Abstract
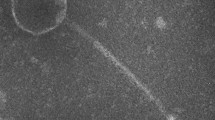
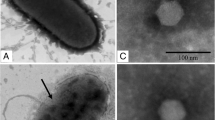
A novel Vibrio alginolyticus lytic bacteriophage was isolated from sewage samples obtained from a local aquatic market. Morphological analysis revealed that the phage, designated as PVA1, belonged to the family Podoviridae. The complete genomic sequence of phage PVA1 contained 41,529 bp with a G + C content of 43.7 % and 75 putative open reading frames. The genome was grouped into four modules, including phage structure, DNA packaging, DNA replication and regulation, and some additional functions. Further genomic comparison of the phage PVA1 with other known phages showed no significant similarities. Genes related to virulence and lysogeny were not detected in the phage genome. Our results suggest that phage PVA1 may be classified as a new Vibrio phage. We believe that these phage genomic sequence data will provide useful basic information for further molecular research on this Vibrio phage and its host as well for determining its infection/interaction mechanisms.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams MH (1959) Bacteriophages. Interscience Publishers, New York
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410. doi:10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2
Besemer J, Borodovsky M (2005) GeneMark: Web software for gene finding in prokaryotes, eukaryotes and viruses. Nucleic Acids Res 33:W451–W454. doi:10.1093/nar/gki487
Carlson K (2005) Working with bacteriophages: common techniques and methodological approaches. In: Kutter E, Sulakvelidze A (eds) Bacteriophages: biology and application. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Delcher AL, Bratke KA, Powers EC, Salzberg SL (2007) Identifying bacterial genes and endosymbiont DNA with Glimmer. Bioinformatics 23:673–679. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btm009
Fischetti VA (2008) Bacteriophage lysins as effective antibacterials. Curr Opin Microbiol 11:393–400. doi:10.1016/j.mib.2008.09.012
Garbe J, Bunk B, Rohde M, Schobert M (2011) Sequencing and characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa phage JG004. BMC Microbiol 11:102. doi:10.1186/1471-2180-11-102
Gomez JM, Fajardo R, Patiño JF, Arias CA (2003) Necrotizing fasciitis due to Vibrio alginolyticus in an immunocompetent patient. J Clin Microbiol 41:3427–3429. doi:10.1128/JCM.41.7.3427-3429.2003
González-Escalona N, Blackstone GM, DePaola A (2006) Characterization of a Vibrio alginolyticus strain, isolated from Alaskan oysters, carrying a hemolysin gene similar to the thermostable direct hemolysin-related hemolysin gene (trh) of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Appl Environ Microb 72:7925–7929. doi:10.1128/AEM.01548-06
Horii T, Morita M, Muramatsu H, Monji A, Miyagishima D, Kanno T, Maekawa M (2005) Antibiotic resistance in Aeromonas hydrophila and Vibrio alginolyticus isolated from a wound infection: A case report. J Trauma 58:196–200. doi:10.1097/01.TA.0000066381.33339.C0
Hornstrup MK, Gahrn-Hansen B (1994) Extraintestinal infections caused by Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio alginolyticus in a Danish county 1987-1992. Ugeskrift Laeger 156:5279. doi:10.3109/00365549309008571
Lagesen K, Hallin P, Rødland EA, Stærfeldt H-H, Rognes T, Ussery DW (2007) RNAmmer: Consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 35:3100–3108. doi:10.1093/nar/gkm160
Laslett D, Canback B (2004) ARAGORN, a program to detect tRNA genes and tmRNA genes in nucleotide sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 32:11–16. doi:10.1093/nar/gkh152
Lee KK, Yu SR, Yang TL, Liu PC, Chen FR (1996) Isolation and characterization of Vibrio alginolyticus isolated from diseased kuruma prawn, Penaeus japonicus. Lett Appl Microbiol 22:111–114. doi:10.1111/j.1472-765X.1996.tb01121.x
Lin YR, Chiu CW, Chang FY, Lin CS (2012) Characterization of a new phage, termed Phi A318, which is specific for Vibrio alginolyticus. Arch Virol 157:917–926. doi:10.1007/s00705-012-1244-8
Lowe TM, Eddy SR (1997) tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 25:0955–0964. doi:10.1093/nar/25.5.0955
Marchler-Bauer A, Anderson JB, Cherukuri PF, DeWeese-Scott C, Geer LY, Gwadz M, He S, Hurwitz DI, Jackson JD, Ke Z (2005) CDD: a conserved domain database for protein classification. Nucleic Acids Res 33:D192–D196. doi:10.1093/nar/gki069
Nakamura K, Kakimoto D, Swafford J, Johnson R (1978) Studies on the characteristics of the bacteriophages of Vibrio alginolyticus strain B-1 isolated from Kinko Bay. Mem Fac Fish Kagoshima Univ 27:59–64
Němeček D, Lander GC, Johnson JE, Casjens SR, Thomas GJ (2008) Assembly architecture and DNA binding of the bacteriophage P22 terminase small subunit. J Mol Biol 383:494–501. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2008.08.050
Oliveira L, Cuervo A, Tavares P (2010) Direct interaction of the bacteriophage SPP1 packaging ATPase with the portal protein. J Biol Chem 285:7366–7373. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.061010
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. CSHL press, New York
Zdobnov EM, Apweiler R (2001) InterProScan-an integration platform for the signature-recognition methods in InterPro. Bioinformatics 17:847–848. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/17.9.847
Acknowledgments
Support for this work was provided by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31001053), the National High-Tech R&D Program of China (863 Program) (No. 2006AA10Z412) and the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (No. 201202034).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Cao, Z., Xu, Y. et al. Complete genomic sequence of the Vibrio alginolyticus lytic bacteriophage PVA1. Arch Virol 159, 3447–3451 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-014-2207-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-014-2207-z