Abstract
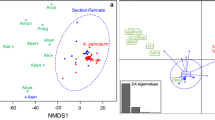
The genealogical and geographic structure of variation in spikelet morphology was analyzed for central Eurasian wild wheat Aegilops tauschii Coss. using a diverse array of 203 sample accessions that represented the entire species range. In this sample set, two subspecies were identified on the basis of sensu-stricto criteria: only the accessions having markedly moniliform spikes were assigned to Ae. tauschii Coss. subspecies strangulata (Eig) Tzvel., whereas those having mildly moniliform and cylindrical spikes to Ae. tauschii Coss. subspecies tauschii. In a graph of the first two axes from a principal component analysis based on nine spikelet traits, the plots of the two subspecies formed separate clusters, indicating that subspecies strangulata sens. str. is a practically usable taxon. Chloroplast-DNA-based genealogical analyses suggested that subspecies strangulata diverged from an ancestor that carried a specific chloroplast DNA type, whereas, after divergence, this subspecies became polyphyletic, likely through hybridization. Geographically, significant longitudinal and latitudinal clines were detected for spikelet size, with spikelets tending to be small in the eastern and southern regions. These results shed some light on the patterns of subspecies divergence and spikelet-shape diversification in the course of Ae. tauschii’s long-distance dispersal from the Transcaucasus to China.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghaei MJ, Mozafari J, Taleei AR, Naghavi MR, Omidi M (2008) Distribution and diversity of Aegilops tauschii in Iran. Genet Resour Crop Evol 55:341–349
Bandelt HJ, Forster P, Sykes BC, Richards MB (1995) Mitochondrial portraits of human populations using median networks. Genetics 141:743–753
Dudnikov A (2000) Multivariate analysis of genetic variation in Aegilops tauschii from the world germplasm collection. Genet Resour Crop Evol 47:185–190
Dudnikov A, Kawahara T (2006) Aegilops tauschii: genetic variation in Iran. Genet Resour Crop Evol 53:579–586
Dvorak J, Luo MC, Yang ZL, Zhang HB (1998) The structure of the Aegilops tauschii genepool and the evolution of hexaploid wheat. Theor Appl Genet 97:657–670
Eig A (1929) Monographisch-kritische Übersicht der Gattung Aegilops. Feddes Repertorium specierum novarum regni vegetabilis Beih 55:1–228
Felsenstein J (2005) PHYLIP (Phylogeny Inference Package) version 3.6. Distributed by the author. Department of Genome Sciences, University of Washington, Seattle
Gororo NN, Eagles HA, Eastwood RF, Nicolas ME, Flood RG (2002) Use of Triticum tauschii to improve yield of wheat in low-yielding environments. Euphytica 123:241–254
Hammer K (1978) Blütenökologische Merkmale und Reproduktionssystem von Aegilops tauschii Coss. (syn. Ae. squarrosa L.). Kulturpflanze 26:271–282
Hammer K (1980) Vorarbeiten zur monographischen Darstellung von Wildpflanzensortimenten: Aegilops L. Kulturpflanze 28:33–180
Huang S, Sirikhachornkit A, Su X, Faris J, Gill B, Haselkorn R, Gornicki P (2002) Genes encoding plastid acetyl-CoA carboxylase and 3-phosphoglycerate kinase of the Triticum/Aegilops complex and the evolutionary history of polyploid wheat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:8133–8138
Innes RL, Kerber ER (1994) Resistance to wheat leaf rust and stem rust in Triticum tauschii and inheritance in hexaploid wheat of resistance transferred from T. tauschii. Genome 37:813–822
Ishii T, Mori N, Ogihara Y (2001) Evaluation of allelic diversity at chloroplast microsatellite loci among common wheat and its ancestral species. Theor Appl Genet 103:896–904
Jaaska V (1981) Aspartate aminotransferase and alcohol dehydrogenase isoenzymes: intraspecific differentiation in Aegilops tauschii and the origin of the D genome polyploids in the wheat group. Pl Syst Evol 137:259–273
Kihara H (1944) Discovery of the DD-analyser, one of the ancestors of Triticum vulgare (abstr) (in Japanese). Agric Hortic 19:889–890
Kihara H, Yamashita K, Takaka M (1965) Morphological, physiological, genetical and cytological studies in Aegilops and Triticum collected from Pakistan, Afghanistan and Iran. In: Yamashita K (ed) Results of the Kyoto University Scientific Expedition to the Karakoram and Hindukush, 1955, vol I. Kyoto University, Kyoto, pp 1–118
Knaggs P, Ambrose MJ, Reader SM, Miller TE (2000) Morphological characterization and evaluation of the subdivision of Aegilops tauschii Coss. Wheat Inf Serv 91:15–19
Lagudah ES, Halloran GM (1988) Phylogenetic relationships of Triticum tauschii the D genome donor to hexaploid wheat. Theor Appl Genet 75:592–598
Lelley T, Stachel M, Grausgruber H, Vollmann J (2000) Analysis of relationships between Aegilops tauschii and the D genome of wheat utilizing microsatellites. Genome 43:661–668
Lubbers EL, Gill KS, Cox TS, Gill BS (1991) Variation of molecular markers among geographically diverse accessions of Triticum tauschii. Genome 34:354–361
Malik R, Michael Smith C, Brown-Guedira GL, Harvey TL, Gill BS (2003) Assessment of Aegilops tauschii for resistance to biotypes of wheat curl mite (Acari: Eriophyidae). J Econ Entomol 96:1329–1333
Matsuoka Y, Mori N, Kawahara T (2005) Genealogical use of chloroplast DNA variation for intraspecific studies of Aegilops tauschii Coss. Theor Appl Genet 111:265–271
Matsuoka Y, Takumi S, Kawahara T (2007) Natural variation for fertile triploid F1 hybrid formation in allohexaploid wheat speciation. Theor Appl Genet 115:509–518
Matsuoka Y, Takumi S, Kawahara T (2008a) Flowering time diversification and dispersal in central Eurasian wild wheat Aegilops tauschii (Poaceae): genealogical and ecological framework. PLoS One 3(9):e3138
Matsuoka Y, Aghaei MJ, Abbasi MR, Totiaei A, Mozafari J, Ohta S (2008b) Durum wheat cultivation associated with Aegilops tauschii in northern Iran. Genet Resour Crop Evol 55:861–868
McFadden ES, Sears ER (1944) The artificial synthesis of Triticum spelta (abstr). Rec Genet Soc Am 13:26–27
Nishikawa K, Furuta Y, Wada T (1980) Genetic studies on α-amylase isozymes in wheat. III. Intraspecific variation in Aegilops squarrosa and birthplace of hexaploid wheat. Jpn J Genet 55:325–336
Pestsova E, Korzun V, Gonchrov NP, Hammer K, Ganal MW, Röder MS (2000) Microsatellite analysis of Aegilops tauschii germplasm. Theor Appl Genet 101:100–106
Tabertlet P, Gielly L, Pautou G, Bouvet J (1991) Universal primers for amplification of three non-coding regions of chloroplast DNA. Plant Mol Biol 17:1105–1109
Tanaka M, Tsujimoto H (1991) Natural habitat of Aegilops squarrosa in Xinjiang Uygur, China. Wheat Inf Serv 73:33–35
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucl Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Van Slageren MW (1994) Wild Wheats: A Monograph of Aegilops L. and Amblyopyrum (Jaub. & Spach) Eig (Poaceae). Wageningen Agricultural University, Wageningen, pp 326–344
Yen C, Yang JL, Liu XD, Li LR (1983) The distribution of Aegilops tauschii Cosson in China and with reference to the origin of the Chinese common wheat. In: Sakamoto S (ed) Proceedings of 6th International Wheat Genetics Symposium, Kyoto, Japan, pp 55–58
Acknowledgments
We thank J. Valkoun (ICARDA), J. Konopka (ICARDA), H. Bockelman (USDA), A. Graner (IPK), L. Visser (CGN), and K. Kato (Okayama Univ.) for the Ae. tauschii accession seeds. This work was supported by a grant from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (Basic Research A, No. 17201045).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Y. Matsuoka and E. Nishioka have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matsuoka, Y., Nishioka, E., Kawahara, T. et al. Genealogical analysis of subspecies divergence and spikelet-shape diversification in central Eurasian wild wheat Aegilops tauschii Coss.. Plant Syst Evol 279, 233–244 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-009-0159-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-009-0159-7