Abstract
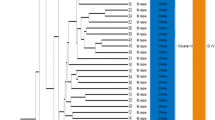
Phyllostachys pubescens is the most important economic bamboo species in China, which grows widely in the South of China. There are more than ten cultivars in this species but their genetic relationship still remains unknown. We used both amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) and inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) techniques to determine genetic similarity among ten cultivars of P. pubescens and two related species. Eight hundred and twenty seven bands, in which 495 are polymorphic, were detected using 15 pairs of AFLP primers whereas total 231 bands, in which 154 bands are polymorphic, were scored using 16 ISSR primers. Statistic analysis showed that the genetic similarity matrices obtained from these two sets of molecular markers had a significant correlation (R = 0.959, P = 0.013). The dendrogram generated with AFLP and ISSR markers could clearly genetically identify ten cultivars of P. pubescens that had high similarity with genetic distances ranging from 0.023 to 0.108, and could be divided into three groups based on their genetic variation and similarity. Our results suggest that these molecular markers are useful to genetically classify cultivars or varieties of a species, particularly a bamboo species.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AFLP:
-
Amplified fragment length polymorphism
- ISSR:
-
Inter-simple sequence repeat
- RFLP:
-
Restriction fragment length polymorphisms
- RAPD:
-
Random amplified polymorphic DNA
- CTAB:
-
Cetyl-trimethylammonium bromide
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- UPGMA:
-
Unweighted pair-group method with arithmetic means
References
Bao JS, Corke H, Sun M (2006) Analysis of genetic diversity and relationships in waxy rice (Oryza sativa L.) using AFLP and ISSR markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 53:323–330
Dice LR (1945) Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology 26:297–302
Ding YL (1998) The taxonomic study on Phyllostachys. PhD dissertation, Nanjing Forestry University, China
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
Friar E, Kochert G (1991) Bamboo germplasm screening with nuclear restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Theor Appl Genet 82:697–703
Friar E, Kochert G (1994) A study of genetic variation and evolution in Phyllostachys (Bambusoideae: Poaceae) using nuclear restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Theor Appl Genet 89:265–270
Geilis J, Everaert I, De Loose M (1997) Genetic variability and relationships in Phyllostachys using random amplified polymorphic DNA. In: Chapman GP (ed) The bamboos. Linnean Society Symposium, vol 19. Academic Press, London, pp 107–124
Geng BJ, Wang ZP (1996) Gramineae Bambusiodeae, Flora Reipublicae Popularis Sinicae, 9(1). Science Press, Beijing
He GH, Prakash C (2001) Evaluation of genetic relationship among botanical varieties of cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) using AFLP markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 48:347–352
Hodkison TR, Renvoize SA, Chongaile GN, Stapleton CMA, Chase MW (2000) A comparison of ITS nuclear rDNA sequence data and AFLP markers for phylogenetic studies in Phyllostachys (Bambusoideae, Poaceae). J Pl Res 113:259–269
Isagi Y, Shimada K, Kushima H, Tanaka N, Ishikawa T, Onodera H, Watanabe S (2004) Clonal structure and flowering traits of a bamboo [Phyllostachys pubescens (Mazel) Ohwi] stand grown from a simultaneous flowering as revealed by AFLP analysis. Molec Ecol 13:2017–2021
Lai CC, Hsiao JY (1997) Genetic variation of Phyllostachys pubescens (Bambusoideae, Poaceae) in Taiwan based on DNA polymorphisms. Bot Bull Acad Sin 38:145–152
Loh JP, Kiew R, Set O, Gan LH, Gan YY (2000) A study of genetic variation and relationships with the bamboo subtribe Bambusinae using amplified fragment length polymorphism. Ann Bot 85:607–612
Mantel NA (1967) The detection of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Cancer Res 27:209–220
Mueller UG, Wolfenbarger LL (1999) AFLP genotyping and fingerprinting. Trends Ecol Evol 14:389–394
Perez T, Albornoz J, Dominguez A (1998) An evaluation of RAPD fragment reproducibility and nature. Molec Ecol 7:1347–1358
Ramanayake SMSD, Meemaduma VN, Weerawardene TE (2007) Genetic diversity and relationship between nine species of bamboo in Sri Lanka, using random amplified polymorphic DNA. Pl Syst Evol 269:55–61
Reddy MP, Sarla N, Siddiq EA (2002) Inter simple sequence (ISSR) polymorphism and its application in plant breeding. Euphytica 128:9–17
Rohlf FJ (2000) Ntsys-pc. Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system. Version 2.10e. Applied Biostatics, New York
Saini N, Jain N, Jain S, Jain RK (2004) Assessment of genetic diversity with and among Basmati and non-Basmati rice varieties using AFLP, ISSR and SSR markers. Euphytica 140:133–146
Shi LH, Yang GY, Lin XC, Guo QR (2002) RAPD studies on the grade of infra-species of Phyllostachys edulis. J NA Univ (Nat Sci Ed) 26:65–68
Sun Y, Xia NH, Stapleton MA (2006) Relationships between Bambusa species (Poaceae, Bambusoideae) revealed by random amplified polymorphic DNA. Biochem Syst Ecol 34:417–423
Suyama Y, Obayashi K, Hayashi I (2000) Clonal structure in a dwarf bamboo (Sasa senanensis) population inferred from amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) fingerprints. Molec Ecol 9:901–906
Upadhyay A, Saboji MD, Reddy S, Deokar K, Karibasappa GS (2007) AFLP and SSR marker analysis of grape rootstocks in Indian grape germplasm. Sci Hortic 112:176–183
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, Van De Lee T, Hornes M, Frijters A, Pot J, Kuiper M, Zabeau M (1995) AFLP:A new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Wei Y (2005) RAPD analysis of thirty-six species Bamboo. Master dissertation. Fujian Normal University, China
Yang GY, Li ZR, Du TZ, Hu YB, Leng DJ, Zou WS (1997) A new cultivated variety of Moso bamboo. Acta Agric Univ Jiangxi 19:97–98
Zhang SF (2005) Study on the genetic diversity of Phyllostachys edulis. Master dissertation. Nanjing Forestry University, China
Zhang WP, Wendel JF, Clark LG (1997) Bamboo again! Inadvertend isolation of fungal rDNA sequences from Bamboos (Poaceae: Bambusoideae). Mol Phylogenet Evol 8:205–217
Zietkiwicz E, Rafalski A, Labuda D (1994) Genome fingerprinting by simple sequence repeat (SSR)-anchored polymerase chain reaction amplification. Genomics 20:176–183
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Xuerong Shi for critical reading of the manuscript, and Mr. Chang Ping Zhou for providing us with bamboo leaf samples. This study was supported by research grants from the Science and Technology Department of Zhejiang Province, China [grants #2004C12034 and #2005C12002–01].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, X.C., Ruan, X.S., Lou, Y.F. et al. Genetic similarity among cultivars of Phyllostachys pubescens . Plant Syst Evol 277, 67–73 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-008-0104-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-008-0104-1