. Collectively, our results indicate that AKG enhances milk protein production by modulating mTOR and ERS signaling pathways in PMECs.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AKG:
-
Alpha-ketoglutarate
- PMECs:
-
Porcine mammary epithelial cells
- ERS:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of the rapamycin
- UPR:
-
Unfolded protein response
- CHOP:
-
C/EBP homologous protein
- BiP:
-
Binding immunoglobulin protein
- PRL:
-
Prolactin
References
Appenzeller-Herzog C, Hall MN (2012) Bidirectional crosstalk between endoplasmic reticulum stress and mTOR signaling. Trends Cell Biol 22:274–282
Assaad H, Zhou L, Carroll RJ et al (2014) Rapid publication-ready MS-Word tables for one-way ANOVA. SpringerPlus 3:474
Assaad H, Hou YQ, Zhou L et al (2015) Rapid publication-ready MS-Word tables for two-way ANOVA. SpringerPlus 4:33
Baldassarre H, Deslauriers J, Neveu N et al (2011) Detection of endoplasmic reticulum stress markers and production enhancement treatments in transgenic goats expressing recombinant human butyrylcholinesterase. Transgenic Res 20:1265–1272
Baldi A, Modina S, Cheli F et al (2002) Bovine somatotropin administration to dairy goats in late lactation: effects on mammary gland function, composition and morphology. J Dairy Sci 85:1093–1102
Basini G, Baioni L, Bussolati S et al (2014) Prolactin is a potential physiological modulator of swine ovarian follicle function. Regul Peptides 189:22–30
Bauman DE, Perfield JW, Harvatine KJ et al (2008) Regulation of fat synthesis by conjugated linoleic acid: lactation and the ruminant model. J Nutr 138:403–409
Boutinaud M, Guinard-Flament J, Jammes H (2004) GH and milking frequency act differently on mammary cells. J Anim Feed Sci 13:467–470
Bromati CR, Lellis-Santos C, Yamanaka TS et al (2011) UPR induces transient burst of apoptosis in islets of early lactating rats through reduced AKT phosphorylation via ATF4/CHOP stimulation of TRB3 expression. Am J Physiol 300:R92–R100
Chan SH, Chen IS, Guh JH (2013) Reevesioside F induces anticancer activity through crosstalk between ER stress and mitochondria insult in leukemia cells. Ann Oncol 24:9
Dahanayaka S, Rezaei R, Porter WW et al (2015) Technical note: isolation and characterization of porcine mammary epithelial cells. J Anim Sci 93:5186–5193
Gessner DK, Schlegel G, Ringseis R et al (2014) Up-regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress induced genes of the unfolded protein response in the liver of periparturient dairy cows. BMC Vet Res 10:46
Gibson GE, Chen HL, Xu H et al (2012) Deficits in the mitochondrial enzyme alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase lead to Alzheimer’s disease-like calcium dysregulation. Neurobiol Aging 33(1121):e13
Hasegawa D, Calvo V, Avivar-Valderas A et al (2015) Epithelial Xbp1 is required for cellular proliferation and differentiation during mammary gland development. Mol Cell Biol 35:1543–1556
He LQ, Xu ZQ, Yao K et al (2015) The physiological basis and nutritional function of alpha-ketoglutarate. Curr Protein Pept Sci 16:576–581
Hou YQ, Yao K, Wang L et al (2011a) Effects of alpha-ketoglutarate on energy status in the intestinal mucosa of weaned piglets chronically challenged with lipopolysaccharide. Br J Nutr 106:357–363
Hou YQ, Wang L, Ding BY et al (2011b) Alpha-ketoglutarate and intestinal function. Front Biosci 16:1186–1196
Invernizzi G, Naeem A, Loor JJ (2012) Short communication: endoplasmic reticulum stress gene network expression in bovine mammary tissue during the lactation cycle. J Dairy Sci 95:2562–2566
Jiao N, Wu ZL, Ji Y et al (2015) l-Glutamate enhances barrier and anti-oxidative functions in intestinal porcine epithelial cells. J Nutr 145:2258–2264
Kato H, Nakajima S, Saito Y et al (2012) mTORC1 serves ER stress-triggered apoptosis via selective activation of the IRE1-JNK pathway. Cell Death Differ 19:310–320
Kim SW, Wu GY (2009) Regulatory role for amino acids in mammary gland growth and milk synthesis. Amino Acids 37:89–95
Lacasse P, Oilier S, Lollivier V et al (2016) New insights into the importance of prolactin in dairy ruminants. J Dairy Sci 99:864–874
Lei J, Feng DY, Zhang YL et al (2012a) Nutritional and regulatory role of branched-chain amino acids in lactation. Front Biosci 17:2725–2739
Lei J, Feng DY, Zhang YL et al (2012b) Regulation of leucine catabolism by metabolic fuels in mammary epithelial cells. Amino Acids 43:2179–2189
Lei J, Feng DY, Zhang YL et al (2013) Hormonal regulation of leucine catabolism in mammary epithelial cells. Amino Acids 45:531–541
Leroux C, Bernard L, Dessauge F et al (2013) The function of lactation: regulation of biosynthesis of the milk components. Prod Anim 26:117–128
Li P, Knabe DA, Kim SW et al (2009) Lactating porcine mammary tissue catabolizes branched-chain amino acids for glutamine and aspartate synthesis. J Nutr 139:1502–1509
Liu XF, Li M, Li QZ et al (2012) Stat5a increases lactation of dairy cow mammary gland epithelial cells cultured in vitro. In Vitro Cell Dev-An 48:554–561
Long LH, Halliwell B (2011) Artefacts in cell culture: alpha-Ketoglutarate can scavenge hydrogen peroxide generated by ascorbate and epigallocatechin gallate in cell culture media. Biochem Bioph Res Co 406:20–24
Madende M, Osthoff G, Patterton HG et al (2015) Characterization of casein and alpha lactalbumin of African elephant (Loxodonta africana) milk. J Dairy Sci 98:8308–8318
Malmkvist J, Pedersen LJ, Kammersgaard TS et al (2012) Influence of thermal environment on sows around farrowing and during the lactation period. J Anim Sci 90:3186–3199
McCormick NH, Hennigar SR, Kiselyov K et al (2014) The biology of zinc transport in mammary epithelial cells: implications for mammary gland development, lactation, and involution. J Mammary Gland Biol 19:59–71
Mullen AR, Hu Z, Shi X et al (2014) Oxidation of alpha-ketoglutarate is required for reductive carboxylation in cancer cells with mitochondrial defects. Cell Rep 7:1679–1690
Noble MS, Hurley WL (1999) Effects of secretion removal on bovine mammary gland function following an extended milk stasis. J Dairy Sci 82:1723–1730
Quesnel H, Meunier-Salaun MC, Hamard A et al (2009) Dietary fiber for pregnant sows: influence on sow physiology and performance during lactation. J Anim Sci 87:532–543
Rainbolt TK, Saunders JM, Wiseman RL (2014) Stress-responsive regulation of mitochondria through the ER unfolded protein response. Trends Endocrinol Metab 25:528–537
Rao RV, Ellerby HM, Bredesen DE (2004) Coupling endoplasmic reticulum stress to the cell death program. Cell Death Differ 11:372–380
Rezaei R, Wang WW, Wu ZL et al (2013) Biochemical and physiological bases for utilization of dietary amino acids by young pigs. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 4:7
Rezaei R, Wu ZL, Hou YQ et al (2016) Amino acids and mammary gland development: nutritional implications for neonatal growth. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 7:20
Safayi S, Theil PK, Hou L et al (2010) Continuous lactation effects on mammary remodeling during late gestation and lactation in dairy goats. J Dairy Sci 93:203–217
Sliwa E, Kowalik S, Tatara MR et al (2005) Effect of alpha-ketoglutarate given to pregnant sows on the development of the humerus and femur in newborns. Bill Vet Inst Pulawy 49:117–120
Sliwa E, Tatara MR, Pierzynowski SG (2006) Total cholesterol, glucose, and electrolytes in piglets serum after alpha-ketoglutarate (AKG) and dexamethasone treatment during prenatal and neonatal life. Bull Vet Inst Pulawy 50:561–566
Sun YL, Chou YC, Kuan TC et al (2008) Expression of recombinant anticoagulant hirudin in the differentiated cultures of the porcine mammary epithelial cell line SI-PMEC. Cell Biol Int 32:739–747
Sun YL, Wu ZL, Li W et al (2015) Dietary l-leucine supplementation enhances intestinal development in suckling piglets. Amino Acids 47:1517–1525
Trott JF, Simpson KJ, Moyle RLC et al (2003) Maternal regulation of milk composition, milk production, and pouch young development during lactation in the tammar wallaby (Macropus eugenii). Biol Reprod 68:929–936
Wang LN, Lin Y, Bian YJ et al (2014) Leucyl-tRNA synthetase regulates lactation and cell proliferation via mTOR signaling in dairy cow mammary epithelial cells. Int J Mol Sci 15:5952–5969
Wang YH, Tian JH, Qiao X et al (2015a) Intermedin protects against renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress. BMC Nephrol 16:169
Wang L, Hou YQ, Yi D et al (2015b) Dietary supplementation with glutamate precursor alpha-ketoglutarate attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury in young pigs. Amino Acids 47:1309–1318
Wang B, Wu ZL, Ji Y et al (2016) l-Glutamine enhances tight junction integrity by activating CaMMK2-AMPK signaling in intestinal porcine epithelial cells. J Nutr 146:501–508
Wu G (2013) Amino acids: biochemistry and nutrition. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Wu G, Bazer FW, Dai ZL et al (2014) Amino acid nutrition in animals: protein synthesis and beyond. Annu Rev Anim Biosci 2:387–417
Wu ZL, Hu CA, Wu G et al (2015) Intimacy and deadly feud: the interplay of autophagy and apoptosis mediated by amino acids. Amino Acids 47:2089–2099
Wu N, Yang M, Gaur U et al (2016) Alpha-ketoglutarate: physiological functions and applications. Biomol Ther 24:1–8
Yao K, Yin Y, Li X et al (2012) Alpha-ketoglutarate inhibits glutamine degradation and enhances protein synthesis in intestinal porcine epithelial cells. Amino Acids 42:2491–2500
Yao K, Fu CX, Yin YL et al (2013) Alpha-ketoglutarate enhances protein synthesis in intestinal porcine epithelial cells. Amino Acids 45:580–581
Yi D, Hou YQ, Wang L et al (2015) l-Glutamine enhances enterocyte growth via activation of the mTOR signaling pathway independently of AMPK. Amino Acids 47:65–78
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Basic Research Program of China (2013CB127306), National Natural Science Foundation of China (31472107), the Chinese Academy of Sciences through its Hundred Talent Program to Kang Yao, the Hubei Hundred Talent program, and Texas A&M AgriLife Research (H-8200).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics statement
This study involved the cultures of an existing cell line and did not require an Animal Use Protocol.
Additional information
Q. Jiang and L. He made equal contributions to this study, so they are joint first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Q., He, L., Hou, Y. et al. Alpha-ketoglutarate enhances milk protein synthesis by porcine mammary epithelial cells. Amino Acids 48, 2179–2188 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2249-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2249-5