Abstract
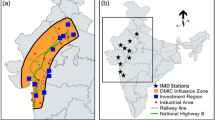
The Kolkata metropolitan region, located in eastern India, is one of the most densely urbanized areas, with significant thunderstorms reported during the pre-monsoon season. The Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) model is used to investigate the influence of urban-induced land use and land cover (LULC) change over Kolkata during the pre-monsoon thunderstorms. Multiple thunderstorm events reported during 2014–2017 are simulated using a high (Hurb) and low (Lurb) urban LULC scenario. The presence of higher urban pixels in Hurb case favors the enhancement in precipitation mainly over central and northern parts of the city in the downwind direction. Urban Heat Island (UHI) effect is more evident during the nighttime, with a temperature difference of up to 0.5 °C. However, the UHI impacts the vertical structure of the boundary layer (BL) more during the daytime due to prevailing higher temperatures and dominant surface heating. The analysis reveals positive contributions of the ground and sensible heat fluxes to the near-surface UHI intensity. The surfaces over the urban patch and surrounding areas experience a relatively drier atmosphere than their rural counterparts. Over the identified urban patches, a significant impact on meteorological variables is seen near the surface and within the BL in the case of Hurb compared to Lurb LULC scenario. The urbanization over Kolkata stimulates the BL and the local meteorology encouraging nighttime UHI, afternoon or evening moist convection, and consequent occurrence of thunderstorms to result in enhanced and distinctly distributed rainfall over the city and its neighborhood during pre-monsoon months.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed in the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Argüeso D, Evans JP, Fita L, Bormann KJ (2014) Temperature response to future urbanization and climate change. Clim Dyn 42(7–8):2183–2199
Argüeso D, Evans JP, Pitman AJ, Di Luca A (2015) Effects of city expansion on heat stress under climate change conditions. PLoS ONE 10(2):e0117066
Bondyopadhyay S, Mohapatra M, Sen Roy S (2021) Determination of suitable thermodynamic indices and prediction of thunderstorm events for Kolkata, India. Meteorol Atmos Phys 133(4):1367–1377
Barlow JF (2014) Progress in observing and modelling the urban boundary layer. Urban Clim 10:216–240
Bhati S, Mohan M (2016) WRF model evaluation for the urban heat island assessment under varying land use/land cover and reference site conditions. Theor Appl Climatol 126(1–2):385–400
Bornstein R, Lin Q (2000) Urban heat islands and summertime convective thunderstorms in Atlanta: three case studies. Atmos Environ 34(3):507–516
Burian SJ, Shepherd JM (2005) Effect of urbanization on the diurnal rainfall pattern in Houston. Hydrol Process 19(5):1089–1103
Chakraborty S, Chowdhury BR, Ghosh S, Sen PK, De UK (2019) Statistical analysis of urban regional pre-monsoon rainfall in and around Kolkata, India. J Earth Syst Sci 128(3):57. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-019-1068-y
Changnon SA (2003) Urban modification of freezing-rain events. J Appl Meteorol Clim 42(6):863–870
Chapman S, Watson JE, Salazar A, Thatcher M, McAlpine CA (2017) The impact of urbanization and climate change on urban temperatures: a systematic review. Landsc Ecol 32(10):1921–1935
Chaudhuri S, Middey A (2012) Appraisal of stability indices for forecasting severe thunderstorms over Kolkata using weighted tree-graph analysis. Asian J Water Environ Pollut 9(4):79–86
Chow WT, Svoma BM (2011) Analyses of nocturnal temperature cooling-rate response to historical local-scale urban land-use/land cover change. J Appl Meteorol Clim 50(9):1872–1883
Comarazamy DE, González JE, Luvall JC, Rickman DL, Mulero PJ (2010) A land–atmospheric interaction study in the coastal tropical city of San Juan, Puerto Rico. Earth Interact 14(16):1–24
Coutts AM, Beringer J, Tapper NJ (2007) Impact of increasing urban density on local climate: spatial and temporal variations in the surface energy balance in Melbourne, Australia. J Appl Meteorol Clim 46(4):477–493
Das S, Mohanty UC, Tyagi A, Sikka DR, Joseph PV, Rathore LS, Habib A, Baidya SK, Sonam K, Sarkar A (2014) The SAARC STORM: a coordinated field experiment on severe thunderstorm observations and regional modeling over the South Asian Region. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 95(4):603–617
Degu AM, Hossain F, Niyogi D, Pielke Sr R, Shepherd JM, Voisin N, Chronis T (2011) The influence of large dams on surrounding climate and precipitation patterns. Geophys Res 38(4). https://doi.org/10.1029/2010GL046482
Dixon PG, Mote TL (2003) Patterns and causes of Atlanta’s urban heat island–initiated precipitation. J Appl Meteorol Clim 42(9):1273–1284
Eresmaa N, Rantamäki M, Karppinen A (2009) Comparison of urban and rural boundary-layer height measurements by ceilometer. In: The seventh international conference on urban climate, 29 June–3 July 2009, Yokohama, Japan.
Ganeshan M, Murtugudde R, Imhoff ML (2013) A multi-city analysis of the UHI-influence on warm season rainfall. Urban Clim 6:1–23
Gao W, Xue L, Liu L, Lu C, Yun Y, Zhou W (2021) A study of the fraction of warm rain in a pre-summer rainfall event over South China. Atmos Res 262:105792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2021.105792
Göndöcs J, Breuer H, Pongrácz R, Bartholy J (2017) Urban heat island mesoscale modelling study for the Budapest agglomeration area using the WRF model. Urban Clim 21:66–86
Guo X, Fu D, Wang J (2006) Mesoscale convective precipitation system modified by urbanization in Beijing City. Atmos Res 82(1–2):112–126
Haberlie AM, Ashley WS, Pingel TJ (2015) The effect of urbanisation on the climatology of thunderstorm initiation. Q J R Meteorol Soc 141(688):663–675
Hale RC, Gallo KP, Loveland TR (2008) Influences of specific land use/land cover conversions on climatological normals of near‐surface temperature. J Geophys Res Atmos 113(D14). https://doi.org/10.1029/2007JD009548
Han L, Zhou W, Li W, Li L (2014) Impact of urbanization level on urban air quality: a case of fine particles (PM2. 5) in Chinese cities. Environ Pollut 194:163–170
Huff FA, Changnon Jr SA (1973) Precipitation modification by major urban areas. Bull Amer Meteor Soc 54(12):1220–1233. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0477(1973)054<1220:PMBMUA>2.0.CO;2
Igri P, Tanessong RS, Vondou DA, Mkankam FK, Panda J (2015) Added-value of 3DVAR data assimilation in the simulation of heavy rainfall events over West and Central Africa. Pure Appl Geophys 172(10):2751–2776
Igri PM, Tanessong RS, Vondou DA, Panda J, Garba A, Mkankam FK, Kamga A (2018) Assessing the performance of WRF model in predicting high-impact weather conditions over Central and Western Africa: an ensemble-based approach. Nat Hazards 93(3):1565–1587
Imran HM, Kala J, Ng AWM, Muthukumaran S (2018) An evaluation of the performance of a WRF multi-physics ensemble for heatwave events over the city of Melbourne in southeast Australia. Clim Dyn 50(7–8):2553–2586
Imran HM, Kala J, Ng AW, Muthukumaran S (2019) Impacts of future urban expansion on urban heat island effects during heatwave events in the city of Melbourne in southeast Australia. Q J R Meteorol Soc 145(723):2586–2602
Jain S, Roy SB, Panda J, Rath SS (2021) Modeling of land-use and land-cover change impact on summertime near-surface temperature variability over the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor. Model Earth Syst Environ 7(2):1309–1319
Kadaverugu R, Matli C, Biniwale R (2021) Suitability of WRF model for simulating meteorological variables in rural, semi-urban and urban environments of Central India. Meteorol Atmos Phys 133(4):1379–1393
Kaufmann RK, Seto KC, Schneider A, Liu Z, Zhou L, Wang W (2007) Climate response to rapid urban growth: evidence of a human-induced precipitation deficit. J Clim 20(10):2299–2306
Kishtawal CM, Niyogi D, Tewari M, Pielke RA Sr, Shepherd JM (2010) Urbanization signature in the observed heavy rainfall climatology over India. Int J Climatol 30(13):1908–1916
Kumar A, Dudhia J, Rotunno R, Niyogi D, Mohanty UC (2008) Analysis of the 26 July 2005 heavy rain event over Mumbai, India using the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) model. Q J R Meteorol Soc 134(636):1897–1910
Kusaka H (2009) The chink in the armor: questioning the reliability of sensitivity experiments in determining urban effects on precipitation patterns. In: Proceedings of the seventh international conference on urban clim, 29 June–3 July 2009, Yokohama. http://www.ide.titech.ac.jp/~icuc7/extended_abstracts/pdf/374679-1-090520195455-004.pdf
Kusaka H, Nawata K, Suzuki-Parker A, Takane Y, Furuhashi N (2014) Mechanism of precipitation increase with urbanization in Tokyo as revealed by ensemble climate simulations. J Appl Meteorol Clim 53(4):824–839
Kusaka H, Nishi A, Mizunari M, Yokoyama H (2019) Urban impacts on the spatiotemporal pattern of short-duration convective precipitation in a coastal city adjacent to a mountain range. Q J R Meteorol Soc 145(722):2237–2254
Lei M, Niyogi D, Kishtawal C, Pielke RA Sr, Beltrán-Przekurat A, Nobis TE, Vaidya SS (2008) Effect of explicit urban land surface representation on the simulation of the 26 July 2005 heavy rain event over Mumbai, India. Atmos Chem Phys 8(20):5975–5995
Li D, Bou-Zeid E (2013) Synergistic interactions between urban heat islands and heat waves: the impact in cities is larger than the sum of its parts. J Appl Meteorol Clim 52(9):2051–2064
Li X, Mitra C, Dong L, Yang Q (2018) Understanding land use change impacts on microclimate using Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) model. Phys Chem Earth 103:115–126
Li XX, Koh TY, Entekhabi D, Roth M, Panda J, Norford LK (2013) A multi-resolution ensemble study of a tropical urban environment and its interactions with the background regional atmosphere. J Geophys Res-Atmos 118(17):9804–9818
Li XX, Koh TY, Panda J, Norford LK (2016) Impact of urbanization patterns on the local climate of a tropical city, Singapore: an ensemble study. J Geophys Res Atmos 121(9):4386–4403
Lin YL, Farley RD, Orville HD (1983) Bulk parameterization of the snow field in a cloud model. J Appl Meteorol Climatol 22(6):1065–1092
Liu J, Niyogi D (2019) Meta-analysis of urbanization impact on rainfall modification. Sci Rep 9(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-42494-2
Mallick J, Rahman A, Singh CK (2013) Modeling urban heat islands in heterogeneous land surface and its correlation with impervious surface area by using nighttime ASTER satellite data in highly urbanizing city, Delhi-India. Adv Space Res 52(4):639–655
Manohar GK, Kandalgaonkar SS, Tinmaker MIR (1999) Thunderstorm activity over India and the Indian southwest monsoon. J Geophys Res Atmos 104(D4):4169–4188
Martilli A (2002) Numerical study of urban impact on boundary layer structure: sensitivity to wind speed, urban morphology, and rural soil moisture. J Appl Meteorol 41(12):1247–1266
Martínez-Zarzoso I, Maruotti A (2011) The impact of urbanization on CO2 emissions: evidence from developing countries. Ecol Econ 70(7):1344–1353
Mathew A, Khandelwal S, Kaul N (2018) Analysis of diurnal surface temperature variations for the assessment of surface urban heat island effect over Indian cities. Energy Build 159:271–295
Miao S, Chen F, Li Q, Fan S (2011) Impacts of urban processes and urbanization on summer precipitation: a case study of heavy rainfall in Beijing on 1 August 2006. J Appl Meteorol Clim 50(4):806–825
Mitra C, Shepherd JM, Jordan T (2012) On the relationship between the premonsoonal rainfall climatology and urban land cover dynamics in Kolkata city, India. Int J Climatol 32(9):1443–1454
Mohan M, Kandya A (2015) Impact of urbanization and land-use/land-cover change on diurnal temperature range: a case study of tropical urban airshed of India using remote sensing data. Sci Total Environ 506:453–465
Mohan M, Kikegawa Y, Gurjar BR, Bhati S, Kolli NR (2013) Assessment of urban heat island effect for different land use–land cover from micrometeorological measurements and remote sensing data for megacity Delhi. Theor Appl Climatol 112(3–4):647–658
Nesbitt SW, Zipser EJ (2003) The diurnal cycle of rainfall and convective intensity according to three years of TRMM measurements. J Clim 16(10):1456–1475
Oke TR, Johnson GT, Steyn DG, Watson ID (1991) Simulation of surface urban heat islands under ‘ideal’ conditions at night Part 2: diagnosis of causation. Bound Layer Meteorol 56(4):339–358
Panda J, Sharan M (2012) Influence of land-surface and turbulent parameterization schemes on regional-scale boundary layer characteristics over northern India. Atmos Res 112:89–111
Panda J, Sharan M, Gopalakrishnan SG (2009) Study of regional-scale boundary layer characteristics over Northern India with a special reference to the role of the Thar Desert in regional-scale transport. J Appl Meteorol Clim 48(11):2377–2402
Paul S, Ghosh S, Mathew M, Devanand A, Karmakar S, Niyogi D (2018) Increased spatial variability and intensification of extreme monsoon rainfall due to urbanization. Sci Rep 8(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-22322-9
Pielke RA Sr, Adegoke J, BeltraáN-Przekurat A, Hiemstra CA, Lin J, Nair US, Niyogi D, Nobis TE (2007) An overview of regional land-use and land-cover impacts on rainfall. Tellus B 59(3):587–601
Powers JG, Klemp JB, Skamarock WC, Davis CA, Dudhia J, Gill DO, Coen JL, Gochis DJ, Ahmadov R, Peckham SE, Duda MG (2017) The weather research and forecasting model: Overview, system efforts, and future directions. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 98(8):1717–1737
Prasad KH, Srinivas CV, Rao TN, Naidu CV, Baskaran R (2017) Performance of WRF in simulating terrain induced flows and atmospheric boundary layer characteristics over the tropical station Gadanki. Atmos Res 185:101–117
Ramamurthy P, Bou-Zeid E (2017) Heatwaves and urban heat islands: a comparative analysis of multiple cities. J Geophys Res Atmos 122(1):168–178
Rath SS, Panda J (2019) A study of near-surface boundary layer characteristics during the 2015 Chennai flood in the context of urban-induced land use changes. Pure Appl Geophys 176(6):2607–2629
Rath SS, Panda J (2020) Urban induced land-use change impact during pre-monsoon thunderstorms over Bhubaneswar-Cuttack urban complex. Urban Clim 32:100628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.uclim.2020.100628
Rath SS, Mohanty S, Panda J (2022) Analyzing the fragmentation of urban footprints in eastern and southern Indian cities and driving factors. J Indian Soc Remote Sens 50:1499–1517. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-022-01546-3
Ray K, Bandopadhyay BK, Sen B, Sharma P, Warsi AH, Mohapatra M, Yadav BP, Debnath GC, Stella S, Rathore LS (2015) Pre-monsoon thunderstorms 2015: a report (SAARC STORM PROJECT-2015). India Meteorological Department, Nowcasting Unit, Scientific Report No. ESSO/IMD/SMRC STORM Project-2015/01/(2015)/4
Ray K, Kannan BAM, Sharma P, Sen B, Warsi AH (2017) Severe thunderstorm activities over India during SAARC STORM project 2014–15: study based on radar. Vayu Mandal 43(2):30–46
Ren G, Zhou Y, Chu Z, Zhou J, Zhang A, Guo J, Liu X (2008) Urbanization effects on observed surface air temperature trends in North China. J Clim 21(6):1333–1348
Rotach MW, Vogt R, Bernhofer C, Batchvarova E, Christen A, Clappier A, Feddersen B, Gryning SE, Martucci G, Mayer H, Mitev V (2005) BUBBLE—an urban boundary layer meteorology project. Theor Appl Climatol 81(3–4):231–261
Rozoff CM, Cotton WR, Adegoke JO (2003) Simulation of St. Louis, Missouri, land use impacts on thunderstorms. J Appl Meteorol Clim 42(6):716–738
Salamanca F, Martilli A, Yagüe C (2012) A numerical study of the Urban Heat Island over Madrid during the DESIREX (2008) campaign with WRF and an evaluation of simple mitigation strategies. Int J Climatol 32(15):2372–2386
Sahu RK, Dadich J, Tyagi B, Vissa NK, Singh J (2020) Evaluating the impact of climate change in threshold values of thermodynamic indices during pre-monsoon thunderstorm season over Eastern India. Nat Hazards 102(3):1541–1569
Sati AP, Mohan M (2018) The impact of urbanization during half a century on surface meteorology based on WRF model simulations over National Capital Region, India. Theor Appl Climatol 134(1):309–323
Sen Roy S, Yuan F (2009) Trends in extreme temperatures in relation to urbanization in the Twin Cities Metropolitan Area, Minnesota. J Appl Meteorol Clim 48(3):669–679
Shastri H, Barik B, Ghosh S, Venkataraman C, Sadavarte P (2017) Flip flop of day-night and summer-winter surface urban heat island intensity in India. Sci Rep 7(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep40178
Shem W, Shepherd M (2009) On the impact of urbanization on summertime thunderstorms in Atlanta: two numerical model case studies. Atmos Res 92(2):172–189
Shepherd JM (2005) A review of current investigations of urban-induced rainfall and recommendations for the future. Earth Interact 9(12):1–27
Singh C, Mohapatra M, Bandyopadhyay BK, Tyagi A (2011) Thunderstorm climatology over northeast and adjoining east India. Mausam 62(2):163–170
Skamarock W, Klemp JB, Dudhia J, Gill D, Barker D, Duda M, Wang W, Powers J (2008) A description of the advanced research WRF version 3. NCAR Technical Note, NCAR/TN\u2013475? STR, 123 pp
Sultana S, Satyanarayana ANV (2018) Urban heat island intensity during winter over metropolitan cities of India using remote-sensing techniques: impact of urbanization. Int J Remote Sens 39(20):6692–6730
Tyagi A (2007) Thunderstorm climatology over Indian region. Mausam 58(2):189
Tyagi B, Krishna VN, Satyanarayana ANV (2011) Study of thermodynamic indices in forecasting pre-monsoon thunderstorms over Kolkata during STORM pilot phase 2006–2008. Nat Hazards 56(3):681–698
UNDESA (2019) World Urbanization Prospects: The 2018 Revision (ST/ESA/SER.A/420). New York: United Nations. Available at https://population.un.org/wup/publications/Files/WUP2018-Report.pdf
Verma S, Panda J, Rath SS (2021) Role of PBL and microphysical parameterizations during WRF simulated monsoonal heavy rainfall episodes over Mumbai. Pure Appl Geophys 178(9):3673–3702
Vitanova LL, Kusaka H, Doan VQ, Nishi A (2019) Numerical study of the urban heat island in Sendai City with potential natural vegetation and the 1850s and 2000s land-use data. J Meteorol Soc Japan Ser II 97(1):227–252
Wan H, Zhong Z, Yang X, Li X (2013) Impact of city belt in Yangtze River Delta in China on a precipitation process in summer: a case study. Atmos Res 125:63–75
Wan H, Zhong Z, Yang X, Li X (2015) Ensembles to model the impact of urbanization for a summertime rainstorm process in Yangtze River Delta, China. Meteorol Appl 22(1):105–112
Wang D, Miao J, Tan Z (2013) Impacts of topography and land cover change on thunderstorm over the Huangshan (Yellow Mountain) area of China. Nat Hazards 67(2):675–699
Wang D, Miao J, Zhang DL (2015) Numerical simulations of local circulation and its response to land cover changes over the Yellow Mountains of China. J Meteorol Res 29(4):667–681
Woldemichael AT, Hossain F, Pielke RA Sr (2014) Impacts of postdam land use/land cover changes on modification of extreme precipitation in contrasting hydroclimate and terrain features. J Hydrometeorol 15(2):777–800
Yang X, Hou Y, Chen B (2011) Observed surface warming induced by urbanization in east China. J Geophys Res-Atmos 116(D14). https://doi.org/10.1029/2010JD015452
Zhang N, Gao Z, Wang X, Chen Y (2010) Modeling the impact of urbanization on the local and regional climate in Yangtze River Delta, China. Theor Appl Climatol 102(3–4):331–342
Zhang T, Mahmood R, Lin X, Pielke RA Sr (2019) Irrigation impacts on minimum and maximum surface moist enthalpy in the Central Great Plains of the USA. Weather Clim 23:100197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wace.2019.100197
Zhang Y, Miao S, Dai Y, Bornstein R (2017) Numerical simulation of urban land surface effects on summer convective rainfall under different UHI intensity in Beijing. J Geophys Res Atmos 122(15):7851–7868
Zhou J, Chen Y, Zhang X, Zhan W (2013) Modelling the diurnal variations of urban heat islands with multi-source satellite data. Int J Remote Sens 34(21):7568–7588
Acknowledgements
The agencies ‘Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB)’, and ‘Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES)’ of Government of India, are sincerely acknowledged for partially funding this research through the projects with file numbers EMR/2015/001358 and MoES/16/09/2018-RDEAS-THUMP-2, respectively. The BHUVAN (http://bhuvan.nrsc.gov.in/bhuvan_links.php) data portal of ISRO is acknowledged for providing LULC datasets. GFS-FNL global analyses atmospheric data sets (https://rda.ucar.edu/datasets/ds083.2/), USGS terrestrial data sets (https://www2.mmm.ucar.edu/wrf/users/download/get_sources_wps_geog.html), Wyoming Weather Web data archive (https://weather.uwyo.edu/upperair/sounding.html), and Weather Underground (https://www.wunderground.com/) are duly acknowledged. The scientific help from Rajesh Kumar Sahu (PhD scholar at the Department of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences, National Institute of Technology Rourkela) is acknowledged.
Funding
Science and Engineering Research Board, EMR/2015/001358, JAGABANDHU PANDA, Ministry of Earth Sciences, MoES/16/09/2018-RDEAS-THUMP-2, JAGABANDHU PANDA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: J.-F. Miao.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rath, S.S., Panda, J. & Sarkar, A. Distinct urban land cover response to meteorology in WRF simulated pre-monsoon thunderstorms over the tropical city of Kolkata. Meteorol Atmos Phys 134, 76 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-022-00916-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-022-00916-3