Abstract.
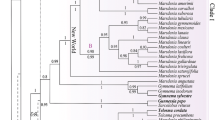
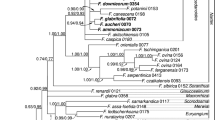
Parsimony analyses based on DNA sequence data of the plastid group II intron rps16 and the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) were performed in order to examine the relationship of the pantropical subfamily Alpinioideae in Zingiberaceae (Zingiberales). Special emphasis was given to the large genus Etlingera placed in the tribe Alpinieae. A total of 50 taxa were included in the analysis. The strict consensus tree obtained by combining all data (280 parsimony informative characters of ITS, rps16, and coded indels) is well resolved with strongly supported clades. The subfamily Alpinioideae (excluding Pommereschea and Rhynchanthus) is strongly supported as monophyletic. The basal part of the tree is unresolved but a clade containing the derived genera of Alpinieae (Geocharis, Amomum, Hornstedtia, and Etlingera) is strongly supported. The establishment of Etlingera as the inclusive name for Achasma, Geanthus, and Nicolaia is also strongly supported: Etlingera is monophyletic with Hornstedtia as sister group.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pedersen, L. Phylogenetic analysis of the subfamily Alpinioideae (Zingiberaceae), particularly Etlingera Giseke, based on nuclear and plastid DNA. Plant Syst. Evol. 245, 239–258 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-004-0126-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-004-0126-2