Abstract
Background
The aim of this study was to provide an outcome and toxicity profile of salvage low-dose-rate iodine-125 (I-125) stereotactic brachytherapy (SBT) in patients with small, circumscribed malignant glioma recurrences.
Methods
Patients with malignant glioma recurrences consecutively undergoing salvage SBT from 2003 to 2011 were identified from our prospective tumor database. SBT was considered a potentially suitable treatment strategy for adult mostly multimodally pretreated patients (Karnofsky score of ≥ 70) with biopsy-proven, circumscribed, small (diameter ≤ 3.5 cm) recurrences. Exclusively temporary I-125 seeds were used (reference dose: 50 Gy, dose rate: < 15 cGy/h). Study endpoints were time-to-treatment failure (TTF) after SBT, postrecurrence survival (PRS), and toxicity. Survival was assessed with the Kaplan–Meier method. Adverse events were categorized according to the RTOG/EORTC classification. Prognostic factors were obtained from proportional hazards models.
Results
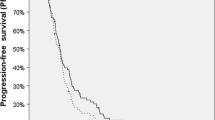
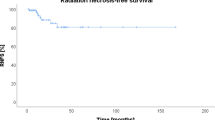
Sixty-eight patients (28 WHO grade III, 40 WHO grade IV gliomas) were included. Fifty-nine patients had previously received external beam radiation. Median TTF and PRS were 8.3 months and 13.4 months, respectively. TTF and PRS were longer for grade III gliomas than for glioblastomas (15.0 vs. 6.2 months and 28.1 vs. 9.3 months, respectively). Patients with grade III tumors were younger (p = 0.002). Favorable factors for TTF and PRS were age ≤ 50 years and a methylated O(6)-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT)-promoter. Alternative models including tumor grade instead of age reached a similar good fit. Three patients suffered from grade I, one from grade II, and two from grade IV toxicity.
Conclusions
Salvage SBT is feasible and safe even after previously performed external beam radiation. Favorable outcome measurements in particular for grade III recurrences deserve further prospective evaluation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barker FG, Chang SM, Gutin PH, Malec MK, McDermott MW, Prados MD, Wilson CB (1998) Survival and functional status after resection of recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. Neurosurgery 42:709–720
Bloch O, Han SJ, Cha S, Sun MZ, Aghi MK, McDermott MW, Berger MS, Parsa AT (2012) Impact of extent of resection for recurrent glioblastoma on overall survival: clinical article. J Neurosurg 117:1032–1038
Dirks P, Bernstein M, Muller PJ, Tucker WS (1993) The value of reoperation for recurrent glioblastoma. Can J Surg 36:271–275
Fabrini MG, Perrone F, De Franco L, Pasqualetti F, Grespi S, Vannozzi R, Cionini L (2009) Perioperative high-dose-rate brachytherapy in the treatment of recurrent malignant gliomas. Strahlenther Onkol 185:524–529
Kickingereder P, Hamisch C, Suchorska B, Galldiks N, Visser-Vandewalle V, Goldbrunner R, Kocher M, Treuer H, Voges J, Ruge MI (2014) Low-dose rate stereotactic iodine-125 brachytherapy for the treatment of inoperable primary and recurrent glioblastoma: single-center experience with 201 cases. J Neurooncol 120:615–623
Mandl ES, Dirven CMF, Buis DR, Postma TJ, Vandertop WP (2008) Repeated surgery for glioblastoma multiforme: only in combination with other salvage therapy. Surg Neurol 69:506–509
McDermott MW, Sneed PK, Gutin PH (1998) Interstitial brachytherapy for malignant brain tumors. Semin Surg Oncol 14:79–87
Niyazi M, Siefert A, Schwarz SB, Ganswindt U, Kreth FW, Tonn JC, Belka C (2011) Therapeutic options for recurrent malignant glioma. Radiother Oncol 98:1–14
Park JK, Hodges T, Arko L, Shen M, Dello Iacono D, McNabb A, Olsen Bailey N, Kreisl TN, Iwamoto FM, Sul J, Auh S, Park GE, Fine HA, Black PM (2010) Scale to predict survival after surgery for recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. J Clin Oncol 28:3838–3843
Pinsker M, Lumenta C (2001) Experiences with reoperation on recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. Zentralbl Neurochir 62:43–47
Ryken TC, Kalkanis SN, Buatti JM, Olson JJ, AANS/CNS Joint Guidelines Committee (2014) The role of cytoreductive surgery in the management of progressive glioblastoma: a systematic review and evidence-based clinical practice guideline. J Neurooncol 118:479–488
Scharfen CO, Sneed PK, Wara WM, Larson DA, Phillips TL, Prados MD, Weaver KA, Malec M, Acord P, Lamborn KR, Lamb SA, Brigid H, Gutin PH (1992) High activity iodine-125 interstitial implant for gliomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 24:583–591
Schwarz SB, Thon N, Nikolajek K, Niyazi M, Tonn JC, Belka C, Kreth FW (2012) Iodine-125 brachytherapy for brain tumours—a review. Radiat Oncol 7:30
Shrieve DC, Alexander E 3rd, Wen PY, Fine HA, Kooy HM, Black PM, Loeffler JS (1995) Comparison of stereotactic radiosurgery and brachytherapy in the treatment of recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. Neurosurgery 36:275–282
Sneed PK, McDermott MW, Gutin PH (1997) Interstitial brachytherapy for brain tumors. Semin Surg Oncol 13:157–166
Weller M, van den Bent M, Hopkins K, Tonn JC, Stupp R, Falini A, Cohen-Jonathan-Moyal E, Frappaz D, Henriksson R, Balana C, Chinot O, Ram Z, Reifenberger G, Soffietti R, Wick W, European Association for Neuro-Oncology (EANO) Task Force on Malignant Glioma (2014) EANO guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of anaplastic gliomas and glioblastoma. Lancet Oncol 15:395–403
Hervey-Jumper SL, Berger MS (2014) Reoperation for recurrent high-grade glioma: a current perspective of the literature. Neurosurg 75:491–499
Oppenlander ME, Wolf AB, Snyder LA, Bina R, Wilson JR, Coons SW, Ashby LS, Brachman D, Nakaji P, Porter RW, Smith KA, Spetzler RF, Sanai N (2014) An extent of resection threshold for recurrent glioblastoma and its risk for neurological morbidity. J Neurosurg 120:846–853
Niyazi M, Sohn M, Schwarz SB, Lang P, Belka C, Ganswindt U (2012) Radiation treatment parameters for re-irradiation of malignant glioma. Strahlenther Onkol 188:328–333
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW, Kleihues P (2007) The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol 114:97–109
Grasbon-Frodl EM, Kreth FW, Ruiter M, Schnell M, Bise O, Felsberg J, Reifenberger G, Tonn JC, Kretzschmar HA (2007) Intratumoral homogeneity of MGMT promoter hypermethylation as demonstrated in serial stereotactic specimens from anaplastic astrocytomas and glioblastomas. Int J Cancer 121:2458–2464
Thon N, Eigenbrod S, Grasbon-Frodl EM, Ruiter M, Mehrkens JH, Kreth S, Tonn JC, Kretzschmar HA, Kreth FW (2009) Novel molecular stereotactic biopsy procedures reveal intratumoral homogeneity of loss of heterozygosity of 1p/19q and TP53 mutations in World Health Organization grade II gliomas. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 68:1219–1228
Thon N, Eigenbrod S, Kreth S, Lutz J, Tonn JC, Kretzschmar H, Peraud A, Kreth FW (2012) IDH1 mutations in grade II astrocytomas are associated with unfavorable progression-free survival and prolonged postrecurrence survival. Cancer 118:452–460
Kreth FW, Thon N, Siefert A, Tonn JC (2010) The place of interstitial brachytherapy and radiosurgery for low-grade gliomas. Adv Tech Stand Neurosurg 35:183–212
la Fougere C, Suchorska B, Bartenstein P, Kreth FW, Tonn JC (2011) Molecular imaging of gliomas with PET: opportunities and limitations. Neuro Oncol 13:806–819
Mehrkens JH, Popperl G, Rachinger W, Herms J, Seelos K, Tatsch K, Tonn JC, Kreth FW (2008) The positive predictive value of O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine (FET) PET in the diagnosis of a glioma recurrence after multimodal treatment. J Neurooncol 88:27–35
Niyazi M, Schnell O, Suchorska B, Schwarz SB, Ganswindt U, Geisler J, Bartenstein P, Kreth FW, Tonn JC, Eigenbrod S, Belka C, la Fougère C (2012) FET-PET assessed recurrence pattern after radio-chemotherapy in newly diagnosed patients with glioblastoma is influenced by MGMT methylation status. Radiother Oncol 104:78–82
Niyazi M, Geisler J, Siefert A, Schwarz SB, Ganswindt U, Garny S, Schnell O, Suchorska B, Kreth FW, Tonn JC, Bartenstein P, la Fougère C, Belka C (2011) FET-PET for malignant glioma treatment planning. Radiother Oncol 99:44–48
Macdonald DR, Cascino TL, Schold SC Jr, Cairncross JG (1990) Response criteria for phase OII studies of supratentorial malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol 8:1277–1280
Jansen NL, Suchorska B, Schwarz SB, Eigenbrod S, Lutz J, Graute V, Bartenstein P, Belka C, Kreth FW, la Fougère C (2013) [18F]fluoroethyltyrosine-positron emission tomography-based therapy monitoring after stereotactic iodine-125 brachytherapy in patients with recurrent high-grade glioma. Mol Imaging 12:137–147
Felsberg J, Thon N, Eigenbrod S, Hentschel B, Sabel MC, Westphal M, Schackert G, Kreth FW, Pietsch T, Löffler M, Weller M, Reifenberger G, Tonn JC, German Glioma Network (2011) Promoter methylation and expression of MGMT and the DNA mismatch repair genes MLH1, MSH2, MSH6 and PMS2 in paired primary and recurrent glioblastomas. Int J Cancer 129:659–670
Stupp R, Tonn JC, Brada M, Pentheroudakis G, Group EGW (2010) High-grade malignant glioma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 21(Suppl 5):v190–v193
Weller M, Tabatabai G, Kästner B, Felsberg J, Steinbach JP, Wick A, Schnell O, Hau P, Herrlinger U, Sabel MC, Wirsching HG, Ketter R, Bähr O, Platten M, Tonn JC, Schlegel U, Marosi C, Goldbrunner R, Stupp R, Homicsko K, Pichler J, Nikkhah G, Meixensberger J, Vajkoczy P, Kollias S, Hüsing J, Reifenberger G, Wick W, DIRECTOR Study Group (2015) MGMT Promoter Methylation Is a Strong Prognostic Biomarker for Benefit from Dose-Intensified Temozolomide Rechallenge in Progressive Glioblastoma: The DIRECTOR Trial. Clin Cancer Res 21:2057–2064
Gutin PH, Prados MD, Phillips TL, Wara WM, Larson DA, Leibel SA, Sneed PK, Levin VA, Weaver KA, Silver P, Lamborn K, Lamb SA, Ham B (1991) External irradiation followed by an interstitial high activity iodine-125 implant "boost" in the initial treatment of malignant gliomas: NCOG study 6G-82-2. Int J Radiat Oncol, Biol, Phys 21:601–606
Laperriere NJ, Leung PM, McKenzie S, Milosevic M, Wong S, Glen J, Pintilie M, Bernstein M (1998) Randomized study of brachytherapy in the initial management of patients with malignant astrocytoma. Int J Radiat Oncol, Biol, Phys 41:1005–1011
Conflict of interest
All authors certify that they have NO affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest (such as honoraria; educational grants; participation in speakers’ bureaus; membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or other equity interest; and expert testimony or patent-licensing arrangements), or non-financial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Comment
Stereotactic brachytherapy of intracranial and paracranial tumors is almost extinct in European neuro-oncological services for two obvious reasons: (a) highly dedicated microneurosurgery and (b) stereotactic radiotherapy from extracranial sources, such as Gamma Knife, rotating or robotic (CyberKnife) linear accelerator, and proton beam facilities. In the early 1990s, this reviewer implanted permanent or temporary I-125 seeds in about 300 globoid or ellipsoid tumors, including meningiomas (1), vestibular schwannomas, craniopharyngiomas, pilocytic astrocytomas, ependymomas and metastases, and also diffuse grade II gliomas.
From their extensive neuro-oncological service, the authors were able to extract small “circumscribed” recurrences of 28 grade III and 40 grade IV gliomas for stereotactic low-dose-rate brachytherapy (SBT) with temporary I-125 seeds. They conclude that favorable results for grade III gliomas after salvage SBT deserve further prospective evaluation.
I am not so optimistic. In our population-based and unselected neuro-oncological service, supported by CyberKnife, it is difficult to find cases of recurrent grade III or IV gliomas that—in our opinion—would be treatable with SBT. This is because most recurrences are not globoid or ellipsoid but highly irregular in shape, diffuse and multiple. The present SBT technology allows implantation of I-125 seeds into one to a few target points, and it is very difficult or impossible to create a dose plan that would cover irregular or multiple volumes of recurrent gliomas.
However, the authors are to be congratulated for their effort to keep alive this fascinating mode of stereotactic radiotherapy. It is to be hoped that novel technologies are developed to support stereotactic brachytherapy in neuro-oncology.
Juha E. Jääskeläinen
Kuopio, Finland
1. Vuorinen V, Heikkonen J, Brander A, Setälä K, Sane T, Randell T, Paetau A, Pohjola J, Mäntylä M, Jääskeläinen J. (1996) Interstitial radiotherapy of 25 parasellar/clival meningiomas and 19 meningiomas in the elderly. Analysis of short-term tolerance and responses. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 138(5):495-508.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schwartz, C., Romagna, A., Thon, N. et al. Outcome and toxicity profile of salvage low-dose-rate iodine-125 stereotactic brachytherapy in recurrent high-grade gliomas. Acta Neurochir 157, 1757–1764 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-015-2550-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-015-2550-1