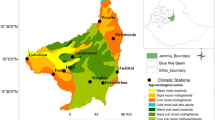
Abstract
The flood risk across the globe is intensified due to global warming and subsequent increase in extreme temperature and precipitation. The long-term trends in extreme rainfall (1944–2013) and temperature (1969–2012) indices have been investigated at annual, seasonal, and monthly time scales using nonparametric Mann-Kendall (MK), modified Mann-Kendall (MMK), and Sen’s slope estimator tests. The extreme rainfall and temperature indices, recommended by the Expert Team on Climate Change Detection Monitoring Indices (ETCCDMI), have been analyzed at finer spatial scales for trend detection. The results of trend analyses indicate decreasing trend in annual total rainfall, significant decreasing trend in rainy days, and increasing trend in rainfall intensity over the basin. The seasonal rainfall has been found to decrease for all the seasons except postmonsoon, which could affect the rain-fed agriculture in the basin. The 1- and 5-day annual maximum rainfalls exhibit mixed trends, wherein part of the basin experiences increasing trend, while other parts experience a decreasing trend. The increase in dry spells and concurrent decrease in wet spells are also observed over the basin. The extreme temperature indices revealed increasing trends in hottest and coldest days, while decreasing trends in coldest night are found over most parts of the basin. Further, the diurnal temperature range is also found to increase due to warming tendency in maximum temperature (T max) at a faster rate compared to the minimum temperature (T min). The increase in frequency and magnitude of extreme rainfall in the basin has been attributed to the increasing trend in maximum and minimum temperatures, reducing forest cover, rapid pace of urbanization, increase in human population, and thereby increase in the aerosol content in the atmosphere. The findings of the present study would significantly help in sustainable water resource planning, better decision-making for policy framework, and setting up infrastructure against flood disasters in Upper Tapi Basin, India.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander LV, Zhang X, Peterson, TC, Caesar J, Gleason B, Klein Tank AMG, Haylock M, Collins D, Trewin B, Rahimzadeh F, Tagipour A, Rupa Kumar K, Revadekar J, Griffiths G, Vincent L, Stephenson DB, Burn J, Aguilar E, Brunet M, Taylor M, New M, Zhai P, Rusticucci M, Vazquez-Aguirre JL (2006) Global observed changes in daily climate extremes of temperature and precipitation. J Geo Res 111(5):D05109-1-22
Ali H, Mishra V, Pai DS (2014) Observed and projected urban extreme rainfall events in India. J Geo Res: Atmos 119(22):12621–12641
Bisht DS, Chatterjee C, Raghuwanshi NS, Sridhar V (2017) Spatio-temporal trends of rainfall across Indian river basins. Theor Appl Climtol:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-017-2095-8
Boccolari M, Malmusi S (2013) Changes in temperature and precipitation extremes observed in Modena, Italy. Atmos Res 122:16–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2012.10.022
Burn DH, Elnur MAH (2002) Detection of hydrologic trends and variability. J Hydrol 255(1):107–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(01)00514-5
Caloiero T (2017) Trend of monthly temperature and daily extreme temperature during 1951–2012 in New Zealand. Theor Appl Climtol 129(1–2):111–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-016-1764-3
Chandniha SK, Meshram SG, Adamowski JF, Meshram C (2016) Trend analysis of precipitation in Jharkhand State, India. Theor Appl Climtol 130(1–2):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-016-1875-x
Chen FW, Liu CW (2012) Estimation of the spatial rainfall distribution using inverse distance weighting (IDW) in the middle of Taiwan. Paddy Water Environ 10(3):209–222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10333-012-0319-1
Cheng J, Xu Z, Zhu R, Wang X, Jin L, Song J, Su H (2014) Impact of diurnal temperature range on human health: a systematic review. Int J Biometeorol 58(9):2011–2024. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-014-0797-5
CWC (2014) Tapi Basin watershed atlas. Central Water Commission, New Delhi
Dai A, Del Genio AD, Fung IY (1997) Clouds, precipitation and temperature range. Nature 386(6626):666
Dash SK, Nair AA, Kulkarni MA, Mohanty UC (2011) Characteristic changes in the long and short spells of different rain intensities in India. Theor Appl Climatol 105(3–4):563–570. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-011-0416-x
Deshpande NR, Kothawale DR, Kulkarni A (2016) Changes in climate extremes over major river basins of India. Int J Climatol 36(14):4548–4559. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.4651
Dhar ON, Nandargi S (1995) On some characteristics of severe rainstorms of India. Theor Appl Climatol 50(3–4):205–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00866117
Duhan D, Pandey A (2013) Statistical analysis of long term spatial and temporal trends of precipitation during 1901–2002 at Madhya Pradesh, India. Atmos Res 122:136–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2012.10.010
Duhan D, Pandey A, Gahalaut KPS, Pandey RP (2013) Spatial and temporal variability in maximum, minimum and mean air temperatures at Madhya Pradesh in central India. Compt Rendus Geosci 345(1):3–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crte.2012.10.016
Easterling DR, Alexander LV, Mokssit A, Detemmerman V (2003) CCI/CLIVAR workshop to develop priority climate indices. Am Met Soc 84(10):1403–1407. https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-84-10-1403
Gadgil A, Dhorde A (2005) Temperature trends in twentieth century at Pune, India. Atmos Environ 39(35):6550–6556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2005.07.032
Ghosh S, Luniya V, Gupta A (2009) Trend analysis of Indian summer monsoon rainfall at different spatial scales. Atmos Sci Let 10(4):285–290
Goswami BN, Venugopal V, Sengupta D, Madhusoodanan MS, Xavier PK (2006) Increasing trend of extreme rain events over India in a warming environment. Science 314(5804):1442–1445. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1132027
Guhathakurta P, Rajeevan M (2008) Trends in the rainfall pattern over India. Int J Climatol 28(11):1453–1469. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1640
Guhathakurta P, Sreejith OP, Menon PA (2011) Impact of climate change on extreme rainfall events and flood risk in India. J Earth Sys Sci 120(3):359–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-011-0082-5
Guhathakurta P, Pai DS, Rajeevan MN (2017) Variability and trends of extreme rainfall and rainstorms. In observed climate variability and change over the Indian region (pp. 37–49). Springer, Singapore
Hamed KH, Rao AR (1998) A modified Mann-Kendall trend test for autocorrelated data. J Hydrol 204(1–4):182–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(97)00125-X
He Y, Tian P, Mu X, Gao P, Zhao G, Wang F, Li P (2017) Changes in daily and monthly rainfall in the Middle Yellow River, China. Theor Appl Climtol 129(1–2):139–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-016-1763-4
Hirsch RM, Slack JR, Smith RA (1982) Techniques of trend analysis for monthly water quality data. Water Resour Res 20(6):727–732
Hutchinson MF, Dowling TI (1991) A continental hydrological assessment of a new grid-based digital elevation model of Australia. Hydrol Process 5(1):45–58. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.3360050105
IPCC (2007) Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change [Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt KB, Tignor M, Miller HL (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
IPCC (2014) Climate change 2014: synthesis report contribution of working groups I, II and III to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change [Core Writing Team, RK Pachauri and LA Meyer (eds.)]. IPCC, Geneva, 151 pp.
Jain SK, Kumar V (2012) Trend analysis of rainfall and temperature data for India. Curr Sci 102(1):37–49
Jain SK, Agarwal PK, Singh VP (2007) Hydrology and water resources of India (vol. 57). Springer, Dordrecht
Jhajharia D, Dinpashoh Y, Kahya E, Choudhary RR, Singh VP (2014) Trends in temperature over Godavari river basin in southern peninsular India. Int J Climatol 34(5):1369–1384. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.3761
Kang Y, Khan S, Ma X (2009) Climate change impacts on crop yield, crop water productivity and food security—a review. Prog Nat Sci 19(12):1665–1674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnsc.2009.08.001
Karl TR, Knight RW, Gallo KP, Peterson TC, Jones PD, Kukla G, Plummer N, Razuvayev V, Lindseay J, Charlson RJ (1993) A new perspective on recent global warming: asymmetric trends of daily maximum and minimum temperature. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 74(6):1007–1023. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0477(1993)074<1007:ANPORG>2.0.CO;2
Kaufmann RK, Seto KC, Schneider A, Liu Z, Zhou L, Wang W (2007) Climate response to rapid urban growth: evidence of a human-induced precipitation deficit. J Clim 20(10):2299–2306. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI4109.1
Kendall MG (1975) Rank correlation methods. Charles Griffin, London
Kendon EJ, Roberts NM, Fowler HJ, Roberts MJ, Chan SC, Senior CA (2014) Heavier summer downpours with climate change revealed by weather forecast resolution model. Nat Clim Chang 4(7):570–576. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate2258
Kharin VV, Zwiers FW (2000) Changes in the extremes in an ensemble of transient climate simulations with a coupled atmosphere–ocean GCM. J Clim 13(21):3760–3788. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(2000)013<3760:CITEIA>2.0.CO;2
Kharol SK, Kaskaoutis DG, Sharma AR, Singh RP (2013) Long-term (1951–2007) rainfall trends around six Indian cities: current state, meteorological, and urban dynamics. Adv Met 2013:572954
Kishtawal CM, Niyogi D, Tewari M, Pielke RA, Shepherd JM (2010) Urbanization signature in the observed heavy rainfall climatology over India. Int J Climatol 30(13):1908–1916. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.2044
Kothawale DR, Revadekar JV, Kumar KR (2010) Recent trends in pre-monsoon daily temperature extremes over India. J Earth Sys Sci 119(1):51–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-010-0008-7
Krishnamurthy CKB, Lall U, Kwon HH (2009) Changing frequency and intensity of rainfall extremes over India from 1951 to 2003. J Clim 22(18):4737–4746. https://doi.org/10.1175/2009JCLI2896.1
Kumar V, Jain SK (2011) Trends in rainfall amount and number of rainy days in river basins of India (1951–2004). Hydrol Res 42(4):290–306. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.2011.067
Kumar V, Jain SK, Singh Y (2010) Analysis of long-term rainfall trends in India. Hydrol Sci J 55(4):484–496. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667.2010.481373
Kundu S, Khare D, Mondal A, Mishra PK (2015) Analysis of spatial and temporal variation in rainfall trend of Madhya Pradesh, India (1901–2011). Environ Earth Sci 73(12):8197–8216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3978-y
Kundu S, Khare D, Mondal A (2016) Interrelationship of rainfall, temperature and reference evapotranspiration trends and their net response to the climate change in Central India. Theor Appl Climtol:1–22
Liu R, Liu SC, Cicerone RJ, Shiu CJ, Li J, Wang J, Zhang Y (2015) Trends of extreme precipitation in eastern China and their possible causes. Adv Atmos Sci 32(8):1027–1037. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-015-5002-1
Liu B, Chen J, Lu W, Chen X, Lian Y (2016) Spatiotemporal characteristics of precipitation changes in the Pearl River Basin, China. Theor Appl Climtol 123(3–4):537–550. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-015-1375-4
Mann HB (1945) Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 13:245–259
Martinez CJ, Maleski JJ, Miller MF (2012) Trends in precipitation and temperature in Florida, USA. J Hydrol 452-453:259–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.05.066
Meshram SG, Singh VP, Meshram C (2016) Long-term trend and variability of precipitation in Chhattisgarh State, India. Theor Appl Climatol:1–16
Milly PCD, Wetherald RT, Dunne KA, Delworth TL (2002) Increasing risk of great floods in a changing climate. Nature 415(6871):514–517. https://doi.org/10.1038/415514a
Min SK, Zhang X, Zwiers FW, Hegerl GC (2011) Human contribution to more-intense precipitation extremes. Nature 470:376–379
Mondal A, Khare D, Kundu S (2015) Spatial and temporal analysis of rainfall and temperature trend of India. Theor Appl Climatol 122(1-2):143–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-014-1283-z
Niyogi D, Kishtawal C, Tripathi S, Govindaraju RS (2010) Observational evidence that agricultural intensification and land use change may be reducing the Indian summer monsoon rainfall. Water Reso Res 46(3). https://doi.org/10.1029/2008WR007082
Pal L (2016) Impact of climate variability and anthropogenic changes in runoff and sediment yield in Upper Tapi basin, India. Master’s thesis, Sardar Vallabhbhai National Institute of Technology, Surat, India
Pal I, Al-Tabbaa A (2011) Monsoon rainfall extreme indices and tendencies from 1954–2003 in Kerala, India. Clim Chang 106(3):407–419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10584-011-0044-6
Panda DK, Kumar A (2014) The changing characteristics of monsoon rainfall in India during 1971–2005 and links with large scale circulation. Int J Climatol 34(15):3881–3899. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.3948
Panda DK, Panigrahi P, Mohanty S, Mohanty RK, Sethi RR (2016) The 20th century transitions in basic and extreme monsoon rainfall indices in India: comparison of the ETCCDI indices. Atmos Res 181:220–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2016.07.002
Parthasarathy B, Munot AA, Kothawale DR (1994) All-India monthly and seasonal rainfall series: 1871–1993. Theor Appl Climatol 49(4):217–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00867461
Pielke RA, Adegoke J, Beltran-Przekurat A, Hiemstra CA, Lin J, Nair US, Niyogi D, Nobis TE (2007) An overview of regional land-use and land-cover impacts on rainfall. Tellus B 59(3):587–601. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0889.2007.00251.x
Pingale SM, Khare D, Jat MK, Adamowski J (2014) Spatial and temporal trends of mean and extreme rainfall and temperature for the 33 urban centers of the arid and semi-arid state of Rajasthan, India. Atmos Res 138:73–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2013.10.024
Rahmat SN, Jayasuriya N, Bhuiyan MA (2015) Precipitation trends in Victoria, Australia. J Water Clim Chang 6(2):278–287. https://doi.org/10.2166/wcc.2014.007
Rai A, Joshi MK, Pandey AC (2012) Variations in diurnal temperature range over India: under global warming scenario. J Geo Res: Atmos 117:D02114
Rajeevan M, Bhate J, Jaswal AK (2008) Analysis of variability and trends of extreme rainfall events over India using 104 years of gridded daily rainfall data. Geophy Res Let 35(18)
Ramanathan V, Crutzen PJ, Kiehl JT, Rosenfeld D (2001) Atmosphere aerosols, climate, and the hydrological cycle. Science 294(5549):2119–2124. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1064034
Revadekar JV, Patwardhan SK, Rupa Kumar K (2011) Characteristic features of precipitation extremes over India in the warming scenarios. Adv Met 2011:138425. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/138425
Riha SJ, Wilks DS, Simoens P (1996) Impact of temperature and precipitation variability on crop model predictions. Clim Chang 32(3):293–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00142466
Sen Roy S, Balling RC (2004) Trends in extreme daily precipitation indices in India. Int J Climatol 24(4):457–466. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.995
Sharma D, Babel MS (2014) Trends in extreme rainfall and temperature indices in the western Thailand. Int J Climatol 34(7):2393–2407. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.3846
Sharma PJ, Loliyana VD, Timbadiya PV, Patel PL (2017) Investigation of long-term trends and temporal variability in annual rainfall across Purna River Basin, India. Proceedings of 49th annual convention of Indian water works association on smart water management at Visvesvaraya National Institute of Technology, Nagpur, India
Singh N, Sontakke NA, Singh HN, Pandey AK (2005) Recent trend in spatiotemporal variation of rainfall over India- an investigation into basin-scale rainfall fluctuations. IAHS-AISH Publ 296:273–282
Singh P, Kumar V, Thomas T, Arora M (2008) Changes in rainfall and relative humidity in river basins in northwest and central India. Hydrol Process 22(16):2982–2992. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.6871
Soltani M, Laux P, Kunstmann H, Stan K, Sohrabi MM, Molanejad M, Zawar-Reza P (2016) Assessment of climate variations in temperature and precipitation extreme events over Iran. Theor Appl Climatol 126(3–4):775–795. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-015-1609-5
Sonali P, Kumar DN (2016) Spatio-temporal variability of temperature and potential evapotranspiration over India. J Water Clim Chang 7(4):810–822. https://doi.org/10.2166/wcc.2016.230
Sonar RB (2014) Observed trends and variations in rainfall events over Ratnagiri (Maharashtra) during southwest monsoon season. Mausam 65(2):171–178
Song X, Zhang J, AghaKouchak A, Roy SS, Xuan Y, Wang G, He R, Wang X, Liu C (2014) Rapid urbanization and changes in spatiotemporal characteristics of precipitation in Beijing metropolitan area. J Geophy Res: Atmos 119(19)
Soro GE, Noufé D, Goula Bi TA, Shorohou B (2016) Trend analysis for extreme rainfall at sub-daily fand daily timescales in Côte d’Ivoire. Climate 4(3):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/cli4030037
Stocker TF, Qin D, Plattner G K, Tignor M, Allen SK, Boschung J, Nauels A, Xia Y, Bex V, Midgley BM (2013) IPCC, 2013: climate change 2013: the physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change
Subash N, Sikka AK (2014) Trend analysis of rainfall and temperature and its relationship over India. Theor Appl Climatol 117(3–4):449–462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-013-1015-9
Taxak AK, Murumkar AR, Arya DS (2014) Long term spatial and temporal rainfall trends and homogeneity analysis in Wainganga basin, Central India. Weather Clim Extrem 4:50–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wace.2014.04.005
Thomas T, Gunthe SS, Ghosh NC, Sudheer KP (2015) Analysis of monsoon rainfall variability over Narmada basin in Central India: implication of climate change. J Water Clim Chang 6(3):615–627. https://doi.org/10.2166/wcc.2014.041
Trenberth KE (2011) Changes in precipitation with climate change. Clim Res 47(1/2):123–138. https://doi.org/10.3354/cr00953
Vittal H, Karmakar S, Ghosh S (2013) Diametric changes in trends and patterns of extreme rainfall over India from pre-1950 to post-1950. Geophy Res Let 40(12):3253–3258. https://doi.org/10.1002/grl.50631
Wehner MF (2004) Predicted twenty-first-century changes in seasonal extreme precipitation events in the parallel climate model. J Clim 17(21):4281–4290. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI3197.1
Xiao C, Wu P, Zhang L, Song L (2016) Robust increase in extreme summer rainfall intensity during the past four decades observed in China. Sci Rep 6:38506. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep38506
Ye Z, Li Z (2017) Spatiotemporal variability and trends of extreme precipitation in the Huaihe River Basin, a climatic transitional zone in East China. Adv Met 2017 Article ID 3197435:1–15
Yue S, Hashino M (2003) Temperature trends in Japan: 1900–1996. Theor Appl Climatol 75(1–2):15–27
Yue S, Pilon P, Phinney B, Cavadias G (2002) The influence of autocorrelation on the ability to detect trend in hydrological series. Hydrol Process 16(9):1807–1829. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.1095
Zhai P, Zhang X, Wan H, Pan X (2005) Trends in total precipitation and frequency of daily precipitation extremes over China. J Clim 18(7):1096–1108. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-3318.1
Zhang Q, Singh VP, Peng J, Chen YD, Li J (2012) Spatial–temporal changes of precipitation structure across the Pearl River basin, China. J Hydrol 440:113–122
Acknowledgements
The first author gratefully acknowledges the financial support received from Department of Science and Technology (DST), Ministry of Science and Technology, Government of India vide their letter no. DST/INSPIRE Fellowship/2015/IF150634 dated January 11, 2016. The authors appreciate the infrastructural and financial support provided by Centre of Excellence (CoE) on “Water Resources and Flood Management”, TEQIP-II, Ministry of Human Resources Development (MHRD), Government of India, for conducting the study reported in the paper. The authors are also thankful to India Meteorological Department (IMD) and Central Water Commission (CWC) for providing necessary data to conduct the present study. The authors are grateful to the Editor-in-Chief and anonymous reviewers for their constructive suggestions to improve the quality of present work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2852 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, P.J., Loliyana, V.D., S. R., R. et al. Spatiotemporal trends in extreme rainfall and temperature indices over Upper Tapi Basin, India. Theor Appl Climatol 134, 1329–1354 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-017-2343-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-017-2343-y