Abstract
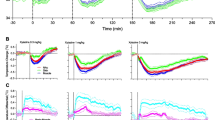
The central effects of L-proline, D-proline and trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline were investigated by using the acute stressful model with neonatal chicks in Experiment 1. Sedative and hypnotic effects were induced by all compounds, while plasma corticosterone release under isolation stress was only attenuated by L-proline. To clarify the mechanism by which L-proline and D-proline induce sedative and hypnotic effects, the contribution of the strychnine-sensitive glycine receptor (glycine receptor) and N-methyl-D-aspartate glutamate receptor (NMDA receptor) were further investigated. In Experiments 2–3, the glycine receptor antagonist strychnine was co-injected intracerebroventricular (i.c.v.) with L-proline or D-proline. The suppression of isolation-induced stress behavior by D-proline was attenuated by strychnine. However, the suppression of stress behavior by L-proline was not attenuated. In Experiment 4, the NMDA receptor antagonist (+)-MK-801 was co-injected i.c.v. with L-proline. The suppression of stress behavior by L-proline was attenuated by (+)-MK-801. These results indicate that L-proline and D-proline differentially induce sedative and hypnotic effects through NMDA and glycine receptors, respectively.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abercrombie ED, Keefe KA, Difrischia DS, Zigmond MJ (1989) Differential effect of stress on in vivo dopamine release in striatum, nucleus accumbens, and medial frontal cortex. J Neurochem 52:1655–1658. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb09224.x
Arco AD, Mora F (2001) Dopamine release in the prefrontal cortex during stress is reduced by the local activation of glutamate receptors. Brain Res Bull 56:125–130. doi:10.1016/S0361-9230(01)00616-5
Asechi M, Tomonaga S, Tachibana T, Han L, Hayamizu K, Denbow DM, Furuse M (2006) Intracerebroventricular injection of L-serine analogs and derivatives induces sedative and hypnotic effects under an acute stressful condition in neonatal chicks. Behav Brain Res 170:71–77. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2006.02.005
Bhattacharjee A, Bansal M (2005) Collagen structure the Madras triple helix and the current scenario. IUBUB Life 57:161–172. doi:10.1080/15216540500090710
Davis JL, Masuoka DT, Gerbrandt LK, Cherkin A (1979) Autoradiographic distribution of L-proline in chicks after intracerebral injection. Physiol Behav 22:693–695. doi:10.1016/0031-9384(79)90233-6
Delport M, Maas S, Van der merwe SW, Laurens JB (2004) Quantitation of hydroxyproline in bone by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 804:345–351
Farah JM Jr, Rao TS, Mick SJ, Coyne KE, Iyengar S (1991) N-methyl-D-aspartate treatment increases circulating adrenocrticotropin and luteinizing hormone in the rat. Endocrinology 128:1875–1880
Feltenstein MW, Lambdin LC, Ganzera M, Ranjith H, Dharmaratne W, Nanayakkara NP (2003a) Anxiolytic properties of Piper methysticum extract samples and fractions in the chick social-separation-stress procedure. Phytother Res 17:210–216. doi:10.1002/ptr.1107
Feltenstein MW, Lambdin LC, Webb HE, Warnick JE, Khan SI, Khan IA, Acevedo ED, Sufka KJ (2003b) Corticosterone response in the chick separation-stress paradigm. Physiol Behav 78:489–493. doi:10.1016/S0031-9384(03)00030-1
Fremeau RT Jr, Caron MG, Blakely RD (1992) Molecular cloning and expression of a high affinity L-proline transporter expressed in putative glutamatergic pathways of rat brain. Neuron 8:915–926. doi:10.1016/0896-6273(92)90206-S
Gogos JA, Sautha M, Takacs Z, Beck KD, Luine V, Lucas LR, Nadler JV, Karayiorgou M (1999) The gene encoding proline dehydrogenase modulates sensorimotor gating in mice. Nat Genet 21:434–439. doi:10.1038/7777
Gruss M, Braun K (1996) Distinct activation of monoaminergic pathways in chick brain in relation to auditory imprinting and stressful situations: a microdialysis study. Neuroscience 76:891–899. doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(96)00385-5
Gruss M, Bredenkotter M, Braun K (1999) N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-mediated modulation of monoaminergic metabolites and amino acids in the chicks forebrain: an in vivo microdialysis and electrophysiology study. J Neurobiol 40:116–135. doi :10.1002/(SICI)1097-4695(199907)40:1<116::AID-NEU10>3.0.CO;2-M
Halpain S, Wieczorek CM, Rainbow TC (1984) Localization of L-glutamate receptors in rat brain by quantitative autoradiography. J Neurosci 4:2247–2258
Hamasu K, Haraguchi T, Kabuki Y, Adachi N, Tomonaga S, Sato H, Denbow DM, Furuse M (2009) L-Proline is a sedative regulator of acute stress in the brain of neonatal chicks. Amino Acids (in press)
Harvey R, Depner U, Wassle H, Ahmadi S, Heindl C, Reinold H, Smart T, Harvey K, Schutz B, Akbari O, Zimmer A, Poisbeau P, Welzl H, Wolfer H, Betz H, Zeilhofer U, Muller U (2004) Gly Ralpha3: an essential target for spinal PGE2-mediated inflammatory pain sensitization. Science 304:884–888. doi:10.1126/science.1094925
Henzi V, Reichling DB, Helm SW, Macdermott AB (1992) L-Proline activates glutamate and glycine receptors in cultured rat dorsal horn neurons. Mol Pharmacol 41:793–801
Jazova D, Tokarev D, Rusnak M (1995) Endogenous excitatory amino acids are involved in stress-induced adrenocorticotropin and catecholamine release. Neuroendocrinology 62:326–332. doi:10.1159/000127021
Joanny P, Steinberg J, Oliver C, Grino M (1997) Glutamate and N-methyl-D-aspartate stimulate rat hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing factor secretion in vitro. J Neuroendocrinol 9:93–97. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2826.1997.00548.x
Koutoku T, Takahashi H, Tomonaga S, Oikawa D, Saito S, Tachibana T, Han L, Hayamizu K, Denbow DM, Furuse M (2005) Central administration of phosphatidylserine attenuates isolation stress-induced behavior in chicks. Neurochem Int 47:183–189. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2005.03.006
Lindstrom P, Ohlsson L (1992) Effect of N-methyl-D, L-aspartate on isolated rat somatotrophs. Endocrinology 131:1903–1907. doi:10.1210/en.131.4.1903
Lopez-Corcuera B, Geerlings A, Aragon C (2001) Glycine neurotransmitter transporters: an update. Mol Membr Biol 18:13–20
Mahesh VB, Zamorano P, Sevilla LD, Lewis D, Brann DV (1999) Characterization of ionotropic glutamate receptors in rat hypothalamus, pituitary and immortalized gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) neurons (GT1–7 cells). Neuroendocrinology 69:397–407. doi:10.1159/000054442
Messia MC, Falco TD, Panfili G, Marconi E (2008) Rapid determination of collagen in meat-based foods by microwave hydrolysis of proteins and HPAEC–PAD analysis of 4-hydroxyproline. Meat Sci (in press)
Ortiz JG, Cordero ML, Rosado A (1996) Proline-glutamate interactions in the CNS. Prog Neuro-Psychoph 21:141–152. doi:10.1016/S0278-5846(96)00164-9
Panksepp J, Bean NJ, Bishop P, Vilberg T, Sahley TL (1980) Opioid blockade and social comfort in chicks. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 13:673–683. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(80)90011-8
Powell J (2006) Skin physiology. Women Health Med 3:130–133. doi:10.1383/wohm.2006.3.3.130
Renick SE, Kleven DT, Chan J, Stenius K, Milner TA, Pickel VM, Fremeau RT Jr (1999) The mammalian brain high-affinity L-proline transporter is enriched preferentially in synaptic vesicles in a subpopulation of excitatory nerve terminals in rat forebrain. J Neurosci 19:21–33
Sahley TL, Panksepp J, Zolovick AJ (1981) Cholinergic modulation of separation distress in the domestic chick. Eur J Pharmacol 72:261–264. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(81)90283-1
Sigemi K, Tsuneyoshi Y, Hamasu K, Han L, Hayamizu K, Denbow PM, Furuse M (2008) L-Serine induces sedative and hypnotic effects acting at GABA (A) receptors in neonatal chicks. Eur J Pharmacol 599:86–90
Snyder SH, Young AB, Bennett JP, Mulder AH (1973) Synaptic biochemistry of amino acids. Fed Proc 32:2039–2047
Takagi T, Ando R, Ohgushi A, Yamashita T, Dobashi E, Hussain-Yusuf H, Onodera R, Bungo T, Sato H, Furuse M (2001) Intracerebroventricular injection of pipecolic acid inhibits food intake and induces sleeping-like behaviors in the neonatal chick. Neurosci Lett 310:97–100. doi:10.1016/S0304-3940(01)02059-6
Tanida M, Katsuyama M, Sakatani K (2007) Relation between mental stress-induced prefrontal cortex activity and skin conditions: a near-infrared spectroscopy study. Brain Res 1184:210–216. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2007.09.058
Uitto J (1971) Collagen biosynthesis in human skin. Ann Clin Res 3:250–258
Van Luijtelaar ELJM, van der Grinten CPM, Blokhuis HJ, Coenen AML (1987) Sleep in the domestic hen (Gallus domesticus). Physiol Behav 41:409–414. doi:10.1016/0031-9384(87)90074-6
Yoneda S, Roberts E (1982) A new synaptosomal biosynthetic pathway of proline from ornithine and its negative feedback inhibition by proline. Brain Res 239:479–488. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(82)90523-6
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (No. 18208023) and the SKYLARK Food Science Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamasu, K., Shigemi, K., Tsuneyoshi, Y. et al. Intracerebroventricular injection of L-proline and D-proline induces sedative and hypnotic effects by different mechanisms under an acute stressful condition in chicks. Amino Acids 38, 57–64 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-008-0204-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-008-0204-9