Abstract
Background
To study the integrity of white matter, we investigated the correlation between the changes in neuroradiological and morphological parameters in an animal model of acute obstructive hydrocephalus.
Methods
Hydrocephalus was induced in New Zealand rabbits (n = 10) by stereotactic injection of kaolin into the lateral ventricles. Control animals received saline in place of kaolin (n = 10). The progression of hydrocephalus was assessed using magnetic resonance imaging. Regional fractional anisotropy (FA) and the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) were measured in several white matter regions before and after the infusion of kaolin. Morphology of myelinated nerve fibers as well as of the blood–brain barrier were studied with the help of transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and light microscopy.
Results
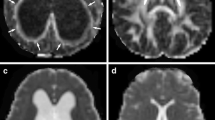
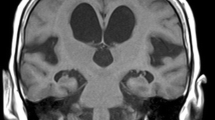
Compared with control animals, kaolin injection into the ventricles resulted in a dramatic increase in ventricular volume with compression of basal cisterns, brain shift and periventricular edema (as observed on magnetic resonance imaging [MRI]). The values of ADC in the periventricular and periaqueductal areas significantly increased in the experimental group (P < 0.05). FA decreased by a factor of 2 in the zones of periventricular, periaqueductal white matter and corpus collosum. Histological analysis demonstrated the impairment of the white matter and necrobiotic changes in the cortex. Microsctructural alterations of the myelin fibers were further proved with the help of TEM. Blood–brain barrier ultrastructure assessment showed the loss of its integrity.
Conclusions
The study demonstrated the correlation of the neuroradiological parameters with morphological changes. The abnormality of the FA and ADC parameters in the obstructive hydrocephalus represents a significant implication for the diagnostics and management of hydrocephalus in patients.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bloch O, Auguste KI, Manley GT, Verkman AS (2006) Accelerated progression of kaolin-induced hydrocephalus in aquaporin-4-deficient mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:1527–1537
Braun KP, de Graaf RA, Vandertop WP, Gooskens RH, Tulleken KA, Nicolay K (1998) In vivo 1H MR spectroscopic imaging and diffusion weighted MRI in experimental hydrocephalus. Magn Reson Med 40:832–839
Braun KP, Dijkhuizen RM, de Graaf RA, Nicolay K, Vandertop WP, Gooskens RH, Tulleken KA (1997) Cerebral ischemia and white matter edema in experimental hydrocephalus: a combined in vivo MRI and MRS study. Brain Res 757:295–298
Braun KP, van Eijsden P, Vandertop WP, de Graaf RA, Gooskens RH, Tulleken KA, Nikolay K (1999) Cerebral metabolism in experimental hydrocephalus: an in vivo 1H and 31P magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. J Neurosurg 91:660–668
Braun KP, Vandertop WP, Gooskens RH, Tulleken KA, Nicolay K (2000) NMR spectroscopic evaluation of cerebral metabolism in hydrocephalus: a review. Neurol Res 22:51–64
Castejón OJ (2009) Blood–brain barrier ultrastructural alterations in human congenital hydrocephalus and Arnold-Chiari malformation. Folia Neuropathol 47:11–19
Cauley KA, Cataltepe O (2014) Axial diffusivity of the corona radiata correlated with ventricular size in adult hydrocephalus. AJR Am J Roentgenol 203:170–179
Cherian S, Whitelaw A, Thoresen M, Love S (2004) The pathogenesis of neonatal post-hemorrhagic hydrocephalus. Brain Pathol 14:305–311
Chua CO, Chahboune H, Braun A, Dummula K, Chua CE, Yu J, Ungvari Z, Sherbany AA, Hyder F, Ballabh P (2009) Consequences of intraventricular hemorrhage in a rabbit pup model. Stroke 40:3369–3377
Collins P (1979) Experimental obstructive hydrocephalus in the rat: a scanning electron microscopic study. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 5:457–468
De Lahunta A (1983) Veterinary neuroanatomy and clinical neurology, 2nd edn. WB Saunders, Philadelphia
Del Bigio MR, Kanfer JN, Zhang YW (1997) Myelination delay in the cerebral white matter of immature rats with kaolin-induced hydrocephalus is reversible. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 56:1053–1066
Del Bigio MR, Khan OH, da Silva LL, Juliet PA (2012) Cerebral white matter oxidation and nitrosylation in young rodents with kaolin-induced hydrocephalus. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 71:274–288
Del Bigio MR, Slobodian I, Schellenberg AE, Buist RJ, Kemp-Buors TL (2011) Magnetic resonance imaging indicators of blood–brain barrier and brain water changes in young rats with kaolin-induced hydrocephalus. Fluids Barriers CNS 8:22
Edvinsson L, West KA (1971) The time-course of intracranial hypertension as recorded in conscious rabbits after treatment with different amounts of intracisternally injected kaolin. Acta Neurol Scand 47:439–450
Eskandari R, Abdullah O, Mason C, Lloyd KE, Oeschle AN, McAllister JP 2nd (2014) Differential vulnerability of white matter structures to experimental infantile hydrocephalus detected by diffusion tensor imaging. Childs Nerv Syst 30:1651–1661
Fishman RA (1992) Cerebrospinal fluid in diseases of the nervous system. W.B. Saunders, Philadelphia
Haworth CS, Sobieski MW, Scheld WM, Park TS (1990) Staphylococcus aureus ventriculitis treated with single-dose intraventricular vancomycin or daptomycin (LY146032): bacterial and antibiotic kinetics in hydrocephalic rabbits. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 34:245–251
Hoza D, Vlasák A, Hořínek D, Sameš M, Alfieri A (2014) DTI-MRI biomarkers in the search for normal pressure hydrocephalus aetiology: a review. Neurosurg Rev. doi:10.1007/s10143-014-0584-0
Ishii K, Hashimoto M, Hayashida K, Hashikawa K, Chang CC, Nakagawara J, Nakayama T, Mori S, Sakakibara R (2011) A multicenter brain perfusion SPECT study evaluating idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus on neurological improvement. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 32:1–10
Ivkovic M, Liu B, Ahmed F, Moore D, Huang C, Raj A, Kovanlikaya I, Heier L, Relkin N (2013) Differential diagnosis of normal pressure hydrocephalus by MRI mean diffusivity histogram analysis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 34:1168–1174
Johnson MJ, Ayzman I, Wood AS, Tkach JA, Klauschie J, Skarupa DJ, McAllister JP, Luciano MG (1999) Development and characterization of an adult model of obstructive hydrocephalus. J Neurosci Methods 91:55–65
Johnston MG, Del Bigio MR, Drake JM, Armstrong D, Di Curzio DL, Bertrand J (2013) Pre- and post-shunting observations in adult sheep with kaolin-induced hydrocephalus. Fluids Barriers CNS 10:24
Klarica M, Oresković D, Bozić B, Vukić M, Butković V, Bulat M (2009) New experimental model of acute aqueductal blockage in cats: effects on cerebrospinal fluid pressure and the size of brain ventricles. Neuroscience 158:1397–1405
Kobayashi S, Kato K, Rodríguez Guerrero A, Baba H, Yoshizawa H (2012) Experimental syringohydromyelia induced by adhesive arachnoiditis in the rabbit: changes in the blood-spinal cord barrier, neuroinflammatory foci, and syrinx formation. J Neurotrauma 29:1803–1816
Kondziella D, Eyjolfsson EM, Saether O, Sonnewald U, Risa O (2009) Gray matter metabolism in acute and chronic hydrocephalus. Neuroscience 159:570–577
Kondziella D, Sonnewald U, Tullberg M, Wikkelso C (2008) Brain metabolism in adult chronic hydrocephalus. J Neurochem 106:1515–1524
Kulkarni AV, Riva-Cambrin J, Browd SR, Drake JM, Holubkov R, Kestle JR, Limbrick DD, Rozzelle CJ, Simon TD, Tamber MS, Wellons JC 3rd, Whitehead WE, Hydrocephalus Clinical Research Network (2014) Endoscopic third ventriculostomy and choroid plexus cauterization in infants with hydrocephalus: a retrospective Hydrocephalus Clinical Research Network study. J Neurosurg Pediatr 14:224–229
Kulkarni AV, Riva-Cambrin J, Butler J, Browd SR, Drake JM, Holubkov R, Kestle JR, Limbrick DD, Simon TD, Tamber MS, Wellons JC 3rd, Whitehead WE, Hydrocephalus Clinical Research Network (2013) Outcomes of CSF shunting in children: comparison of Hydrocephalus Clinical Research Network cohort with historical controls: clinical article. J Neurosurg Pediatr 12:334–338
Kurt G, Cemil B, Borcek AO, Borcek P, Akyurek N, Sepici A, Ceviker N (2010) Infliximab administration reduces neuronal apoptosis on the optic pathways in a rabbit hydrocephalus model: a preliminary report. Br J Neurosurg 24:275–279
Leliefeld PH, Gooskens RH, Braun KP, Ramos LM, Uiterwaal CS, Regli LP, Tulleken CA, Kappelle LJ, Hanlo PW (2009) Longitudinal diffusion-weighted imaging in infants with hydrocephalus: decrease in tissue water diffusion after cerebrospinal fluid diversion. J Neurosurg Pediatr 4:56–63
Leliefeld PH, Gooskens RH, Vincken KL, Ramos LM, van der Grond J, Tulleken CA, Kappelle LJ, Hanlo PW (2008) Magnetic resonance imaging for quantitative flow measurement in infants with hydrocephalus: a prospective study. J Neurosurg Pediatr 2:163–170
Lu Y, Qian L, Zhang Q, Chen B, Gui L, Huang D, Cheng G, Chen L (2013) Palmitateinduces apoptosis in mouse aortic endothelial cells and endothelial dysfunction in mice fed high-calorie and high-cholesterol diets. Life Sci 92:1165–1173
Massicotte EM, Buist R, Del Bigio MR (2000) Altered diffusion and perfusion in hydrocephalic rat brain: a magnetic resonance imaging analysis. J Neurosurg 92:442–447
Reddy GK, Bollam P, Caldito G (2014) Long-term outcomes of ventriculoperitoneal shunt surgery in patients with hydrocephalus. World Neurosurg 81:404–410
Scheel M, Diekhoff T, Sprung C, Hoffmann KT (2012) Diffusion tensor imaging in hydrocephalus—findings before and after shunt surgery. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 154:1699–1706
Slobodian I, Krassioukov-Enns D, Del Bigio MR (2007) Protein and synthetic polymer injection for induction of obstructive hydrocephalus in rats. Cerebrospinal Fluid Res 4:9
Tarnaris A, Toma AK, Pullen E, Chapman MD, Petzold A, Cipolotti L, Kitchen ND, Keir G, Lemieux L, Watkins LD (2011) Cognitive, biochemical, and imaging profile of patients suffering from idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Alzheimers Dement 7:501–508
Torvik A, Stenwig AE, Finseth I (1981) The pathology of experimental obstructive hydrocephalus. A scanning electron microscopic study. Acta Neuropathol 54:143–147
Tully HM, Dobyns WB (2014) Infantile hydrocephalus: a review of epidemiology, classification and causes. Eur J Med Genet 57:359–368
Ueno M, Tomita S, Nakagawa T, Ueki M, Iwanaga Y, Ono J, Onodera M, Huang CL, Kanenishi K, Shimada A, Maekawa N, Sakamoto H (2006) Effects of aging and HIF-1alpha deficiency on permeability of hippocampal vessels. Microsc Res Tech 69:29–35
Vullo T, Manzo R, Gomez DG, Deck MD, Cahill PT (1998) A canine model of acute hydrocephalus with MR correlation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1123–1125
Weller RO, Mitchell J, Griffin RL, Gardner MJ (1978) The effects of hydrocephalus upon the developing brain. Histological and quantitative studies of the ependyma and subependyma in hydrocephalic rats. J Neurol Sci 36:383–402
Wen YD, Wang H, Kho SH, Rinkiko S, Sheng X, Shen HM, Zhu YZ (2013) Hydrogen sulfide protects HUVECs against hydrogen peroxide induced mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress. PLoS One 8:e53147
Yuan W, McAllister JP 2nd, Lindquist DM, Gill N, Holland SK, Henkel D, Rajagopal A, Mangano FT (2012) Diffusion tensor imaging of white matter injury in a rat model of infantile hydrocephalus. Childs Nerv Syst 28:47–54
Ziegelitz D, Starck G, Kristiansen D, Jakobsson M, Hultenmo M, Mikkelsen IK, Hellström P, Tullberg M, Wikkelsø C (2014) Cerebral perfusion measured by dynamic susceptibility contrast MRI is reduced in patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. J Magn Reson Imaging 39:1533–1542
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Olga G. Genbach, Nelly V. Koroleva, Dmitriy N. Suslov, Oleg V. Galibin, Tatiana V. Zakoldaeva, Irina V. Kononova, Yulia E. Shevchuk, Oleg A. Don for assistance in animal experiments.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, nos. 140800614 and 130401299.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Comment
This is a well-written and illustrated study investigating the correlation between the changes of neuroradiological and morphological parameters in an experimental model of acute obstructive hydrocephalus. It is clear that conventional MRI sequences provide accurate data to help the diagnosis of acute and chronic hydrocephalus. Nonetheless, the use of diffusion sequences demonstrated that values of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) in the periventricular and periaqueductal areas were significantly increased and fractional anisotropy was decreased in the zones of periventricular, periaqueductal white matter and corpus callosum. These features could be attributed to the integrity loss of the blood–brain barrier. Histological analysis confirms this hypothesis and results presented here by the authors are in accordance with previously published observations of ultrastructural changes in blood–brain barrier in patients with congenital hydrocephalus. Together, the results of this study suggest that restoration of blood–brain barrier permeability may play a role in some stage of the treatment of hydrocephalus. Further studies are warranted.
Alfredo Conti
Messina, Italy
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shevtsov, M.A., Senkevich, K.A., Kim, A.V. et al. Changes of fractional anisotropy (FA) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) in the model of experimental acute hydrocephalus in rabbits. Acta Neurochir 157, 689–698 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-014-2339-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-014-2339-7