Abstract
In celiac disease (CD), gluten, the disease-inducing toxic component in wheat, induces the secretion of IgA-class autoantibodies which target tissue transglutaminase (tTG). These autoantibodies are produced in the small-intestinal mucosa, and, during gluten consumption, they can also be detected in patients’ serum but disappear slowly from the circulation on a gluten-free diet. Interestingly, after adoption of a gluten-free diet the serum autoantibodies disappear from the circulation more rapidly than the small-intestinal mucosal autoantibody deposits. The finding of IgA deposits on extracellular tTG in the liver, kidney, lymph nodes and muscles of patients with CD indicates that tTG is accessible to the gut-derived autoantibodies. Although the specific autoantibody response directed against tTG is very characteristic in celiac patients, their role in the immunopathology of the celiac mucosal lesion is a matter of debate. Here we report a brief summary of anti-tTG antibody effects demonstrating that these antibodies are functional and not mere bystanders in the disease pathogenesis. In fact, they inhibit intestinal epithelial cell differentiation, induce intestinal epithelial cell proliferation, increase epithelial permeability and activate monocytes and disturb angiogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CD:
-
Celiac disease
- tTG:
-
Tissue transglutaminase
- TGF β:
-
Trasforming growth factor β
- GA:
-
Gluten ataxia
References
Aeschlimann D, Thomazy V (2000) Protein crosslinking in assembly and remodelling of extracellular matrices: the role of transglutaminases. Connect Tissue Res 41:1–27
Akimov SS, Belkin AM (2001) Cell surface tissue transglutaminase is involved in adhesion and migration of monocytic cells on fibronectin. Blood 98:1567–1576
Akimov SS, Krylov D, Fleischman LF et al (2000) Tissue transglutaminase is an integrin-binding adhesion coreceptor for fibronectin. J Cell Biol 148(4):825–838
Arentz-Hansen H, Körner R, Molberg O et al (2000) The intestinal T cell response to alpha-gliadin in adult celiac disease is focused on a single deamidated glutamine targeted by tissue transglutaminase. J Exp Med 191:603–612
Bakker EN, Buus CL, Spaan JA et al (2005) Small artery remodeling depends on tissue-type transglutaminase. Circ Res 96:119–126
Balklava Z, Verderio E, Collighan R et al (2002) Analysis of tissue transglutaminase function in the migration of Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts: the active-state conformation of the enzyme does not affect cell motility but is important for its secretion. J Biol Chem 277:16567–16575
Barone MV, Caputo I, Ribecco MT et al (2007) Humoral immune response to tissue transglutaminase is related to epithelial cell proliferation in celiac disease. Gastroenterology 132:1245–1253
Bergamini CM, Griffin M, Pansini FS (2005) Transglutaminase and vascular biology: physiopathologic implications and perspectives for therapeutic interventions. Curr Med Chem 12:2357–2372
Boscolo S, Sarich A, Lorenzon A et al (2007) Gluten ataxia: passive transfer in a mouse model. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1107:319–328
Byrne G, Ryan F, Jackson J et al (2007) Mutagenesis of the catalytic triad of tissue transglutaminase abrogates celiac disease serum IgA autoantibody binding. Gut 56:336–341
Cervio E, Volta U, Verri M et al (2007) Sera of patients with celiac disease and neurologic disorders evoke a mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis in vitro. Gastroenterology 133:195–206
Crovella S, Brandao L, Guimaraes R et al (2007) Speeding up coeliac disease diagnosis in the developing countries. Dig Liver Dis 39:900–902
Di Niro R, Sblattero D, Florian F et al (2008) Anti-idiotypic response in mice expressing human autoantibodies. Mol Immunol 45:1782–1791
Dieterich W, Ehnis T, Bauer M et al (1997) Identification of tissue transglutaminase as the autoantigen of celiac disease. Nat Med 3:797–801
Dieterich W, Trapp D, Esslinger B et al (2003) Autoantibodies of patients with coeliac disease are insufficient to block tissue transglutaminase activity. Gut 52:1562–1566
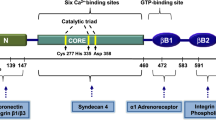
Esposito C, Caputo I (2005) Mammalian transglutaminases. Identification of substrates as a key to physiological function and physiopathological relevance. FEBS J 272:615–631
Esposito C, Paparo F, Caputo I et al (2002) Anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies from coeliac patients inhibit transglutaminase activity both in vitro and in situ. Gut 51:177–181
Esposito C, Paparo F, Caputo I et al (2003) Expression and enzymatic activity of small intestinal tissue transglutaminase in celiac disease. Am J Gastroenterol 98:1813–1820
Falasca L, Iadevaia V, Ciccosanti F et al (2005) Transglutaminase type II is a key element in the regulation of the anti-inflammatory response elicited by apoptotic cell engulfment. J Immunol 174(11):7330–7340
Ferrara F, Dal Bo S, Quaglia S et al (2007) Protective role of anti-idiotypic network in celiac disease prone subjects. Gastroenterology 132(supp 1):762
Gentile V, Saydak M, Chiocca EA et al (1991) Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones to mouse macrophage and human endothelial cell tissue transglutaminases. J Biol Chem 266478–266483
Griffin M, Casadio R, Bergamini CM (2002) Transglutaminases: nature’s biological glues. Biochem J 368:377–396
Hadjivassiliou M, Mäki M, Sanders DS et al (2006) Autoantibody targeting of brain and intestinal transglutaminase in gluten ataxia. Neurology 66:373–377
Halttunen T, Mäki M (1999) Serum immunoglobulin A from patients with celiac disease inhibits human T84 intestinal crypt epithelial cell differentiation. Gastroenterology 116:566–572
Hasegawa G, Suwa M, Ichikawa Y et al (2003) A novel function of tissue-type transglutaminase: protein disulphide isomerase. Biochem J 373:793–803
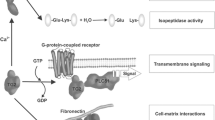
Im MJ, Russell MA, Feng JF (1997) Transglutaminase II: a new class of GTP-binding protein with new biological functions. Cell Signal 9:477–482
Jabri B, de Serre NP, Cellier C et al (2000) Selective expansion of intraepithelial lymphocytes expressing the HLA-E-specific natural killer receptor CD94 in celiac disease. Gastroenterology 118:867–879
Kagnoff MF (2005) Overview and pathogenesis of celiac disease. Gastroenterology 128:S10–S18
Kaukinen K, Halme L, Collin P et al (2002) Celiac disease in patients with severe liver disease: gluten-free diet may reverse hepatic failure. Gastroenterology 122:881–888
Kim SY, Jeitner TM, Steinert PM (2002) Transglutaminases in disease. Neurochem Int 40:85–103
Király R, Vecsei Z, Deményi T et al (2006) Coeliac autoantibodies can enhance transamidating and inhibit GTPase activity of tissue transglutaminase: dependence on reaction environment and enzyme fitness. J Autoimmun 26:278–287
Korponay-Szabó IR, Halttunen T, Szalai Z et al (2004) In vivo targeting of intestinal and extraintestinal transglutaminase 2 by celiac autoantibodies. Gut 53:641–648
Lesort M, Attanavanich K, Zhang J et al (1998) Distinct nuclear localization and activity of tissue transglutaminase. J Biol Chem 273:11991–11994
Lorand L, Graham RM (2003) Transglutaminases: crosslinking enzymes with pleiotropic functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:140–156
Maiuri L, Ciacci C, Ricciardelli I et al (2005) Unexpected role of surface transglutaminase type II in celiac disease. Gastroenterology 129:1400–1413
Mangala LS, Mehta K (2005) Tissue transglutaminase (TG2) in cancer biology. Prog Exp Tumor Res 38:125–138
Marzari R, Sblattero D, Florian F et al (2001) Molecular dissection of the tissue transglutaminase autoantibody response in celiac disease. J Immunol 166:4170–4176
Meresse B, Curran SA, Ciszewski C et al (2006) Reprogramming of CTLs into natural killer-like cells in celiac disease. J Exp Med 203:1343–1355
Mishra S, Murphy LJ (2004) Tissue transglutaminase has intrinsic kinase activity: identification of transglutaminase 2 as an insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 kinase. J Biol Chem 279:23863–23868
Molberg O, Mcadam SN, Körner R et al (1998) Tissue transglutaminase selectively modifies gliadin peptides that are recognized by gut-derived T cells in celiac disease. Nat Med 4:713–717
Molberg O, McAdam SN, Sollid LM (2000) Role of tissue transglutaminase in celiac disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 30:232–240
Moss SF, Attia L, Scholes JV et al (1996) Increased small intestinal apoptosis in coeliac disease. Gut 39:811–817
Myrsky E, Kaukinen K, Syrjänen M et al (2008) Coeliac disease-specific autoantibodies targeted against transglutaminase 2 disturb angiogenesis. Clin Exp Immunol 152:111–119
Pinkas DM, Strop P, Brunger AT et al (2007) Transglutaminase 2 undergoes a large conformational change upon activation. PLoS Biol 5:e327
Roth EB, Sjöberg K, Stenberg P (2003) Biochemical and immuno-pathological aspects of tissue transglutaminase in celiac disease. Autoimmunity 36:221–226
Ruan Q, Johnson GV (2007) Transglutaminase 2 in neurodegenerative disorders. Front Biosci 12:891–904
Schuppan D, Dieterich W, Riecken EO (1998) Exposing gliadin as a tasty food for lymphocytes. Nat Med 4:666–667
Sollid LM (2000) Molecular basis of celiac disease. Annu Rev Immunol 18:53–81
Sollid LM (2002) Coeliac disease: dissecting a complex inflammatory disorder. Nat Rev Immunol 2:647–655
Sollid LM, Molberg O, Mc Adam S et al (1997) Autoantibodies in coeliac disease: tissue transglutaminase guilt by association? Gut 41:851–852
Stenberg P, Roth EB, Sjöberg K (2008) Transglutaminase and the pathogenesis of coeliac disease. Eur J Intern Med 19:83–91
Stenman SM, Lindfors K, Korponay-Szabo IR et al (2008) Secretion of celiac disease autoantibodies after in vitro gliadin challenge is dependent on small-bowel mucosal transglutaminase 2-specific IgA deposits. BMC Immunol 9:6
Ventura A, Magazzù G, Greco L (1999) Duration of exposure to gluten and risk for autoimmune disorders in patients with celiac disease. SIGEP Study Group for Autoimmune Disorders in Celiac Disease. Gastroenterology 117:297–303
Verderio EA, Johnson T, Griffin M (2004) Tissue transglutaminase in normal and abnormal wound healing: review article. Amino Acids 26:387–404
Watts T, Berti I, Sapone A et al (2005) Role of the intestinal tight junction modulator zonulin in the pathogenesis of type I diabetes in BB diabetic-prone rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci 102:2916–2921
Zanoni G, Navone R, Lunardi C et al (2006) In celiac disease, a subset of autoantibodies against transglutaminase binds toll-like receptor 4 and induces activation of monocytes. PLoS Med 3:e358
Zemskov EA, Janiak A, Hang J et al (2006) The role of tissue transglutaminase in cell-matrix interactions. Front Biosci 11:1057–1076
Zemskov EA, Mikhailenko I, Strickland DK et al (2007) Cell-surface transglutaminase undergoes internalization and lysosomal degradation: an essential role for LRP1. J Cell Sci 120:3188–3199
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caputo, I., Barone, M.V., Martucciello, S. et al. Tissue transglutaminase in celiac disease: role of autoantibodies. Amino Acids 36, 693–699 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-008-0120-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-008-0120-z