Abstract
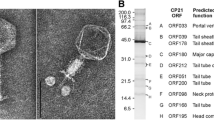
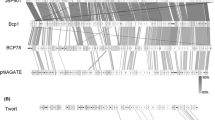
Campylobacter phage vB_CjeM_Los1 was recently isolated from a slaughterhouse in the Republic of Ireland using the host Campylobacter jejuni subsp. jejuni PT14, and full-genome sequencing and annotation were performed. The genome was found to be 134,073 bp in length and to contain 169 predicted open reading frames. Transmission electron microscopy images of vB_CjeM_Los1 revealed that it belongs to the family Myoviridae, with tail fibres observed in both extended and folded conformations, as seen in T4. The genome size and morphology of vB_CjeM_Los1 suggest that it belongs to the genus Cp8virus, and seven other Campylobacter phages with similar size characteristics have also been fully sequenced. In this work, comparative studies were performed in relation to genomic rearrangements and conservation within each of the eight genomes. None of the eight genomes were found to have undergone internal rearrangements, and their sequences retained more than 98% identity with one another despite the widespread geographical distribution of each phage. Whole-genome phylogenetics were also performed, and clades were shown to be representative of the differing number of tRNAs present in each phage. This may be an indication of lineages within the genus, despite their striking homology.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Health Protection Surveillance Centre (2014) Epidemiology of campylobacter in Ireland, 2013. http://www.hpsc.ie/A-Z/Gastroenteric/Campylobacter/Publications/AnnualReportsonCampylobacteriosis/. Accessed 12 Feb 2017
Danis K, Di Renzi M, O’Neill W, Smyth B, McKeown P, Foley B, Tohani V, Devine M (2009) Risk factors for sporadic Campylobacter infection: an all-Ireland case–control study. Euro Surveillance 14(7)
European Food Safety Authority (2011) Scientific opinion on Campylobacter in broiler meat production: control options and performance objectives and/or targets at different stages of the food chain. EFSA J. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2011.2105
Health Protection Surveillance Centre (2004-2015) Epidemiology of campylobacter in Ireland. http://www.hpsc.ie/A-Z/Gastroenteric/Campylobacter/Publications/AnnualReportsonCampylobacteriosis/. Accessed 12 Feb 2017
European Food Safety Authority (2010) Analysis of the baseline survey on the prevalence of Campylobacter in broiler batches and of Campylobacter and Salmonella on broiler carcasses in the EU, 2008—Part A: Campylobacter and Salmonella pr. EFSA J. https://doi.org/10.2903/j.efsa.2010.1503
Engberg J, Aarestrup FM, Taylor DE, Gerner-Smidt P, Nachamkin I (2001) Quinolone and macrolide resistance in Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli: resistance mechanisms and trends in human isolates. Emerg Infect Dis 7(1):24–34. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid0701.700024
Wittebole X, De Rooke S, Opal SM (2013) A historical overview of bacteriophage therapy as an alternative to antibiotics for the treatment of bacterial pathogens. Virulence 5(1):226–235. https://doi.org/10.4161/viru.25991
Loc-Carrillo C, Abedon ST (2011) Pros and cons of phage therapy. Bacteriophage 1(2):111–114. https://doi.org/10.4161/bact.1.2.14590
Siringan P, Connerton PL, Payne RJH, Connerton IF (2011) Bacteriophage-mediated dispersal of Campylobacter jejuni biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(10):3320–3326. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02704-10
Chibani-Chennoufi S, Bruttin A, Dillmann ML, Brüssow H (2004) Phage-host interaction: an ecological perspective. J Bacteriol 186(12):3677–3686. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.186.12.3677-3686.2004
Hansen VM, Rosenquist H, Baggesen DL, Brown S, Christensen BB (2007) Characterization of Campylobacter phages including analysis of host range by selected Campylobacter Penner serotypes. BMC Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-7-90
Grajewski BA, Kusek JW, Gelfand HM (1985) Development of a bacteriophage typing system for Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. J Clin Microbiol 22(1):13–18
Atterbury RJ, Connerton PL, Dodd CER, Rees CED, Connerton IF (2003) Isolation and characterization of Campylobacter bacteriophages from retail poultry. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(8):4511–4518. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.8.4511-4518.2003
Sails AD, Wareing DRA, Bolton FJ, Fox AJ, Curry A (1998) Characterisation of 16 Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli typing bacteriophages. Med Microbiol 47(1):123–128. https://doi.org/10.1099/00222615-47-2-123
Javed MA, Ackermann H, Azeredo J, Kropinski A (2013) A suggested classification for two groups of Campylobacter Myoviruses. Arch Virol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-013-1788-2
Adams MJ, Lefkowitz EJ, King AMQ, Harrach B, Harrison RL, Knowles NJ, Kropinski A, Krupovic M, Kuhn JH, Mushegian A, Nibert M, Sabandzovic S, Sanfacon H, Siddel SG, Simmonds P, Varsani A, Zerbini FM, Gorbalenya AE, Davidson AJ (2016) Ratification vote on taxonomic proposals to the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (2016). Adv Virol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-016-2977-6
Connerton PL, Timms AR, Connerton IF (2011) Campylobacter bacteriophages and bacteriophage therapy. J Appl Microbiol 111(1):255–265. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2011.05012.x
El-Shibiny A, Connerton PL, Connerton IF (2007) Campylobacter succession in broiler chickens. Vet Microbiol 125(3–4):323–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2007.05.023
Hwang S, Yun J, Kim KP, Heu S, Lee S, Ryu S (2009) Isolation and characterization of bacteriophages specific for Campylobacter jejuni. Microbiol Immunol 53(10):559–566. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1348-0421.2009.00163.x
Loc Carrillo CM, Atterbury RJ, El-Shibiny A, Connerton PL, Dillon E, Scott A, Connerton IF (2005) Bacteriophage therapy to reduce Campylobacter jejuni colonization of broiler chickens. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(11):6554–6563. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.11.6554-6563.2005
Loc Carrillo CM, Connerton PL, Pearson T, Connerton IF (2007) Free-range layer chickens as a source of Campylobacter bacteriophage. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 92(3):275–284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-007-9156-4
Coward C, Grant AJ, Swift C, Philp J, Towler R, Heydarian M, Frost JA, Maskell DJ (2006) Phase-variable surface structures are required for infection of Campylobacter jejuni by bacteriophages. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(7):4638–4647. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00184-06
Goode D, Allen VM, Barrow PA (2003) Reduction of experimental Salmonella and Campylobacter contamination of chicken skin by application of lytic bacteriophages. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(8):5032–5036. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.69.8.5032-5036.2003
Brathwaite KJ, Siringan P, Moreton J, Wilson R, Connerton IF (2013) Complete genome sequence of universal bacteriophage host strain Campylobacter jejuni subsp. jejuni PT14. Genome Announc 1(6):e00969–13. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomea.00969-13
Arutyunov D, Szymanski CM, Calendar R (2015) A novel DNA-binding protein from Campylobacter jejuni bacteriophage NCTC12673. FEMS Microbiol Lett 362(21). https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fnv160
Bankevich A, Nurk S, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Dvorkin M, Kulikov AS, Lesin VM, Nikolenko SI, Pham S, Prjibelski AD, Pyshkin AV, Sirotkin AV, Vyahhi N, Tesler G, Alekseyev MA, Pevzner PA (2012) SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol 19(5):455–477. https://doi.org/10.1089/cmb.2012.0021
Delcher AL, Harmon D, Kasif S, White O, Salzberg SL (1999) Improved microbial gene identification with GLIMMER. Nucleic Acids Res 27(23):4636–4641
Hyatt D, Chen GL, Locascio PF, Land ML, Larimer FW, Hauser LJ (2010) Prodigal: prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinform 11(1):119. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-11-119
Finn RD, Coggill P, Eberhardt RY, Eddy SR, Mistry J, Mitchell AL, Potter SC, Punta M, Qureshi M, Sangrador-Vegas A, Salazar GA, Tate J, Bateman A (2016) The Pfam protein families database: towards a more sustainable future. Nucleic Acids Res 44(D1):D279–D285. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1344
Petersen TN, Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H (2011) SignalP 4.0: discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat Methods 8:785–786. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1701
Bailey TL, Elkan C. 1994. Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers. In: Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Intelligent Systems for Molecular Biology. AAAI Press, Menlo Park, California, pp 28–36
Lowe TM, Eddy SR (1997) tRNAscan-SE: A program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 25(5):955–964
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33(7):1870–1874. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msw054
Darling AE, Mau B, Perna NT (2010) progressiveMauve: multiple genome alignment with gene gain, loss and rearrangement. PLoS One 5(6):e11147. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0011147
Alikhan NF, Petty NK, Ben Zakour NL, Beatson SA (2011) BLAST ring image generator (BRIG): simple prokaryote genome comparisons. BMC Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-12-4
Krumsiek J, Arnold R, Rattei T (2007) Gepard: a rapid and sensitive tool for creating dotplots on genome scale. Bioinformatics 23(8):1026–1028. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm039
Ovcharenko I, Loots GG, Giardine BM, Hou M, Ma J, Hardison RC, Stubbs L, Miller W (2005) Mulan: Multiple-sequence local alignment and visualization for studying function and evolution. Genome Res 15(1):184–194. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.3007205
Kropinski AM, Arutyunov D, Foss M, Cunningham A, Ding W, Singh A, Pavlov AR, Henry M, Evoy S, Kelly J, Szymanski CM (2011) Genome and proteome of Campylobacter jejuni bacteriophage NCTC 12673. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(23):8265–8271. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.05562-11
Hammerl JA, Jäckel C, Reetz J, Beck S, Alter T, Lurz R, Barretto C, Brüssow H, Hertwig S (2011) Campylobacter jejuni group III phage CP81 contains many T4-Like genes without belonging to the T4-type phage group: Implications for the evolution of T4 phages. J Virol 85(17):8597–8605. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.00395-11
Loc Carrillo C, Atterbury RJ, El-Shibiny A, Connerton PL, Dillon E, Scott A, Connerton IF (2005) Bacteriophage therapy to reduce Campylobacter jejuni colonization of broiler chickens. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(11):6554–6563. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.11.6554-6563.2005
Janež N, Kokošin A, Zaletel E, Vranac T, Kovač J, Vučković D, Možina SS, Šerbec VC, Zhang Q, Accetto T, Podgornik A, Peterka M (2014) Identification and characterisation of new Campylobacter group III phages of animal origin. FEMS Microbiol Lett 359(1):64–71
Sørensen MCH, Gencay YE, Birk T, Baldvinsson SB, Jäckel C, Hammerl JA, Vegge CS, Neve H, Brøndsted L (2015) Primary isolation strain determines both phage type and receptors recognised by Campylobacter jejuni bacteriophages. PLoS One 10(1):e0116287. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0116287
Conley MP, Wood WB (1975) Bacteriophage T4 whiskers: a rudimentary environment-sensing device. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72(9):3701–3705
Javed MA, van Alphen LB, Sacher J, Ding W, Kelly J, Nargang C, Smith DF, Cummings RD, Szymanski CM (2015) A receptor-binding protein of Campylobacter jejuni bacteriophage NCTC 12673 recognizes flagellin glycosylated with acetamidino-modified pseudaminic acid. Mol Microbiol 95(1):101–115. https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.12849
Firlieyanti AS, Connerton PL, Connerton IF (2016) Campylobacters and their bacteriophages from chicken liver: The prospect for phage biocontrol. Int J Food Microbiol 237(1):121–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2016.08.026
Miller ES, Kutter E, Mosig G, Arisaka F, Kunisawa T, Rüger W (2003) Bacteriophage T4 genome. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 67(1):86–156. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.67.1.86-156.2003
Noble E, Spiering MM, Benkovic SJ (2015) Coordinated DNA replication by the bacteriophage T4 replisome. Viruses. 7(6):3186–3200. https://doi.org/10.3390/v7062766
Labrie SJ, Samson JE, Moineau S (2010) Bacteriophage resistance mechanisms. Nat Rev Microbiol 8(5):317–327. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2315
Wösten MMSM, Boeve M, Koot MGA, van Nuenen AC, van der Zeijst BAM (1998) Identification of Campylobacter jejuni promoter sequences. J Bacteriol 180(3):594–599
Oliveira H, Melo LDR, Santos SB, Nobrega FL, Ferreira EC, Cerca N, Azeredo J, Kluskens LD (2013) Molecular aspects and comparative genomics of bacteriophage endolysins. J Virol 87(8):4558–4570. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.03277-12
São-José C, Parreira R, Vieira G, Santos MA. 2000. The N-terminal region of the Oenococcus oeni bacteriophage fOg44 lysin behaves as a bona fide signal peptide in Escherichia coli and as a cis-inhibitory element, preventing lytic activity on oenococca. Journal of Bacteriology. 182 (20), 5823 - 5831
Kakikawa M, Yokoi KJ, Kimoto H, Nakano M, Kawasaki K, Taketo A, Kodaira K (2002) Molecular analysis of the lysis protein Lys encoded by Lactobacillus plantarum phage phig1e. Gene 299(1–2):227–234
Park T, Struck DK, Dankenbring CA, Young R (2007) The Pinholin of lambdoid phage 21: control of lysis by membrane depolarization. J Bacteriol 189(24):9135–9139. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00847-07
Yasmin A, Kenny JG, Shankar J, Darby AC, Hall N, Edwards C, Horsburgh MJ (2010) Comparative genomics and transduction potential of Enterococcus faecalis temperate bacteriophages. J Bacteriol 192(4):1122–1130. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.01293-09
Merrill BD, Grose JH, Breakwell DP, Burnett SH (2014) Characterization of Paenibacillus larvae bacteriophages and their genomic relationships to firmicute bacteriophages. BMC Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-745
Kolodziejek AM, Schnider DR, Rohde HN, Wojtowicz AJ, Bohach GA, Minnich SA, Hovde CJ (2010) Outer membrane protein X (Ail) contributes to Yersinia pestis virulence in pneumonic plague and its activity is dependent on the lipopolysaccharide core length. Infect Immun 78(12):5233–5243. https://doi.org/10.1128/IAI.00783-10
Friedrich NC, Torrents E, Gibb EA, Sahlin M, Sjöberg BM, Edgell DR (2007) Insertion of a homing endonuclease creates a genes-in-pieces ribonucleotide reductase that retains function. PNAS 104(15):6176–6181. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0609915104
Sandegren L, Nord D, Sjöberg BM (2005) SegH and Hef: two novel homing endonucleases whose genes replace the mobC and mobE genes in several T4-related phages. Nucleic Acids Res 33(19):6203–6213. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gki932
Wood WB, Revel HR (1976) The genome of bacteriophage T4. Bacteriol Rev 40(4):847–868
Javed MA, Poshtiban S, Arutyunov D, Evoy S, Szymanski CM (2013) Bacteriophage receptor binding protein based assays for the simultaneous detection of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. PLoS One 8(7):e69770. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0069770
Kropinski AM, Lavigne R, Ackermann HW, Szymanski C, Javed MA, Connerton I, Timms A, Azeredo J, Carvalho CM, Hertwig S, Hammerl JA (2013) Proposal: create two genera (Cp220likevirus and Cp8unalikevirus) within a new subfamily (Eucampyvirinae) in the family Myoviridae. In: International Committee on the Taxonomy of Viruses. http://www.ictvonline.org/proposals-14/2013.004a-kB.A.v4.Eucampyvirinae.pdf
Acknowledgements
Lisa O’Sullivan was funded by a Teagasc Walsh Fellowship (Project ref: 2013003) and by Teagasc (Project ref: 6323).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Handling Editor: T. K. Frey.
This paper is dedicated to the memory of Alan Lucid, who passed away suddenly on the 31st of August 2017 during the manuscript preparation.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O’Sullivan, L., Lucid, A., Neve, H. et al. Comparative genomics of Cp8viruses with special reference to Campylobacter phage vB_CjeM_los1, isolated from a slaughterhouse in Ireland. Arch Virol 163, 2139–2154 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-018-3845-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-018-3845-3