Abstract
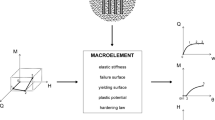
The present paper deals with the computational simulation of a pile of thin sheets. The sheets are not laminated or glued, but they interact by frictional contact. In general, it is not possible to perform a full-scale finite element contact computation for piles containing thousands of sheets; the problem size becomes too large, and numerical solution methods suffer from severe convergence problems due to the large number of strongly coupled contact conditions. In this paper, a macroscopic material model is presented for the two-dimensional case. The pile of sheets is homogenized by introducing an effective anisotropic constitutive law, which is motivated by formulations of the theory of elasto-plasticity. This macroscopic material law models the behavior of a pile of sheets, allowing for no tensile stresses in the direction normal to the sheets and obeying Coulomb’s law of friction in the tangential contact plane. Applying this macroscopic material model, an equivalent homogeneous body can be treated using much coarser discretizations. Computational results for the problems are provided, and a comparison with simplified contact computations is done.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aigner, L., Sinwel, A., Gerstmayr, J., Irschik, H.: The constitutive modeling of homogenized contact and friction conditions in thin-sheet packages. In: Proceedings of the 7th EUROMECH Solid Mechanics Conference, Lisbon, Portugal (7–11 September 2009)
Angelillo M.: Constitutive relations for no-tension materials. Meccanica 28, 195–202 (1993)
Bufler H.: Planar elastic laminates and their homogenization. Acta Mech. 141, 1–36 (2000)
Cherouat A., Radi B., Hami A.E.: The frictional contact of the composite fabric’s shaping. Acta Mech. 199, 29–41 (2008)
FEA, A.U.: Dassault Systèmes (Simulia, 2008), http://www.simulia.com
Greco F.: Homogenized mechanical behavior of composite micro-structures including micro-cracking and contact evolution. Eng. Fract. Mech. 76, 182–208 (2009)
Heyman J.: The stone skeleton. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2, 249–279 (1966)
Ladevéze P., Lubineau G., Marsal D.: Towards a bridge between the micro- and mesomechanics of delamination for laminated composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 66, 698–712 (2006)
Luenberger, D.G., Ye, Y.: Linear and Nonlinear Programming, Third edition, International Series in Operations Research & Management Science, 116. Springer, New York (2008)
Miehe C., Schröder J., Bayreuther C.: On the homogenization analysis of composite material based on discretized fluctuations on the micro-structure. Acta Mech. 155, 1–16 (2002)
Milani G., Lourenço P., Tralli A.: Homogenised limit analysis of masonry walls, part i: failure surfaces. Comput. Struct. 84, 166–180 (2006)
Milani G., Lourenço P., Tralli A.: Homogenised limit analysis of masonry walls, part ii: structural examples. Comput. Struct. 84, 181–195 (2006)
Nemat-Nasser S., Hori M.: Micromechanics: Overall Properties of Heterogeneous Materials, North-Holland Series in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, vol. 37. North-Holland Publishing Co, Amsterdam (1993)
Omri A.E., Fennan A., Sidoroff F., Hihi A.: Elastic-plastic homogenization of layered composites. Eur. J. Mech. A/Solids 19, 585–601 (2000)
Pasquale S.D.: New trends in the analysis of masonry structures. Meccanica 27, 173–184 (1992)
Pellegrino C., Galvanetto U., Schrefler B.: Numerical homogenization of periodic composite materials with non-linear material components. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 46, 1609–1637 (1999)
Pfeiffer F., Glocker C.: Multibody Dynamics with Unilateral Contacts, Wiley Series in Nonlinear Science. Wiley, New York (1996)
Simo J.C., Hughes T.J.R.: Computational Inelasticity, Interdisciplinary Applied Mathematics: Mechanics and Materials, vol. 7. Springer, New York (1998)
Vetyukov Y., Gerstmayr J., Irschik H.: Plastic multipliers as driving variables of numerical simulation in elastoplasticity. Mech. Res. Commun. 30, 421–430 (2003)
Vorhauer L., Gerstmayr J.: Mechanically homogenized material model for a pack of sheets. PAMM 9, 423–424 (2009)
Wriggers P.: Computational Contact Mechanics, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin (2006)
Ziegler F.: Mechanics of Solids and Fluids. Springer, Berlin (1995)
Zienkiewicz O.C., Taylor R.L.: The finite element method, vol. 1, 5th edn. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford (2000) The basis
Zienkiewicz O.C., Taylor R.L.: The finite element method, vol. 2, 5th edn. Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford (2000) Solid mechanics
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aigner, L.G., Gerstmayr, J. & Pechstein, A.S. A two-dimensional homogenized model for a pile of thin elastic sheets with frictional contact. Acta Mech 218, 31–43 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-010-0399-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-010-0399-1