Summary.
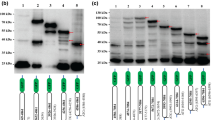
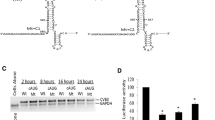
Due to several incomplete splicing reactions, budgerigar fledgling disease virus (BFDV) late mature mRNAs are either bicistronic or polycistronic with an agnogene located upstream of viral protein (VP) genes. While the bicistronic mRNAs code for the vast majority of VP1, the polycistronic mRNAs contain the coding sequences of VP2, VP3, and VP1 (as the most distal cistron relative to VP2 and VP3). In this work, the translation initiation mechanism of VP3 was investigated in chicken embryo fibroblast cells by transfection of a series of BFDV mutant clones and transient reporter gene chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) expression assay, leading to the conclusion that BFDV VP3 was translated by leaky ribosomal scanning. Furthermore, thanks to the high sensitivity of CAT assay experiment, we were able to demonstrate that ribosomes could reach VP1-AUG and initiate translation after scanning through 900 nucleotides on the unspliced polycistronic mRNA.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted August 28, 1999/Received June 4, 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Q., Hobom, G. Evidence for translation of VP3 of avian polyomavirus BFDV by leaky ribosomal scanning. Arch. Virol. 145, 407–416 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007050050032
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007050050032