Abstract
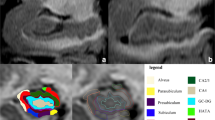
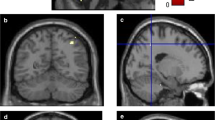
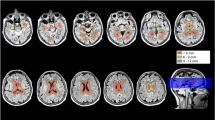
The volume of the hippocampus decreases more slowly than the volume of the cortex during normal aging. We explored changes in the hippocampus-to-cortex volume (HV:CTV) ratio with increasing age in non-demented Parkinson’s disease (PD) patients as compared to healthy controls (HC). We also evaluated the association between the HV:CTV ratio and cognitive outcomes. Altogether 130 participants without dementia aged 51–88 years were consecutively enrolled, including 54 PD patients (mean age 67, standard deviation (SD) 8 years) and 76 HC (mean age 69, SD 7 years). All participants underwent structural magnetic resonance examination and psychological evaluation. Hippocampal and cortex volumes were determined from T1 and FLAIR scans using FreeSurfer software, and the HV:CTV ratio was calculated. Regression lines for age-dependence of the HV:CTV ratio for PD and HC groups were calculated. We further assessed the association between the HV:CTV ratio and cognitive tests examining hippocampus-related cognitive functions. PD patients and age-matched HC showed a significant difference in age-dependence of HV:CTV ratio (p value = 0.012), with a decreasing slope in PD and increasing slope in HC. In the PD group, a significant correlation (R = 0.561, p = 0.024) was observed between the HV:CTV ratio and the Digit Symbol-Coding test. The reduction of HV:CTV ratio is accelerated in pathological aging due to PD pathology. The HV:CTV ratio was associated with impaired processing speed, i.e., the cognitive function that is linked to subcortical alterations of both associated basal ganglia circuitry and the hippocampus.

Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
All data are available upon request at the Repository CEITEC Masaryk University, MAFIL CF.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- CSF:
-
Cerebrospinal fluid
- GDS:
-
Geriatric Depression Scale
- GLM:
-
General linear model
- GM:
-
Gray matter
- HC:
-
Healthy controls
- HV:CTV ratio:
-
Hippocampus-to-cortex volume ratio
- JLO:
-
Judgment of Line Orientation
- MCI:
-
Mild cognitive impairment
- MoCA:
-
Montreal cognitive assessment
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- UPDRS:
-
Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale
References
Aarsland D, Batzu L, Halliday GM, Geurtsen GJ, Ballard C, Ray Chaudhuri K, Weintraub D (2021) Parkinson disease-associated cognitive impairment. Nat Rev Dis Primers 7(1):47. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-021-00280-3
Benton AL, Sivan AB, de Hamsher KS, Varney NR, Spreen O (1994) Contributions to neuropsychological assessment: a clinical manual, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Biundo R, Weis L, Facchini S, Formento-Dojot P, Vallelunga A, Pilleri M, Antonini A (2014) Cognitive profiling of Parkinson disease patients with mild cognitive impairment and dementia. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 20(4):394–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2014.01.009
Chung SJ, Yoo HS, Lee YH, Lee HS, Ye BS, Sohn YH, Kwon H, Lee PH (2019) Frontal atrophy as a marker for dementia conversion in Parkinson’s disease with mild cognitive impairment. Hum Brain Mapp. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.24631
David W (1997). In: Tulsky David LM, Zhu J (eds) WAIS-III WMS-III technical manual. Harcourt Brace and Company, San Diego
Desikan RS, Ségonne F, Fischl B, Quinn BT, Dickerson BC, Blacker D, Buckner RL, Dale AM, Maguire RP, Hyman BT, Albert MS, Killiany RJ (2006) An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. Neuroimage 31(3):968–980. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.01.021
Ferrazzoli D, Ortelli P, Madeo G, Giladi N, Petzinger GM, Frazzitta G (2018) Basal ganglia and beyond: The interplay between motor and cognitive aspects in Parkinson’s disease rehabilitation. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 90:294–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2018.05.007
Fjell AM, McEvoy L, Holland D, Dale AM, Walhovd KB (2014) What is normal in normal aging? Effects of aging, amyloid and Alzheimer’s disease on the cerebral cortex and the hippocampus. Prog Neurobiol 117:20–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PNEUROBIO.2014.02.004
Friston KJ, Ashburner JT, Kiebel SJ, Nichols TE, Penny WD (2007) Statistical parametric mapping, 1st edn. Elsevier Press, Amsterdam
Halliday GM, McCann H (2010) The progression of pathology in Parkinson’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1184(1):188–195. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.05118.x
Hardcastle C, O’Shea A, Kraft JN, Albizu A, Evangelista ND, Hausman HK, Boutzoukas EM, Van Etten EJ, Bharadwaj PK, Song H, Smith SG, Porges EC, Dekosky S, Hishaw GA, Wu SS, Marsiske M, Cohen R, Alexander GE, Woods AJ (2020) Contributions of hippocampal volume to cognition in healthy older adults. Front Aging Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2020.593833
Irwin DJ, White MT, Toledo JB, Xie SX, Robinson JL, Van Deerlin V, Lee VM-Y, Leverenz JB, Montine TJ, Duda JE, Hurtig HI, Trojanowski JQ (2012) Neuropathologic substrates of Parkinson disease dementia. Ann Neurol 72(4):587–598. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.23659
Jack CR, Bennett DA, Blennow K, Carrillo MC, Dunn B, Haeberlein SB, Holtzman DM, Jagust W, Jessen F, Karlawish J, Liu E, Molinuevo JL, Montine T, Phelps C, Rankin KP, Rowe CC, Scheltens P, Siemers E, Snyder HM, Silverberg N (2018) NIA-AA research framework: toward a biological definition of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement 14(4):535–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2018.02.018
Kandiah N, Zainal NH, Narasimhalu K, Chander RJ, Ng A, Mak E, Au WL, Sitoh YY, Nadkarni N, Tan LCS (2014) Hippocampal volume and white matter disease in the prediction of dementia in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 20(11):1203–1208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2014.08.024
Kehagia AA, Barker RA, Robbins TW (2013) Cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease: the dual syndrome hypothesis. Neurodegener Dis 11(2):79–92. https://doi.org/10.1159/000341998
Krajcovicova L, Klobusiakova P, Rektorova I (2019) Gray matter changes in Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease and relation to cognition. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 19(11):85. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-019-1006-z
Kravitz DJ, Saleem KS, Baker CI, Mishkin M (2011) A new neural framework for visuospatial processing. Nat Rev Neurosci 12(4):217–230. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3008
Lawson RA, Yarnall AJ, Duncan GW, Breen DP, Khoo TK, Williams-Gray CH, Barker RA, Collerton D, Taylor J-P, Burn DJ (2016) Cognitive decline and quality of life in incident Parkinson’s disease: the role of attention. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 27:47–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2016.04.009
Litvan I, Goldman JG, Tröster AI, Schmand BA, Weintraub D, Petersen RC, Mollenhauer B, Adler CH, Marder K, Williams-Gray CH, Aarsland D, Kulisevsky J, Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Burn DJ, Barker RA, Emre M (2012) Diagnostic criteria for mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease: Movement Disorder Society Task Force guidelines. Mov Disord 27(3):349–356. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.24893
Nobis L, Manohar SG, Smith SM, Alfaro-Almagro F, Jenkinson M, Mackay CE, Husain M (2019) Hippocampal volume across age: Nomograms derived from over 19,700 people in UK Biobank. Neuroimage 23:101904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2019.101904
O’Shea A, Cohen RA, Porges EC, Nissim NR, Woods AJ (2016) Cognitive aging and the hippocampus in older adults. Front Aging Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2016.00298
Papp KV, Kaplan RF, Springate B, Moscufo N, Wakefield DB, Guttmann CRG, Wolfson L (2014) Processing speed in normal aging: Effects of white matter hyperintensities and hippocampal volume loss. Aging Neuropsychol Cogn 21(2):197–213. https://doi.org/10.1080/13825585.2013.795513
Postuma RB, Berg D, Adler CH, Bloem BR, Chan P, Deuschl G, Gasser T, Goetz CG, Halliday G, Joseph L, Lang AE, Liepelt-Scarfone I, Litvan I, Marek K, Oertel W, Olanow CW, Poewe W, Stern M (2016) The new definition and diagnostic criteria of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 15(6):546–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(16)00116-2
Ray NJ, Bradburn S, Murgatroyd C, Toseeb U, Mir P, Kountouriotis GK, Teipel SJ, Grothe MJ (2018) In vivo cholinergic basal forebrain atrophy predicts cognitive decline in de novo Parkinson’s disease. Brain 141(1):165–176. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awx310
Rektorova I, Rektor I, Bares M, Dostal V, Ehler E, Fanfrdlova Z, Fiedler J, Klajblova H, Kulistak P, Ressner P, Svatova J, Urbanek K, Veliskova J (2005) Cognitive performance in people with Parkinson’s disease and mild or moderate depression: effects of dopamine agonists in an add-on to l-dopa therapy. Eur J Neurol 12(1):9–15. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2004.00966.x
Rektorova I, Biundo R, Marecek R, Weis L, Aarsland D, Antonini A (2014) Grey matter changes in cognitively impaired Parkinson’s disease patients. PLoS ONE 9(1):e85595. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0085595
Risacher SL, Anderson WH, Charil A, Castelluccio PF, Shcherbinin S, Saykin AJ, Schwarz AJ (2017) Alzheimer disease brain atrophy subtypes are associated with cognition and rate of decline. Neurology 89(21):2176–2186. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000004670
Ruiz NA, Meager MR, Agarwal S, Aly M (2020) The medial temporal lobe is critical for spatial relational perception. J Cogn Neurosci 32(9):1780–1795. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn_a_01583
Thomann PA, Wüstenberg T, Nolte HM, Menzel PB, Wolf RC, Essig M, Schröder J (2013) Hippocampal and entorhinal cortex volume decline in cognitively intact elderly. Psychiatry Res 211(1):31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.PSCYCHRESNS.2012.06.002
Tropea TF, Xie SX, Rick J, Chahine LM, Dahodwala N, Doshi J, Davatzikos C, Shaw LM, Van Deerlin V, Trojanowski JQ, Weintraub D, Chen-Plotkin AS (2018) APOE, thought disorder, and SPARE-AD predict cognitive decline in established Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 33(2):289–297. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.27204
Weintraub D, Dietz N, Duda JE, Wolk DA, Doshi J, Xie SX, Davatzikos C, Clark CM, Siderowf A (2012) Alzheimer’s disease pattern of brain atrophy predicts cognitive decline in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 135(1):170–180. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awr277
Whitwell JL, Dickson DW, Murray ME, Weigand SD, Tosakulwong N, Senjem ML, Knopman DS, Boeve BF, Parisi JE, Petersen RC, Jack CR, Josephs KA (2012) Neuroimaging correlates of pathologically defined subtypes of Alzheimer’s disease: a case-control study. Lancet Neurol 11(10):868–877. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70200-4
Yamamoto N, Philbeck JW, Woods AJ, Gajewski DA, Arthur JC, Potolicchio SJ, Levy L, Caputy AJ (2014) Medial temporal lobe roles in human path integration. PLoS ONE 9(5):e96583. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0096583
Zatorre RJ, Fields RD, Johansen-Berg H (2012) Plasticity in gray and white: neuroimaging changes in brain structure during learning. Nat Neurosci 15(4):528–536. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3045
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Michal Mikl for statistics assistance and Anne Johnson for English language assistance. This project received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement no. 734718 (CoBeN), from a grant from the Czech Ministry of Health, NU20-04-00294, and from the Czech Science Foundation GAČR 21-25953S. We acknowledge the help of the core facility multimodal and functional imaging laboratory (MAFIL) of the Central European Institute for Technology – Masaryk University (CEITEC MU), supported by the Czech Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports (MEYS CR) (LM2018129 Czech-BioImaging).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by ethics committees of the participating institutions.
Consent to participate
All participants gave their informed consent before the study started.
Consent for publication
Corresponding author has the right to publish any and all data separate and apart from any sponsor.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Říha, P., Brabenec, L., Mareček, R. et al. The reduction of hippocampal volume in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 129, 575–580 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-021-02451-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-021-02451-8