Abstract
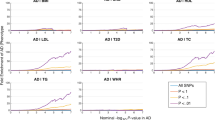
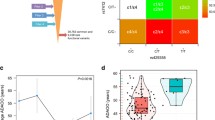
Altered glucose metabolism has been described in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). We re-investigated the interaction of the insulin (INS) and the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARA) genes in AD risk in the Epistasis Project, including 1,757 AD cases and 6,294 controls. Allele frequencies of both SNPs (PPARA L162V, INS intron 0 A/T) differed between Northern Europeans and Northern Spanish. The PPARA 162LL genotype increased AD risk in Northern Europeans (p = 0.04), but not in Northern Spanish (p = 0.2). There was no association of the INS intron 0 TT genotype with AD. We observed an interaction on AD risk between PPARA 162LL and INS intron 0 TT genotypes in Northern Europeans (Synergy factor 2.5, p = 0.016), but not in Northern Spanish. We suggest that dysregulation of glucose metabolism contributes to the development of AD and might be due in part to genetic variations in INS and PPARA and their interaction especially in Northern Europeans.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertram L, McQueen MB, Mullin K, Blacker D, Tanzi RE (2007) Systematic meta-analyses of Alzheimer disease genetic association studies: the AlzGene database. Nat Genet 39:17–23
Brune S, Kölsch H, Ptok U, Majores M, Schulz A, Schlosser R, Rao ML, Maier W, Heun R (2003) Polymorphism in the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha gene influences the risk for Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm 110:1041–1050
Capurso C, Solfrizzi V, D’Introno A, Colacicco AM, Capurso SA, Mastroianni F, Liaci M, Vendemiale G, Capurso A, Panza F (2005) The cathepsin D gene exon 2 (C224T) polymorphism and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease in European populations. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 60:991–996
Combarros O, Van Duijn CM, Hammond N, Belbin O, Arias-Vásquez A, Cortina-Borja M, Lehmann MG, Aulchenko YS, Schuur M, Kölsch H, Heun R, Wilcock GK, Brown K, Kehoe PG, Harrison R, Coto E, Alvarez V, Deloukas P, Mateo I, Gwilliam R, Morgan K, Warden DR, Smith AD, Lehmann DJ (2009) Replication by the Epistasis Project of the interaction between the genes for IL-6 and IL-10 in the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflamm 6:22
Combarros O, Warden DR, Hammond N, Cortina-Borja M, Belbin O, Lehmann MG, Wilcock GK, Brown K, Kehoe PG, Barber R, Coto E, Alvarez V, Deloukas P, Gwilliam R, Heun R, Kolsch H, Mateo I, Oulhaj A, Arias-Vasquez A, Schuur M, Aulchenko YS, Ikram MA, Breteler MM, Van Duijn CM, Morgan K, Smith AD, Lehmann DJ (2010) The dopamine beta-hydroxylase-1021C/T polymorphism is associated with the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in the Epistasis Project. BMC Med Genet 11:162
Combs CK, Bates P, Karlo JC, Landreth GE (2001) Regulation of beta-amyloid stimulated proinflammatory responses by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha. Neurochem Int 39:449–457
Comings DE, MacMurray JP (2000) Molecular heterosis: a review. Mol Genet Metab 71:19–31
Cortina-Borja M, Smith AD, Combarros O, Lehmann DJ (2009) The synergy factor: a statistic to measure interactions in complex diseases. BMC Res Notes 2:105
Craft S, Peskind E, Schwartz MW, Schellenberg GD, Raskind M, Porte D Jr (1998) Cerebrospinal fluid and plasma insulin levels in Alzheimer’s disease—relationship to severity of dementia and apolipoprotein E genotype. Neurology 50:164–168
De la Monte SM, Wands JR (2006) Molecular indices of oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction occur early and often progress with severity of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 9:167–181
Desvergne B, Wahli W (1999) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: nuclear control of metabolism. Endocr Rev 20:649–688
Escher P, Wahli W (2000) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: insight into multiple cellular functions. Mutat Res 448:121–138
Evans D, Aberle J, Wendt D, Wolf A, Beisiegel U, Mann WA (2001) A polymorphism, L162V, in the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) gene is associated with lower body mass index in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Mol Med 79:198–204
Flavell DM, Pineda TI, Jamshidi Y, Evans D, Diamond JR, Elkeles RS, Bujac SR, Miller G, Talmud PJ, Staels B, Humphries SE (2000) Variation in the PPARalpha gene is associated with altered function in vitro and plasma lipid concentrations in Type II diabetic subjects. Diabetologia 43:673–680
Flavell DM, Jamshidi Y, Hawe E, Pineda Torra I, Taskinen MR, Frick MH, Nieminen MS, Kesaniemi YA, Pasternack A, Staels B, Miller G, Humphries SE, Talmud PJ, Syvanne M (2002) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha gene variants influence progression of coronary atherosclerosis and risk of coronary artery disease. Circulation 105:1440–1445
Frölich L, Blum-Degen D, Bernstein HG, Engelsberger S, Humrich J, Laufer S, Muschner D, Thalheimer A, Türk A, Hoyer S, Zöchling R, Boissl KW, Jellinger K, Riederer P (1998) Brain insulin and insulin receptors in aging and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. J Neural Transm 105:423–438
Guerre-Millo M, Gervois P, Raspé E, Madsen L, Poulain P, Derudas B, Herbert JM, Winegar DA, Willson TM, Fruchart JC, Berge RK, Staels B (2000) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha activators improve insulin sensitivity and reduce adiposity. J Biol Chem 275:16638–16642
Harold D, Abraham R, Hollingworth P, Sims R, Gerrish A, Hamshere ML, Pahwa JS, Moskvina V, Dowzell K, Williams A et al (2009) Genome-wide association study identifies variants at CLU and PICALM associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet 41:1088–1093
Hofman A, Breteler MM, Van Duijn CM, Krestin GP, Pols HA, Stricker BH, Tiemeier H, Uitterlinden AG, Vingerling JR, Witteman JC (2007) The Rotterdam Study: objectives and design update. Eur J Epidemiol 22:819–829
Hollingworth P, Harold D, Sims R, Gerrish A, Lambert JC, Carrasquillo MM, Abraham R, Hamshere ML, Pahwa JS, Moskvina V et al (2011) Common variants at ABCA7, MS4A6A/MS4A4E, EPHA1, CD33 and CD2AP are associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet 43:429–435
Hoyer S (2002) The brain insulin signal transduction system and sporadic (type II) Alzheimer disease: an update. J Neural Transm 109:341–360
Hoyer S (2003) Memory function and brain glucose metabolism. Pharmacopsychiatry 36(Suppl 1):S62–S67
Kersten S, Desvergne B, Wahli W (2000) Roles of PPARs in health and disease. Nature 405:421–424
Lehmann DJ, Cortina-Borja M, Warden DR, Smith AD, Sleegers K, Prince JA, Van Duijn CM, Kehoe PG (2005) Large meta-analysis establishes the ACE insertion-deletion polymorphism as a marker of Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Epidemiol 162:305–317
Lehmann DJ, Schuur M, Warden DR, Hammond N, Belbin O, Kölsch H, Lehmann MG, Wilcock GK, Brown K, Kehoe PG, Morris CM, Barker R, Coto E, Alvarez V, Deloukas P, Mateo I, Gwilliam R, Combarros O, Arias-Vásquez A, Aulchenko YS, Ikram MA, Breteler MM, Van Duijn CM, Oulhaj A, Heun R, Cortina-Borja M, Morgan K, Robson K, Smith AD (2010) Transferrin and HFE genes interact in Alzheimer’s disease risk: the Epistasis Project. Neurobiol Aging [Epub ahead of print]
Majores M, Kölsch H, Bagli M, Ptok U, Kockler M, Becker K, Rao ML, Maier W, Heun R (2002) The insulin gene VNTR polymorphism in Alzheimer’s disease: results of a pilot study. J Neural Transm 109:1029–1034
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 34:939–944
Merryweather-Clarke AT, Pointon JJ, Jouanolle AM, Rochette J, Robson KJ (2000) Geography of HFE C282Y and H63D mutations. Genet Test 4:183–198
Miller SA, Dykes DD, Polesky HF (1988) A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucleic Acids Res 16:1215
Mirra SS, Heyman A, McKeel D, Sumi SM, Crain BJ, Brownlee LM, Vogel FS, Hughes JP, Van Belle G, Berg L (1991) The consortium to establish a registry for Alzheimer’s Disease (CERAD). Part II. Standardization of the neuropathologic assessment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 41:479–486
Roduit R, Morin J, Masse F, Segall L, Roche E, Newgard CB, Assimacopoulos-Jeannet F, Prentki M (2000) Glucose down-regulates the expression of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha gene in the pancreatic beta-cell. J Biol Chem 275:35799–35806
Sandhu MS, Heude B, Young EH, Luben R, Luan J, Khaw KT, Todd J, Wareham NJ (2005) INS VNTR class genotype and indexes of body size and obesity: population-based studies of 7,999 middle-aged men and women. Diabetes 54:2812–2815
Shalev A, Siegrist-Kaiser CA, Yen PM, Wahli W, Burger AG, Chin WW, Meier CA (1996) The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha is a phosphoprotein: regulation by insulin. Endocrinology 137:4499–4502
Swaab DF, Lucassen PJ, Salehi A, Scherder EJ, van Someren EJ, Verwer RW (1998) Reduced neuronal activity and reactivation in Alzheimer’s disease. Prog Brain Res 117:343–377
Vafiadis P, Ounissi-Benkalha H, Palumbo M, Grabs R, Rousseau M, Goodyer CG, Polychronakos C (2001) Class III alleles of the variable number of tandem repeat insulin polymorphism associated with silencing of thymic insulin predispose to type 1 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:3705–3710
Vohl MC, Lepage P, Gaudet D, Brewer CG, Betard C, Perron P, Houde G, Cellier C, Faith JM, Despres JP, Morgan K, Hudson TJ (2000) Molecular scanning of the human PPARa gene: association of the L162V mutation with hyperapobetalipoproteinemia. J Lipid Res 41:945–952
Vu-Hong TA, Durand E, Deghmoun S, Boutin P, Meyre D, Chevenne D, Czernichow P, Froguel P, Levy-Marchal C (2006) The INS VNTR locus does not associate with smallness for gestational age (SGA) but interacts with SGA to increase insulin resistance in young adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91:2437–2440
Whitmer RA, Karter AJ, Yaffe K, Quesenberry CP Jr, Selby JV (2009) Hypoglycemic episodes and risk of dementia in older patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA 301:1565–1572
Zhu Y, Qi C, Korenberg JR, Chen XN, Noya D, Rao MS, Reddy JK (1995) Structural organization of mouse peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (mPPAR gamma) gene: alternative promoter use and different splicing yield two mPPAR gamma isoforms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:7921–7925
Acknowledgments
We are most grateful to the Moulton Charitable Foundation for a grant to fund the Epistasis Project, to all those who have provided support for the individual clinical studies and to the Alzheimer’s Research Trust. GKW was partly funded by the NIHR Biomedical Research Centre Programme, Oxford.
Conflict of interest
Professor Maier received research grants from the following companies, respectively, is member of the Advisory Boards or draws a fee for speech from: AstraZeneca, Bayer Vital, Böhringer-Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, General Electrics, Janssen-Cilag, Lundbeck, Merck, Merz, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi-Aventis, Schering. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kölsch, H., Lehmann, D.J., Ibrahim-Verbaas, C.A. et al. Interaction of insulin and PPAR-α genes in Alzheimer’s disease: the Epistasis Project. J Neural Transm 119, 473–479 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-011-0732-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-011-0732-4