Abstract
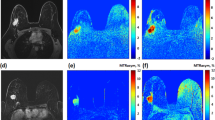
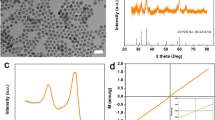
Modern imaging technologies such as mMRI employ contrast agents to visualize the tumor microenvironment; therefore, demand for contrast agents, with an enhanced sensitivity and tissue tumor-specific target, is very high. The purpose of this study synthesizes novel metabolic contrast agent (Gd-DTPA-DG) and evaluates accumulation in tumor tissue for early diagnostic cancer. The contrast agent was synthesized and characterized with using different techniques including dynamic light scattering, high resolution transmission electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES). Finally, MRI imaging performed to determine in vitro and in vivo relaxometry. Gd-DTPA-DG was specifically investigated in tissue tumor over a 45 min in vivo because of its ability to target metabolically active tumor tissue, and comparison with conventional contrast agent [Gd-DTPA (Magnevist, Bayer-USA)]. According to the result, the maximum image signal intensity in different concentrations (0.02 to approximately 0.8 mM), longitudinal relaxation time (T 1) and transverse relaxation time (T 2) were obtained. Signal intensity of tumor tissue was shown at 15 and 30 min after injection reaches maximum for Gd-DTPA-DG and Gd-DTPA (Magnevist, Bayer-USA), respectively. But Gd-DTPA-DG shown signal intensity higher of Gd-DTPA (Magnevist, Bayer-USA) over 45 min, comparison with Gd-DTPA (Magnevist, Bayer-USA). Images showed metabolic contrast agent penetrate into cells and accumulated in tumor. These results showed that the novel metabolic contrast agent could become a useful tool in early detection of cancer.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.M. New cancer cases will grow 30 % by 2020. Economist Intelligence Unit. Available from http://www.eiu.com (2009)
K. Brindle, Nat. Rev. Cancer 8(2), 107–194 (2008)
S.S. Gambhir, Nat. Rev. Cancer 2(9), 683–693 (2002)
N.K. Logothetis, Nature 453, 869–878 (2008)
D.G. Mitchell, MRI principles (W. B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia, 1999)
E.J. Delikatny, H. Poptani, Radiol. Clin. North Am. 43, 205–220 (2005)
G.A. Pereira, C.F.G.C. Geraldes, Ann. Magn. Reson. 6(1),1–33 (2007)
A. Hengerer, J. Grimm, Biomed Imaging Interv J. 2(2), 1–7 (2006)
J.S. Ananta, B. Godin, R. Sethi, L. Moriggi, X. Liu, R.E. Serda, R. Krishnamurthy, R. Muthupillai, R.D. Bolskar, L. Helm, M. Ferrari, L.J. Wilson, P. Decuzzi, Nat. Nanotechnol. 5, 815–821 (2007)
S. Geninatti Crich, C. Cabella, A. Barge, S. Belfiore, C. Ghirelli, L. Lattuada, S. Lanzardo, A. Mortillaro, L. Tei, M. Visigalli, G. Forni, S. Aime, J. Med. Chem. 49, 4926–4936 (2006)
G. Kroemer, J. Pouyssegur, Cancer Cell. 13, 472–482 (2008)
R.A. Gatenby, R.J. Gillies, Nat. Rev. Cancer 4, 891–899 (2004)
V.K. Jain, V.K. Kalia, R. Sharma, V. Maharajan, M. Memnon, Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 11, 943–950 (1985)
E.K. Pauwels, Nucl. Med. Biol. 25, 317–322 (1998)
D.J. Yang, C.G. Kim, N.R. Schechter, A. Azhdarinia, D.F. Yu, C.S. Oh, J.L. Bryant, J.J. Won, E.E. Kim, D.A. Podoloff, Radiology 226, 465–473 (2003)
W. Zhang, Y. Chen, J. Guo da, Z.W. Huang, L. Cai, L. He, Eur. J. Radiol. 79, 369–374 (2011)
M. Amanlou, S.D. Siadat, S.E.S. Ebrahimi, A. Alavi, M.R. Aghasadeghi, M.S. Ardestani, S. Shanehsaz, M. Ghorbani, B. Mehravi, M. Shafiee Alavidjeh, A. Jabbari-Arabzadeh, M. Abbasi, Int. J. Nanomedicine 6, 747–763 (2011)
G. Azizian, N. Riyahi-Alam, S. Haghoo, H.R. Moghimi, R. Zohdiaghdam, B. Rafiei, E. Gorji, Mater. Sci. Pol. 20133. 8, 425–429 (2013)
N. Riyahi-Alam, Z. Behrouzkia, A. Seifalian, S. Haghgoo Jahromi, Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 137(3), 324–334 (2010)
V. Ganapathy, M. Thangaraju, P.D. Prasad, Pharmacol. Ther. 121(1), 29–40 (2009)
C. Cheze-Le Rest, J.P. Metges, P. Teyton, V. Jestin-Le Tallec, P. Lozac'h, A. Volant, D. Visvikis, Nucl. Med. Commun. 29, 628–663 (2008)
P. Parente, A. Coli, G. Massi, A. Mangoni, M.M. Fabrizi, G.I. Bigotti, J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 27, 34–40 (2008)
D. Yang, M. Yukihiro, D.F. Yu, M. Ito, C.S. Oh, S. Kohanim, A. Azhdarinia, C.G. Kim, J. Bryant, E.E. Kim, D. Podoloff, Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 19(4), 443–456 (2004)
Y. Chen, Z.W. Huang, L. He, S.L. Zheng, J.L. Li, D.L. Qin, Appl. Radiat. Isot. 64(3), 342–347 (2006)
Y.Y. Sun, Y. Chen, Curr. Pharm. Des. 15(9), 983–987 (2009)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the research chancellor of Tehran University of Medical Sciences (TUMS) Tehran-Iran. We thank Mr. Mehdi Gholami and Ahmad Shamsa for them valuable help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heydarnezhadi, S., Riahi Alam, N., Haghgoo, S. et al. Glycosylated Gadolinium as Potential Metabolic Contrast Agent vs Gd-DTPA for Metabolism of Tumor Tissue in Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Appl Magn Reson 47, 375–385 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-015-0756-2
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-015-0756-2