Abstract
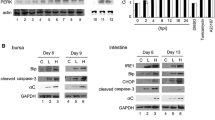
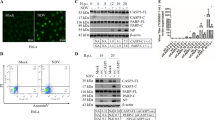
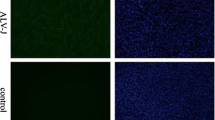
In this study, intracellular signaling in ARV S1133-mediated apoptosis was investigated. A microarray was used to examine the gene expression profiles of cells upon ARV S1133 infection and ARV-encoded pro-apoptotic protein σC overexpression. The analysis indicated that in the set of DNA-damage-responsive genes, DDIT-3 and GADD45α were both upregulated by viral infection and σC overexpression. Further investigation demonstrated that both treatments caused DNA breaks, which increased the expression and/or phosphorylation of DNA damage response proteins. ROS and lipid peroxidation levels were increased, and ARV S1133 and σC caused apoptosis mediated by DNA damage signaling. ROS scavenger NAC, caffeine and an ATM-specific inhibitor significantly reduced ARV S1133- and σC-induced DNA breaks, DDIT-3 and GADD45α expression, H2AX phosphorylation, and apoptosis. Overexpression of DDIT-3 and GADD45α enhanced the oxidative stress and apoptosis induced by ARV S1133 and σC. In conclusion, our results demonstrate the involvement of the DNA-damage-signaling pathway in ARV S1133- and σC-induced apoptosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benavente J, Martinez-Costas J (2007) Avian reovirus: structure and biology. Virus Res 123:105–119
Bodelon G, Labrada L, Martinez-Costas J, Benavente J (2002) Modification of late membrane permeability in avian reovirus-infected cells: viroporin activity of the S1-encoded nonstructural p10 protein. J Biol Chem 277:17789–17796
Brenner B, Koppenhoefer U, Weinstock C, Linderkamp O, Lang F, Gulbins E (1997) Fas- or ceramide-induced apoptosis is mediated by a Rac1-regulated activation of Jun N-terminal kinase/p38 kinases and GADD153. J Biol Chem 272:22173–22181
Brune B, Zhou J, von Knethen A (2003) Nitric oxide, oxidative stress, and apoptosis. Kidney Int Suppl:S22–S24
Carriere A, Carmona MC, Fernandez Y, Rigoulet M, Wenger RH, Penicaud L, Casteilla L (2004) Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species control the transcription factor CHOP-10/GADD153 and adipocyte differentiation: a mechanism for hypoxia-dependent effect. J Biol Chem 279:40462–40469
Chalfie M, Tu Y, Euskirchen G, Ward WW, Prasher DC (1994) Green fluorescent protein as a marker for gene expression. Science 263:802–805
Chan SW, Egan PA (2005) Hepatitis C virus envelope proteins regulate CHOP via induction of the unfolded protein response. FASEB J 19:1510–1512
Chen YT, Lin CH, Ji WT, Li SK, Liu HJ (2008) Proteasome inhibition reduces avian reovirus replication and apoptosis induction in cultured cells. J Virol Methods 151:95–100
Choi J, Ou JH (2006) Mechanisms of liver injury. III. Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of hepatitis C virus. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 290:G847–G851
Chulu JL, Lee LH, Lee YC, Liao SH, Lin FL, Shih WL, Liu HJ (2007) Apoptosis induction by avian reovirus through p53 and mitochondria-mediated pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 356:529–535
Chulu JL, Huang WR, Wang L, Shih WL, Liu HJ (2010) Avian reovirus non-structural protein p17-induced G2/M cell cycle arrest and host cellular protein translation shutoff involve activation of p53-dependent pathways. J Virol 84:7683–7694
Desmyter J, Melnick JL, Rawls WE (1968) Defectiveness of interferon production and of rubella virus interference in a line of African green monkey kidney cells (Vero). J Virol 2:955–961
Du F, Wang L, Zhang Y, Jiang W, Sheng H, Cao Q, Wu J, Shen B, Shen T, Zhang JZ, Bao C, Li D, Li N (2008) Role of GADD45 beta in the regulation of synovial fluid T cell apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Immunol 128:238–247
Flory E, Kunz M, Scheller C, Jassoy C, Stauber R, Rapp UR, Ludwig S (2000) Influenza virus-induced NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression is mediated by overexpression of viral proteins and involves oxidative radicals and activation of IkappaB kinase. J Biol Chem 275:8307–8314
Fontanier-Razzaq N, McEvoy TG, Robinson JJ, Rees WD (2001) DNA damaging agents increase gadd153 (CHOP-10) messenger RNA levels in bovine preimplantation embryos cultured in vitro. Biol Reprod 64:1386–1391
Friedman AD (1996) GADD153/CHOP, a DNA damage-inducible protein, reduced CAAT/enhancer binding protein activities and increased apoptosis in 32D c13 myeloid cells. Cancer Res 56:3250–3256
Gargouri B, Van Pelt J, El Feki Ael F, Attia H, Lassoued S (2009) Induction of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) lytic cycle in vitro causes oxidative stress in lymphoblastoid B cell lines. Mol Cell Biochem 324:55–63
Gouvea V, Schnitzer TJ (1982) Pathogenicity of avian reoviruses: examination of six isolates and a vaccine strain. Infect Immun 38:731–738
Harkin DP, Bean JM, Miklos D, Song YH, Truong VB, Englert C, Christians FC, Ellisen LW, Maheswaran S, Oliner JD, Haber DA (1999) Induction of GADD45 and JNK/SAPK-dependent apoptosis following inducible expression of BRCA1. Cell 97:575–586
Hsieh YH, Su IJ, Wang HC, Chang WW, Lei HY, Lai MD, Chang WT, Huang W (2004) Pre-S mutant surface antigens in chronic hepatitis B virus infection induce oxidative stress and DNA damage. Carcinogenesis 25:2023–2032
Hsu CJ, Wang CY, Lee LH, Shih WL, Chang CI, Cheng HL, Chulu JL, Ji WT, Liu HJ (2006) Development and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against avian reovirus sigma C protein and their application in detection of avian reovirus isolates. Avian Pathol 35:320–326
Jones RC, Kibenge FS (1984) Reovirus-induced tenosynovitis in chickens: the effect of breed. Avian Pathol 13:511–528
Kannan R, Gukasyan HJ, Zhang W, Trousdale MD, Kim KJ, Lee VH (2004) Impairment of conjunctival glutathione secretion and ion transport by oxidative stress in an adenovirus type 5 ocular infection model of pigmented rabbits. Free Radic Biol Med 37:229–238
Kavouras JH, Prandovszky E, Valyi-Nagy K, Kovacs SK, Tiwari V, Kovacs M, Shukla D, Valyi-Nagy T (2007) Herpes simplex virus type 1 infection induces oxidative stress and the release of bioactive lipid peroxidation by-products in mouse P19N neural cell cultures. J Neurovirol 13:416–425
Kuo YF, Su YZ, Tseng YH, Wang SY, Wang HM, Chueh PJ (2010) Flavokawain B, a novel chalcone from Alpinia pricei Hayata with potent apoptotic activity: Involvement of ROS and GADD153 upstream of mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in HCT116 cells. Free Radic Biol Med 49:214–226
Labrada L, Bodelon G, Vinuela J, Benavente J (2002) Avian reoviruses cause apoptosis in cultured cells: viral uncoating, but not viral gene expression, is required for apoptosis induction. J Virol 76:7932–7941
Lassoued S, Ben Ameur R, Ayadi W, Gargouri B, Ben Mansour R, Attia H (2008) Epstein-Barr virus induces an oxidative stress during the early stages of infection in B lymphocytes, epithelial, and lymphoblastoid cell lines. Mol Cell Biochem 313:179–186
Lawrence MC, McGlynn K, Naziruddin B, Levy MF, Cobb MH (2007) Differential regulation of CHOP-10/GADD153 gene expression by MAPK signaling in pancreatic beta-cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:11518–11525
Leutner S, Eckert A, Muller WE (2001) ROS generation, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzyme activities in the aging brain. J Neural Transm 108:955–967
Lin CH, Shih WL, Lin FL, Hsieh YC, Kuo YR, Liao MH, Liu HJ (2009) Bovine ephemeral fever virus-induced apoptosis requires virus gene expression and activation of Fas and mitochondrial signaling pathway. Apoptosis 14:864–877
Lin HY, Chuang ST, Chen YT, Shih WL, Chang CD, Liu HJ (2007) Avian reovirus-induced apoptosis related to tissue injury. Avian Pathol 36:155–159
Lin PY, Liu HJ, Liao MH, Chang CD, Chang CI, Cheng HL, Lee JW, Shih WL (2010) Activation of PI 3-kinase/Akt/NF-kappaB and Stat3 signaling by avian reovirus S1133 in the early stages of infection results in an inflammatory response and delayed apoptosis. Virology 400:104–114
Lin YL, Liu CC, Chuang JI, Lei HY, Yeh TM, Lin YS, Huang YH, Liu HS (2000) Involvement of oxidative stress, NF-IL-6, and RANTES expression in dengue-2-virus-infected human liver cells. Virology 276:114–126
Lu HF, Hsueh SC, Ho YT, Kao MC, Yang JS, Chiu TH, Huamg SY, Lin CC, Chung JG (2007) ROS mediates baicalin-induced apoptosis in human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cells through the expression of the Gadd153 and mitochondrial-dependent pathway. Anticancer Res 27:117–125
Martinez-Costas J, Gonzalez-Lopez C, Vakharia VN, Benavente J (2000) Possible involvement of the double-stranded RNA-binding core protein sigmaA in the resistance of avian reovirus to interferon. J Virol 74:1124–1131
Mayerhofer T, Kodym R (2003) Gadd153 restores resistance to radiation-induced apoptosis after thiol depletion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 310:115–120
Nakabayashi H, Taketa K, Miyano K, Yamane T, Sato J (1982) Growth of human hepatoma cells lines with differentiated functions in chemically defined medium. Cancer Res 42:3858–3863
Ni Y, Kemp MC (1995) A comparative study of avian reovirus pathogenicity: virus spread and replication and induction of lesions. Avian Dis 39:554–566
Nicolini A, Ajmone-Cat MA, Bernardo A, Levi G, Minghetti L (2001) Human immunodeficiency virus type-1 Tat protein induces nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB activation and oxidative stress in microglial cultures by independent mechanisms. J Neurochem 79:713–716
Norbury CJ, Zhivotovsky B (2004) DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 23:2797–2808
Olive PL, Banath JP (2009) Kinetics of H2AX phosphorylation after exposure to cisplatin. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 76:79–90
Pal S, Polyak SJ, Bano N, Qiu WC, Carithers RL, Shuhart M, Gretch DR, Das A (2010) Hepatitis C virus induces oxidative stress, DNA damage and modulates the DNA repair enzyme NEIL1. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 25:627–634
Paranjpe A, Cacalano NA, Hume WR, Jewett A (2008) Mechanisms of N-acetyl cysteine-mediated protection from 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate-induced apoptosis. J Endod 34:1191–1197
Paranjpe A, Cacalano NA, Hume WR, Jewett A (2009) N-acetyl cysteine mediates protection from 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate induced apoptosis via nuclear factor kappa B-dependent and independent pathways: potential involvement of JNK. Toxicol Sci 108:356–366
Pauklin S, Kristjuhan A, Maimets T, Jaks V (2005) ARF and ATM/ATR cooperate in p53-mediated apoptosis upon oncogenic stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 334:386–394
Pereg Y, Shkedy D, de Graaf P, Meulmeester E, Edelson-Averbukh M, Salek M, Biton S, Teunisse AF, Lehmann WD, Jochemsen AG, Shiloh Y (2005) Phosphorylation of Hdmx mediates its Hdm2- and ATM-dependent degradation in response to DNA damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:5056–5061
Ping-Yuan L, Hung-Jen L, Meng-Jiun L, Feng-Ling Y, Hsue-Yin H, Jeng-Woei L, Wen-Ling S (2006) Avian reovirus activates a novel proapoptotic signal by linking Src to p53. Apoptosis 11:2179–2193
Quadrilatero J, Hoffman-Goetz L (2004) N-Acetyl-l-cysteine prevents exercise-induced intestinal lymphocyte apoptosis by maintaining intracellular glutathione levels and reducing mitochondrial membrane depolarization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 319:894–901
Reed LJ, Muench H (1938) A simple method of estimating fifty percent endpoints. Am J Epidemiol 27:493–497
Reisner AH, Nemes P, Bucholtz C (1975) The use of Coomassie Brilliant Blue G250 perchloric acid solution for staining in electrophoresis and isoelectric focusing on polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 64:509–516
Roos WP, Kaina B (2006) DNA damage-induced cell death by apoptosis. Trends Mol Med 12:440–450
Sarkaria JN, Busby EC, Tibbetts RS, Roos P, Taya Y, Karnitz LM, Abraham RT (1999) Inhibition of ATM and ATR kinase activities by the radiosensitizing agent, caffeine. Cancer Res 59:4375–4382
Schaefer-Klein J, Givol I, Barsov EV, Whitcomb JM, VanBrocklin M, Foster DN, Federspiel MJ, Hughes SH (1998) The EV-O-derived cell line DF-1 supports the efficient replication of avian leukosis-sarcoma viruses and vectors. Virology 248:305–311
Shih WL, Hsu HW, Liao MH, Lee LH, Liu HJ (2004) Avian reovirus sigmaC protein induces apoptosis in cultured cells. Virology 321:65–74
Shmulevitz M, Corcoran J, Salsman J, Duncan R (2004) Cell-cell fusion induced by the avian reovirus membrane fusion protein is regulated by protein degradation. J Virol 78:5996–6004
Sinclair A, Yarranton S, Schelcher C (2006) DNA-damage response pathways triggered by viral replication. Expert Rev Mol Med 8:1–11
Spagnuolo G, D’Anto V, Cosentino C, Schmalz G, Schweikl H, Rengo S (2006) Effect of N-acetyl-L-cysteine on ROS production and cell death caused by HEMA in human primary gingival fibroblasts. Biomaterials 27:1803–1809
Tang KN, Fletcher OJ, Villegas P (1987) The effect on newborn chicks of oral inoculation of reovirus isolated from chickens with tenosynovitis. Avian Dis 31:584–590
Van de Zande S, Kuhn EM (2007) Central nervous system signs in chickens caused by a new avian reovirus strain: a pathogenesis study. Vet Microbiol 120:42–49
Yang F, Yan S, He Y, Wang F, Song S, Guo Y, Zhou Q, Wang Y, Lin Z, Yang Y, Zhang W, Sun S (2008) Expression of hepatitis B virus proteins in transgenic mice alters lipid metabolism and induces oxidative stress in the liver. J Hepatol 48:12–19
Zhang W, Hoffman B, Liebermann DA (2001) Ectopic expression of MyD118/Gadd45/CR6 (Gadd45beta/alpha/gamma) sensitizes neoplastic cells to genotoxic stress-induced apoptosis. Int J Oncol 18:749–757
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant from the National Science Council of Taiwan (NSC 98-2313-B-020-004-MY3). We also thank Sarah Parkin for copy-editing the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, PY., Liu, HJ., Chang, CD. et al. Avian reovirus S1133-induced DNA damage signaling and subsequent apoptosis in cultured cells and in chickens. Arch Virol 156, 1917–1929 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-011-1063-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-011-1063-3