Abstract
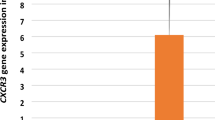
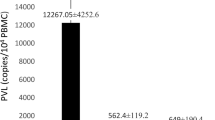
The main aim of this study was to evaluate the expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) as host factors, and proviral load as the viral parameter, in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL) individuals and healthy carrier (HC(s)) groups. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from ATLL patients (n = 17) and HC subjects (as the control group, n = 17) were evaluated using real-time PCR to determine the levels of HTLV-1 proviral load and mRNA expression of ICAM, VCAM-1, and iNOS. ICAM-1 was significantly lower in ATLL patients than in control subjects. Although the expression of VCAM-1 was higher in ATLL individuals, there was no significant difference between the studied groups. In addition, no iNOS expression was found in ATLL patients, when compared to the HCs subjects, while ATLL patients demonstrated a higher level of proviral load when compared to the control group. Considering the importance of ICAM-1 in facilitating immune recognition of infected cells, it is posited that reduction of ICAM-1 expression is a unique strategy for circumventing appropriate immune responses that are mediated by different accessory proteins. Additionally, as the viral regulatory protein Tax and the NF-κB pathway play pivotal roles in expression of iNOS, lack of the latter in ATLL patients may be related to the level of Tax expression, disruption of the NF-κB pathway, or the occurrence of epigenetical mechanisms in the human iNOS promoter. Further studies are recommended to gain a better understanding of the interaction between host and viral factors in HTLV-1 pathogenesis and to identify a possible therapeutic target for ATLL.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bangham CR (2000) HTLV-1 infections. J Clin Pathol 53(8):581–586
Satou Y, Matsuoka M (2012) Molecular and cellular mechanism of leukemogenesis of ATL: emergent evidence of a significant role for HBZ in HTLV-1-induced pathogenesis. Leuk Res Treat 2012:213653. doi:10.1155/2012/213653
Morales-Sanchez A, Fuentes-Panana EM (2014) Human viruses and cancer. Viruses 6(10):4047–4079. doi:10.3390/v6104047
Journo C, Mahieux R (2011) HTLV-1 and innate immunity. Viruses 3(8):1374–1394. doi:10.3390/v3081374
Muhleisen A, Giaisi M, Kohler R, Krammer PH, Li-Weber M (2014) Tax contributes apoptosis resistance to HTLV-1-infected T cells via suppression of Bid and Bim expression. Cell Death Dis 5:e1575. doi:10.1038/cddis.2014.536
Wycuff DR, Marriott SJ (2005) The HTLV-I Tax oncoprotein: hyper-tasking at the molecular level. Front Biosci J Virtual Libr 10:620–642
Kannian P, Green PL (2010) Human T lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1): molecular biology and oncogenesis. Viruses 2(9):2037–2077. doi:10.3390/v2092037
Arnold J, Yamamoto B, Li M, Phipps AJ, Younis I, Lairmore MD, Green PL (2006) Enhancement of infectivity and persistence in vivo by HBZ, a natural antisense coded protein of HTLV-1. Blood 107(10):3976–3982. doi:10.1182/blood-2005-11-4551
Zhao T, Matsuoka M (2012) HBZ and its roles in HTLV-1 oncogenesis. Front Microbiol 3:247. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2012.00247
Ilinskaya A, Derse D, Hill S, Princler G, Heidecker G (2013) Cell-cell transmission allows human T-lymphotropic virus 1 to circumvent tetherin restriction. Virology 436(1):201–209. doi:10.1016/j.virol.2012.11.012
Ishitsuka K, Tamura K (2014) Human T-cell leukaemia virus type I and adult T-cell leukaemia-lymphoma. Lancet Oncol 15(11):e517–e526. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70202-5
Valentin H, Hamaia S, Konig S, Gazzolo L (2001) Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 induced by human T-cell leukaemia virus type 1 Tax protein in T-cells stimulates proliferation of human T-lymphocytes. J Gener Virol 82(Pt 4):831–835. doi:10.1099/0022-1317-82-4-831
Yu Z, Kuncewicz T, Dubinsky WP, Kone BC (2006) Nitric oxide-dependent negative feedback of PARP-1 trans-activation of the inducible nitric-oxide synthase gene. J Biol Chem 281(14):9101–9109. doi:10.1074/jbc.M511049200
Baydoun HH, Cherian MA, Green P, Ratner L (2015) Inducible nitric oxide synthase mediates DNA double strand breaks in human T-Cell leukemia virus type 1-induced leukemia/lymphoma. Retrovirology 12:71. doi:10.1186/s12977-015-0196-y
Molteni CG, Principi N, Esposito S (2014) Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species during viral infections. Free Rad Res 48(10):1163–1169. doi:10.3109/10715762.2014.945443
Kolb JP (2000) Mechanisms involved in the pro- and anti-apoptotic role of NO in human leukemia. Leukemia 14(9):1685–1694
Farid Hosseni R, Jabbari F, Shabestari M, Rezaee SA, Gharivani Y, Valizadeh N, Sobhani M, Moghiman T, Mozayani F (2013) Human T lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) is a risk factor for coronary artery disease. Iran J Basic Med Sci 16(3):217–220
Kchour G, Tarhini M, Kooshyar MM, El Hajj H, Wattel E, Mahmoudi M, Hatoum H, Rahimi H, Maleki M, Rafatpanah H, Rezaee SA, Yazdi MT, Shirdel A, de The H, Hermine O, Farid R, Bazarbachi A (2009) Phase 2 study of the efficacy and safety of the combination of arsenic trioxide, interferon alpha, and zidovudine in newly diagnosed chronic adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATL). Blood 113(26):6528–6532. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-03-211821
Nagai M, Kubota R, Greten TF, Schneck JP, Leist TP, Jacobson S (2001) Increased activated human T cell lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) Ta11–19-specific memory and effector CD8+ cells in patients with HTLV-I-associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis: correlation with HTLV-I provirus load. J Infect Dis 183(2):197–205. doi:10.1086/317932
Nagai M, Usuku K, Matsumoto W, Kodama D, Takenouchi N, Moritoyo T, Hashiguchi S, Ichinose M, Bangham CR, Izumo S, Osame M (1998) Analysis of HTLV-I proviral load in 202 HAM/TSP patients and 243 asymptomatic HTLV-I carriers: high proviral load strongly predisposes to HAM/TSP. J Neurovirol 4(6):586–593
Rafatpanah H, Rezaee A, Etemadi MM, Hosseini RF, Khorram B, Afsahr L, Taylor G, Mokhber N, Mahmoudi M, Abbaszadegan MR, Foroghipor M, Hashemi P, Amiri A, Tehrani M, Azarpazhooh A, Azarpazhooh MR (2012) The impact of interferon-alpha treatment on clinical and immunovirological aspects of HTLV-1-associated myelopathy in northeast of Iran. J Neuroimmunol 250(1–2):87–93. doi:10.1016/j.jneuroim.2012.05.004
Fazeli B, Rafatpanah H, Ravari H, Farid Hosseini R, Tavakol Afshari J, Hamidi Alamdari D, Valizadeh N, Moheghi N, Rezaee SA (2014) Sera of patients with thromboangiitis obliterans activated cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and changed their adhesive properties. Int J Rheum Dis 17(1):106–112. doi:10.1111/1756-185X.12214
Fazeli B, Rafatpanah H, Ravari H, Hosseini RF, Rezaee SA (2014) Investigation of the expression of mediators of neovascularization from mononuclear leukocytes in thromboangiitis obliterans. Vascular 22(3):174–180. doi:10.1177/1708538113477068
Desdouits M, Cassar O, Maisonobe T, Desrames A, Aouba A, Hermine O, Mikol J, Polivka M, Penisson-Besnier I, Marcorelles P, Zagnoli F, Papo T, Lacour A, Amoura Z, Haroche J, Cherin P, Teixeira A, Benveniste O, Herson S, Morin AS, Mortreux F, Wattel E, Huerre M, Cumont MC, Martin-Latil S, Butler-Browne G, Gout O, Taylor G, Gessain A, Ozden S, Ceccaldi PE (2013) HTLV-1-associated inflammatory myopathies: low proviral load and moderate inflammation in 13 patients from West Indies and West Africa. J Clin Virol Off Publ Pan Am Soc Clin Virol 57(1):70–76. doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2012.12.016
Vakili R, Sabet F, Aahmadi S, Boostani R, Rafatpanah H, Shamsian A, Rezaee SA (2013) Human T-lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-I) proviral load and clinical features in Iranian HAM/TSP patients: comparison of HTLV-I proviral load in HAM/TSP patients. Iran J Basic Med Sci 16(3):268–272
Akbarin MM, Rahimi H, Hassannia T, Shoja Razavi G, Sabet F, Shirdel A (2013) Comparison of HTLV-I proviral load in adult T cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATL), HTLV-I-associated myelopathy (HAM-TSP) and healthy carriers. Iran J Basic Med Sci 16(3):208–212
Nakayama Y, Ishikawa C, Tamaki K, Senba M, Fujita J, Mori N (2011) Interleukin-1 alpha produced by human T-cell leukaemia virus type I-infected T cells induces intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression on lung epithelial cells. J Med Microbiol 60(Pt 12):1750–1761. doi:10.1099/jmm.0.033456-0
Valentin H, Lemasson I, Hamaia S, Casse H, Konig S, Devaux C, Gazzolo L (1997) Transcriptional activation of the vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 gene in T lymphocytes expressing human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax protein. J Virol 71(11):8522–8530
Teruya H, Tomita M, Senba M, Ishikawa C, Tamayose M, Miyazato A, Yara S, Tanaka Y, Iwakura Y, Fujita J, Mori N (2008) Human T-cell leukemia virus type I infects human lung epithelial cells and induces gene expression of cytokines, chemokines and cell adhesion molecules. Retrovirology 5:86. doi:10.1186/1742-4690-5-86
Kress AK, Grassmann R, Fleckenstein B (2011) Cell surface markers in HTLV-1 pathogenesis. Viruses 3(8):1439–1459. doi:10.3390/v3081439
Nejmeddine M, Negi VS, Mukherjee S, Tanaka Y, Orth K, Taylor GP, Bangham CR (2009) HTLV-1-Tax and ICAM-1 act on T-cell signal pathways to polarize the microtubule-organizing center at the virological synapse. Blood 114(5):1016–1025. doi:10.1182/blood-2008-03-136770
Tanaka Y, Hayashi M, Takagi S, Yoshie O (1996) Differential transactivation of the intercellular adhesion molecule 1 gene promoter by Tax1 and Tax2 of human T-cell leukemia viruses. J Virol 70(12):8508–8517
Matsuoka M, Jeang KT (2007) Human T-cell leukaemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) infectivity and cellular transformation. Nat Rev Cancer 7(4):270–280. doi:10.1038/nrc2111
Rosadas C, Puccioni-Sohler M (2015) HTLV-1 ORF-I encoded proteins and the regulation of host immune response: viral induced dysregulation of intracellular signaling. J Immunol Res 2015:498054. doi:10.1155/2015/498054
Goto H, Nakamura T, Shirabe S, Ueki Y, Nishiura Y, Furuya T, Tsujino A, Nakane S, Eguchi K, Nagataki S (1997) Up-regulation of iNOS mRNA expression and increased production of NO in human monoblast cell line, U937 transfected by HTLV-I tax gene. Immunobiology 197(5):513–521
Lavorgna A, Harhaj EW (2014) Regulation of HTLV-1 tax stability, cellular trafficking and NF-kappaB activation by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Viruses 6(10):3925–3943. doi:10.3390/v6103925
Lee CH, Jeon YT, Kim SH, Song YS (2007) NF-kappaB as a potential molecular target for cancer therapy. BioFactors 29(1):19–35
Sonoki T, Matsuzaki H, Nagasaki A, Hata H, Yoshida M, Matsuoka M, Kuribayashi N, Kimura T, Harada N, Takatsuki K, Mitsuya H, Mori M (1999) Detection of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) mRNA by RT-PCR in ATL patients and HTLV-I infected cell lines: clinical features and apoptosis by NOS inhibitor. Leukemia 13(5):713–718
Adamson DC, Wildemann B, Sasaki M, Glass JD, McArthur JC, Christov VI, Dawson TM, Dawson VL (1996) Immunologic NO synthase: elevation in severe AIDS dementia and induction by HIV-1 gp41. Science 274(5294):1917–1921
Pautz A, Art J, Hahn S, Nowag S, Voss C, Kleinert H (2010) Regulation of the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Nitric Oxide Biol Chem Off J Nitric Oxide Soc 23(2):75–93. doi:10.1016/j.niox.2010.04.007
Fabisiewicz A, Pacholewicz K, Paszkiewicz-Kozik E, Walewski J, Siedlecki JA (2013) Polymorphisms of DNA repair and oxidative stress genes in B-cell lymphoma patients. Biomed Rep 1(1):151–155. doi:10.3892/br.2012.31
Gross TJ, Kremens K, Powers LS, Brink B, Knutson T, Domann FE, Philibert RA, Milhem MM, Monick MM (2014) Epigenetic silencing of the human NOS2 gene: rethinking the role of nitric oxide in human macrophage inflammatory responses. J Immunol 192(5):2326–2338. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1301758
Acknowledgement
The authors appreciate Mrs. Sheri Lynn jalalian as an English expert for reviewing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This project was financially supported by Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Iran
Competing interests
None declared.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committees of Medical Sciences Research at Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Iran.
Additional information
M. Jafarian and S.-H. Mozhgani are co-first authors and contributed equally to this article.
The original version of this article was revised: One of the author name “Mohammad Mehdi Akbarin” in the authorship was incorrectly published in this original version and the same is corrected here.
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00705-017-3272-x.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jafarian, M., Mozhgani, SH., Patrad, E. et al. Evaluation of INOS, ICAM-1, and VCAM-1 gene expression: A study of adult T cell leukemia malignancy associated with HTLV-1. Arch Virol 162, 1009–1015 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-016-3213-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-016-3213-0