Abstract
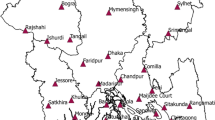
The precipitation patterns of seventeen locations in Bangladesh from 1961 to 2014 were studied using a cluster analysis and metric multidimensional scaling. In doing so, the current research applies four major hierarchical clustering methods to precipitation in conjunction with different dissimilarity measures and metric multidimensional scaling. A variety of clustering algorithms were used to provide multiple clustering dendrograms for a mixture of distance measures. The dendrogram of pre-monsoon rainfall for the seventeen locations formed five clusters. The pre-monsoon precipitation data for the areas of Srimangal and Sylhet were located in two clusters across the combination of five dissimilarity measures and four hierarchical clustering algorithms. The single linkage algorithm with Euclidian and Manhattan distances, the average linkage algorithm with the Minkowski distance, and Ward’s linkage algorithm provided similar results with regard to monsoon precipitation. The results of the post-monsoon and winter precipitation data are shown in different types of dendrograms with disparate combinations of sub-clusters. The schematic geometrical representations of the precipitation data using metric multidimensional scaling showed that the post-monsoon rainfall of Cox’s Bazar was located far from those of the other locations. The results of a box-and-whisker plot, different clustering techniques, and metric multidimensional scaling indicated that the precipitation behaviour of Srimangal and Sylhet during the pre-monsoon season, Cox’s Bazar and Sylhet during the monsoon season, Maijdi Court and Cox’s Bazar during the post-monsoon season, and Cox’s Bazar and Khulna during the winter differed from those at other locations in Bangladesh.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderberg MR (1973) Cluster analysis for applications. Academic, New York
Asakereh H, Shadman H (2016) On the relationship between tropospheric conditions and widespread hot days in Iran. Theory Appl Climatol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-016-2009-1
Ertoz L, Steinbach M, Kumar V (2003) Finding clusters of different sizes, shapes, and densities in noisy, high dimensional data. Proceedings of Third SIAM International Conference on Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA
Everitt BS, Landau S, Leese M, Stahl D (2011) Cluster analysis, 5th edn. John Wiley and Sons, New Jersey
Huth R, Nemesova I, Klimperova N (1993) Weather categorization based on the average linkage clustering technique: an application to European mid-latitudes. Int J Climatol 13:817–835
Jamous BA, Fa R, Nandi AK (2015) Integrative Cluster Analysis in Bioinformatics, 1st edn. John Wiley and Sons Ltd., United Kingdom, p 162
Kakade S, Kulkarni A (2016) Prediction of summer monsoon rainfall over India and its homogeneous regions. Meteorol Appl 23:1–13, Wiley. https://doi.org/10.1002/met.1524
Kaufman L, Rousseeuw PJ (1990) Finding groups in data: an introduction to cluster analysis. Wiley, New York
Kulkarni A (2016) Homogeneous clusters over India using probability density function of daily rainfall. Theor Appl Climatol, Springer-Verlag, Wien. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-016-1808-8
Legendre P, Legendre L (2012) Numerical Ecology (3rd English edn). Elsevier, Amsterdam
Littmann T (2000) An empirical classification of weather types in the Mediterranean Basin and their interrelation with rainfall. Theor Appl Climatol 66:161–171
Liu S, George R (2005) Mining weather data using fuzzy cluster analysis. Springer, Berlin
Marghny MH, Abd El-Aziz RM, Taloba AI (2011) An effective evolutionary clustering algorithm: hepatitis C case study. Int J Comput Appl 34:1–6
Montazeri M (2011) A cluster analysis of thermal seasons of Iran. Quarterly Geogr Res 101:173–198
Murtagh F, Legendre P (2014) Ward’s hierarchical agglomerative clustering method: which algorithms implement Ward’s criterion? J Classif 31:274–295. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00357-014-9161-z
Saha M, Mitra P (2015) Co-clustering based approach for Indian monsoon prediction. ICCS 2015 International Conference on Computational Science, Procedia Computer Science, 51:2938–2942, Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2015.05.485
Tenenbaum JB, Silva VD, Langford JC (2000) A global geometric frame-work for nonlinear dimensionality reduction. Science 290:2319–2323
Ward JH (1963) Hierarchical grouping to optimize an objective function. J Am Stat Assoc 58(301):236–244
Yarnal B (1993) Synoptic climatology in environmental analysis. Belhaven Press, London
Yarnal B, Comrie AC, Frakes B, Brown DP (2001) Developments and prospects in synoptic climatology review. Int J Climatol 21:1923–1950
Yoskoi S, Takayabu YN, Nishii K, Nakamura H, Endo H, Ichikawa H, Inoue T, Kimoto M, Kosaka Y, Miyasaka T, Oshima K, Sato N, Tsushima Y, Watanabe M (2011) Application of cluster analysis to climate model performance metrics. J Appl Meteorol Climatol 50:1666–1675. https://doi.org/10.1175/2011JAMC2643.1
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Bangladesh Meteorological Department for providing the data necessary for the present study. The authors especially thank the Editor and anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions that improved the quality of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix A
Appendix A
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahman, M.H., Matin, M.A. & Salma, U. Analysis of precipitation data in Bangladesh through hierarchical clustering and multidimensional scaling. Theor Appl Climatol 134, 689–705 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-017-2319-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-017-2319-y