Abstract
Background
Intraoperative ultrasound for intracranial neurosurgery was largely abandoned in the 1980s due to poor image resolution. Despite many technological advances in ultrasound since then, the use of this imaging modality in contemporary practice remains limited. Our aim was to evaluate the utility of modern intraoperative ultrasound in the resection of a wide variety of intracranial pathologies.
Methods
A total of 105 patients who underwent intracranial lesion resection in a contiguous fashion were prospectively included in the study. Ultrasound images acquired intraoperatively were used to stratify lesions into one of four grades (grades 0–3) on the basis of their ultrasonic echogenicity and border visibility.
Results
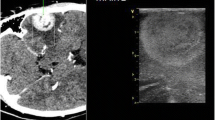
Forty-two out of 105 lesions (40 %) were clearly identifiable and had a clear border with normal tissue (grade 3). Fifty-five of 105 lesions (52 %) were clearly identifiable but had no clear border with normal tissue (grade 2). Eight of 105 lesions (8 %) were difficult to identify and had no clear border with normal tissue (grade 1). None (0 %) of the lesions could not be identified (grade 0). High-grade gliomas, cerebral metastases, meningiomas, ependymomas, and haemangioblastomas all demonstrated a median ultrasonic visibility grade of 2 or greater. Low-grade astrocytomas and oligodendrogliomas demonstrated a median ultrasonic visibility grade of 2 or less.
Conclusion
Intraoperative ultrasound can be of tremendous benefit in allowing the surgeon to appraise the location, extent, and local environment of their target lesion, as well as to reduce the risk of preventable complications. We believe that our grading system will provide a useful adjunct to the neurosurgeon when deciding for which lesions intraoperative ultrasound would be useful.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballantine HT Jr, Bolt RH, Hueter TF, Ludwig GD (1950) On the detection of intracranial pathology by ultrasound. Science 112(2914):525–528
Claus EB, Horlacher A, Hsu L, Schwartz RB, Dello-Iacono D, Talos F, Jolesz FA, Black PM (2005) Survival rates in patients with low-grade glioma after intraoperative magnetic resonance image guidance. Cancer 103:1227–1233
Gerganov VM, Samii A, Giordano M, Samii M, Fahlbusch R (2011) Two dimensional high-end ultrasound imaging compared to intraoperative MRI during resection of low grade gliomas. J Clin Neurosci 18:669–673
Goren O, Monteith SJ, Hadani M, Bakon M, Harnof S (2013) Modern intraoperative imaging modalities for the vascular neurosurgeon treating intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurosurg Focus 34(5):E2
Ivanov M, Wilkins S, Poeata I, Brodbelt A (2010) Intraoperative ultrasound in neurosurgery - a practical guide. Br J Neurosurg 24(5):510–517
Rygh OM, Selbekk T, Torp SH, Lydersen S, Hernes TA, Unsgaard G (2008) Comparison of navigated 3D ultrasound findings with histopathology in subsequent phases of glioblastoma resection. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 150(10):1033–1041
Scoccianti S, Magrini SM, Ricardi U, Detti B, Buglione M, Sotti G, Krengli M, Maluta S, Parisi S, Bertoni F, Mantovani C, Tombolini V, De Renzis C, Lioce M, Fatigante L, Fusco V, Muto P, Berti F, Rubino G, Cipressi S, Fariselli L, Lupattelli M, Santoni R, Pirtoli L, Biti G (2010) Patterns of care and survival in a retrospective analysis of 1059 patients with glioblastoma multiforme treated between 2002 and 2007: a multicentre study by the Central Nervous System Study Group of Airo. Neurosurgery 67(2):446–458
Senft C, Bink A, Franz K, Vatter H, Gasser T, Seifert V (2011) Intraoperative MRI guidance and extent of resection in glioma surgery: a randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Oncol 12(11):997–1003
Smith JS, Chang EF, Lamborn KR, Chang SM, Prados MD, Cha S, Tihan T, Vandenberg S, McDermott MW, Berger MS (2008) Role of extent of resection in the long-term outcome of low-grade hemispheric gliomas. J Clin Oncol 26:1338–1345
Solheim O, Selbekk T, Jakola AS, Unsgård G (2010) Ultrasound-guided operations in unselected high grade gliomas—overall results, impact of image quality and patient selection. Acta Neurochir 152:1873–1886
Solheim O, Selbekk T, Lindseth F, Unsgard G (2009) Navigated resection of giant intracranial meningiomas based on intraoperative 3D ultrasound. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 151:1143–1151
Stummer W, Pichlmeier U, Meinel T, Wiestler OD, Zanella F, Reulen HJ; ALA-Glioma Study Group (2006) Fluorescence-guided surgery with 5-aminolevulinic acid for resection of malignant glioma: a randomised controlled multicentre phase III trial. Lancet Oncol 7:392–401
Tang H, Sun H, Xie L, Tang Q, Gong Y, Mao Y, Xie Q, Zheng M, Wang D, Zhu H, Zhu J, Feng X, Yao Z, Chen X, Zhou L (2013) Intraoperative ultrasound assistance in resection of intracranial meningiomas. Chin J Cancer Res 25:339–345
Unsgaard G, Rygh OM, Selbekk T, Müller TB, Kolstad F, Lindseth F, Hernes TA (2006) Intra-operative 3D ultrasound in neurosurgery. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 148(3):235–253
Wang J, Liu X, Hou WH, Dong G, Wei Z, Zhou H, Duan YY (2008) The relationship between intra-operative ultrasonography and pathological grade in cerebral glioma. J Int Med Res 36:1426–1434
Wirtz CR, Albert FK, Schwaderer M, Heuer C, Staubert A, Tronnier VM, Knauth M, Kunze S (2000) The benefit of neuronavigation for neurosurgery analysed by its impact on glioblastoma surgery. Neurol Res 22(4):354–360
Xiao F, Tseng MY, Teng LJ, Tseng HM, Tsai JC (2005) Brain abscess: clinical experience and analysis of prognostic factors. Surg Neurol 63(5):442–450
Acknowledgements
The lead author would like to express his great appreciation to Mr. Andrew Brodbelt (Consultant Neurosurgeon at the Walton Centre for Neurology and Neurosurgery, Liverpool, UK) for his valuable support with the data collection and for his enthusiastic encouragement of this research.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
*This study has not been presented at a conference
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mair, R., Heald, J., Poeata, I. et al. A practical grading system of ultrasonographic visibility for intracerebral lesions. Acta Neurochir 155, 2293–2298 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-013-1868-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-013-1868-9