Abstract
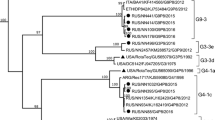
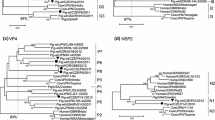
The G1 and G9 rotavirus strains MMC71 and MMC38 (subgroup II, NSP4 genogroup B), respectively, isolated from children in Bangladesh, were analyzed genetically. Full-length VP4 genes of these strains had 98.9% identity to each other and showed 83.9–89.4% identity to those of the P[4] and P[8] rotaviruses. Phylogenetic analysis of VP4 nucleotide sequences revealed that strains MMC38 and MMC71 were located in a lineage of P[8] strains. However, the cluster was highly divergent from the previously established P[8] strains. The VP8* portions of strains MMC38 and MMC71 showed more than 93.9% nucleotide sequence identity to OP354-like P[8] strains, and these strains were clustered into the same lineage. These findings indicate that the VP4 of these strains should be classified into a subtype of the P[8] genotype (P[8]b) that is distinct from that of common P[8] rotaviruses (P[8]a).



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed MU, Kobayashi N, Wakuda M, Sanekata T, Taniguchi K, Kader A, Naik TN, Ishino M, Alam MM, Kojima K, Mise K, Sumi A (2004) Genetic analysis of group B human rotaviruses detected in Bangladesh in 2000 and 2001. J Med Virol 72:149–155
Ball JM, Tian P, Zeng CQ, Morris AP, Estes MK (1996) Age-dependent diarrhea induced by a rotaviral nonstructural glycoprotein. Science 272:101–104
Bányai K, Gentsch JR, Griffin DD, Holmes JL, Glass RI, Szücs G (2003) Genetic variability among serotype G6 human rotaviruses: identification of a novel linage isolated in Hungary. J Med Virol 71:124–134
Bishop RF (1996) Natural history of human rotavirus infection. Arch Virol Suppl 12:119–128
Ciarlet M, Estes MK, Conner ME (1997) Comparative amino acid sequence analysis of the outer capsid protein VP4 from four lapine rotavirus strains reveals identity with genotype P[14] human rotaviruses. Arch Virol 142:1059–1069
Ciarlet M, Liprandi F, Conner ME, Estes MK (2000) Species specificity and interspecies relatedness of NSP4 genetic groups by comparative NSP4 sequence analyses of animal rotaviruses. Arch Virol 145:371–383
Cooney MA, Gorrell RJ, Palombo EA (2001) Characterization and phylogenetic analysis of the VP7 proteins of serotype G6 and G8 human rotaviruses. J Med Microbiol 50:462–467
Cunliffe NA, Gondwe JS, Graham SM, Thindwa BDM, Dove W, Broadhead RL, Molyneux ME, Hart CA (2001) Rotavirus strain diversity in Blantyre, Malawi, from 1977 to 1999. J Clin Microbiol 39:836–843
Das M, Dunn SJ, Woode GN, Greenberg HB, Rao CD (1993) Both surface proteins (VP4 and VP7) of an asymptomatic neonatal rotavirus strain (I321) have high levels of sequence identity with the homologous proteins of serotype 10 bovine rotavirus. Virology 194:374–379
Dennehy PH (2008) Rotavirus vaccine: an overview. Clin Microbiol Rev 21:198–208
Dong Y, Zeng CQ, Ball JM, Estes MK, Morris AP (1997) The rotavirus enterotoxin NSP4 mobilizes intracellular calcium in human intestinal cells by stimulating phospholipase C-mediated inositol 1, 4, 5-trisphosphate production. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:3960–3965
Esona MD, Armah GE, Geyer A, Steele AD (2004) Detection of unusual human rotavirus strains with G5P[8] specificity in Cameroonian child with diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol 42:441–444
Estes MK, Kapikian AZ (2007) Rotaviruses. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM, Griffin DE, Lamb RA, Martin MA, Roizman B, Straus SE (eds) Fields virology, 5th edn. Lippincott, Philadelphia, pp 1917–1974
Fukai K, Takahashi T, Tajima K, Koike S, Iwane K, Inoue K (2007) Molecular characterization of a novel bovine group A rotavirus. Vet Microbiol 123:217–224
Gentsch JR, Glass RI, Woods P, Gouvea V, Gorziglia M, Flores J, Das BK, Bhan MK (1992) Identification of group A rotavirus gene 4 types by polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol 30:1365–1373
Gentsch JR, Woods PA, Ramachandran M, Das BK, Leite JP, Alfieri A, Kumar R, Bhan MK, Glass RI (1996) Review of G and P typing results from a global collection of rotavirus strains: implications for vaccine development. J Infect Dis 174:S30–S36
Gerna G, Sarasini A, Parea M, Arista S, Miranda P, Brüssow H, Hoshino Y, Flores J (1992) Isolation and characterization of two distinct human rotavirus strains with G6 specificity. J Clin Microbiol 30:9–16
Gorziglia M, Hoshino Y, Buckler-White A, Blumentals M, Glass R, Flores J, Kapikian AZ, Chanock RM (1986) Conservation of amino acid sequence of VP8 and cleavage region of 84-kDa outer capsid protein among rotaviruses recovered from asymptomatic neonatal infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:7039–7043
Gorziglia M, Larralde G, Kapikian AZ, Chanock RM (1990) Antigenic relationships among human rotaviruses as determined by outer capsid protein VP4. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:7155–7159
Gorziglia M, Larralde G, Ward RL (1990) Neutralization epitopes on rotavirus SA11 4fM outer capsid proteins. J Virol 64:4534–4539
Gouvea V, Glass RI, Woods P, Taniguchi K, Clark HF, Forrester B, Fang ZY (1990) Polymerase chain reaction amplification and typing of rotavirus nucleic acid from stool specimens. J Clin Microbiol 28:276–282
Green KY, Hoshino Y, Ikegami N (1989) Sequence analysis of the gene encoding the serotype-specific glycoprotein (VP7) of two new human rotavirus serotypes. Virology 168:429–433
Green KY, Sears JF, Taniguchi K, Midthun K, Hoshino Y, Gorziglia M, Nishikawa K, Urasawa S, Kapikian AZ, Chanock RM, Flores J (1988) Prediction of human rotavirus serotype by nucleotide sequence analysis of the VP7 protein gene. J Virol 62:1819–1823
Greenberg H, McAuliffe V, Valdesuso J, Wyatt R, Flores J, Kalica A, Hoshino Y, Singh N (1983) Serological analysis of the subgroup protein of rotavirus, using monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun 39:91–99
Hasegawa A, Inouye S, Matsuno S, Yamaoka K, Eko R, Suharyono W (1984) Isolation of human rotavirus with a distinct RNA electrophoretic pattern from Indonesia. Microbiol Immunol 6:719–722
Iturriza-Gómara M, Wong C, Blome S, Desselberger U, Gray J (2002) Molecular characterization of VP6 genes of human rotavirus isolates: correlation of genogroups with subgroups and evidence of independent segregation. J Virol 76:6596–6601
Kobayashi N, Taniguchi K, Urasawa S (1990) Identification of operationally overlapping and independent cross-reactive neutralization regions on human rotavirus VP4. J Gen Virol 71:2615–2623
Kobayashi N, Taniguchi K, Urasawa T, Urasawa S (1991) Preparation and characterization of a neutralizing monoclonal antibody directed to VP4 of rotavirus strain K8 which has unique VP4 neutralization epitopes. Arch Virol 121:153–162
Larralde G, Gorziglia M (1992) Distribution of conserved and specific epitopes on the VP8 subunit of rotavirus VP4. J Virol 66:7438–7443
Larralde G, Li BG, Kapikian AZ, Gorziglia M (1991) Serotype-specific epitope(s) present on the VP8 subunit of rotavirus VP4 protein. J Virol 65:3213–3218
Li B, Clark HF, Gouvea V (1993) Nucleotide sequence of the VP4-encoding gene of an unusual human rotavirus (HCR3). Virology 196:825–830
Mackow ER, Shaw RD, Matsui SM, Vo PT, Dang MN, Greenberg HB (1988) The rhesus rotavirus gene encoding protein VP3: location of amino acids involved in homologous and heterologous rotavirus neutralization and identification of a putative fusion region. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:645–649
Matthijnssens J, Ciarlet M, Heiman E, Arijs I, Delbeke T, McDonald SM, Palombo EA, Iturriza-Gómara M, Maes P, Patton JT, Rahman M, Ranst MV (2008) Full genome-based classification of rotaviruses reveals a common origin between human Wa-like and porcine rotavirus strains and human DS-1-like and bovine rotavirus strains. J Virol 82:3204–3219
Mphahlele MJ, Peenze I, Steele AD (1999) Rotavirus strains bearing the VP4P[14] genotype recovered from South African children with diarrhoea. Arch Virol 144:1027–1034
Nguyen TA, Hoang LP, Pham LD, Hoang KT, Okitsu S, Mizuguchi M, Ushijima H (2008) Use of sequence analysis of the VP4 gene to classify recent Vietnamese rotavirus isolates. Clin Microbiol Infect 14:235–241
Okada J, Urasawa T, Kobayashi N, Taniguchi K, Hasegawa A, Mise K, Urasawa S (2000) New P serotype of group A human rotavirus closely related to that of a porcine rotavirus. J Med Virol 60:63–69
Parra GI, Galeano ME, Arbiza J (2007) Genetic relationship between porcine rotavirus strains bearing a new P-type. Vet Microbiol 125:193–195
Paul SK, Kobayashi N, Nagashima S, Ishino M, Watanabe S, Alam MM, Ahmed MU, Hossain MA, Naik TN (2008) Phylogenetic analysis of rotaviruses with genotypes G1, G2, G9 and G12 in Bangladesh: evidence for a close relationship between rotaviruses from children and adults. Arch Virol 153:1999–2012
Rahman M, De Leener K, Goegebuer T, Wollants E, Van der Donck I, Van Hoovels L, Van Ranst M (2003) Genetic characterization of a novel, naturally occurring recombinant human G6P[6] rotavirus. J Clin Microbiol 41:2088–2095
Rahman M, Matthijnssens J, Nahar S, Podder G, Sack DA, Azim T, Van Ranst M (2005) Characterization of a novel P[25], G11 group A rotavirus. J Clin Microbiol 43:3208–3212
Samajdar S, Ghosh S, Dutta D, Chawla-Sarkar M, Kobayashi N, Naik TN (2008) Human group A rotavirus P[8] Hun9-like and rare OP354-like strains are circulating among diarrhoeic children in Eastern India. Arch Virol 153:1933–1936
Samajdar S, Varghese V, Barman P, Ghosh S, Mitra U, Dutta P, Bhattacharya SK, Narasimham MV, Panda P, Krishnan T, Kobayashi N, Naik TN (2006) Changing pattern of human group A rotaviruses: emergence of G12 as an important pathogen among children in eastern India. J Clin Virol 36:183–188
Santos N, Hoshino H (2005) Global distribution of rotavirus serotypes/genotypes and its implication for the development and implementation of an effective vaccine. Rev Med Virol 15:29–56
Taniguchi K, Maloy WL, Nishikawa K, Green KY, Hoshino Y, Urasawa S, Kapikian AZ, Chanock RM, Gorziglia M (1988) Identification of cross-reactive and serotype 2-specific neutralization epitopes on VP3 of human rotavirus. J Virol 62:2421–2426
Taniguchi K, Nishikawa K, Urasawa T, Urasawa S, Midthun K, Kapikian AZ, Gorziglia M (1989) Complete nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding VP4 of a human rotavirus (strain K8) which has unique VP4 neutralization epitopes. J Virol 63:4101–4106
Taniguchi K, Urasawa T, Kobayashi N, Gorziglia M, Urasawa S (1990) Nucleotide sequence of VP4 and VP7 genes of human rotaviruses with subgroup I specificity and long RNA pattern: implication for new G serotype specificity. J Virol 64:5640–5644
Taniguchi K, Urasawa T, Urasawa S, Yasuhara T (1984) Production of subgroup-specific monoclonal antibodies against human rotaviruses and their application to an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for subgroup determination. J Med Virol 14:115–125
Taniguchi K, Wakasugi F, Pongsuwanna Y, Urasawa T, Ukae S, Chiba S, Urasawa S (1992) Identification of human and bovine rotavirus serotypes by polymerase chain reaction. Epidemiol Infect 109:303–312
Theamboonlers A, Bhattarakosol P, Chongsrisawat V, Sungkapalee T, Wutthirattanakowit N, Poovorawan Y (2008) Molecular characterization of group A human rotaviruses in Bangkok and Buriram, Thailand during 2004–2006 reveals the predominance of G1P[8], G9P[8] and a rare G3P[19] strain. Virus Genes 36:289–298
Urasawa T, Urasawa S, Taniguchi K (1981) Sequential passages of human rotavirus in MA-104 cells. Microbiol Immunol 25:1025–1035
Zhang M, Zeng CQ, Morris AP, Estes MK (2000) A functional NSP4 enterotoxin peptide secreted from rotavirus-infected cells. J Virol 74:11663–11670
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (No. 18406018), the Program of Founding Research Centers for Emerging and Reemerging Infectious Diseases (Okayama University, National Institute of Cholera and Enteric Diseases, India) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan, and a Grant for International Health Cooperation Research from the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagashima, S., Kobayashi, N., Paul, S.K. et al. Characterization of full-length VP4 genes of OP354-like P[8] human rotavirus strains detected in Bangladesh representing a novel P[8] subtype. Arch Virol 154, 1223–1231 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-009-0436-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-009-0436-3