Abstract
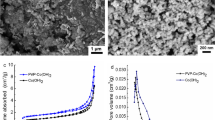
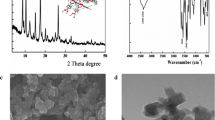
An amperometric nitrite sensor is reported based on a screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE) modified with copper(II)-benzene-1,4-dicarboxylate (Cu-BDC) frameworks and iron(III) oxide nanoparticles (Fe2O3 NPs). First, copper(I) oxide (Cu2O) nanocubes were synthesized, followed by a solvothermal reaction between Cu2O and H2BDC to form square plate-like Cu-BDC frameworks. Then, Fe2O3 NPs were electrodeposited on Cu-BDC frameworks using a potentiostatic method. The Fe2O3@Cu-BDC nanocomposite benefits from high conductivity and large active surface area, offering excellent electrocatalytic activity for nitrite oxidation. Under optimal amperometric conditions (0.55 V vs. Ag/AgCl), the sensor has a linear range of 1 to 2000 µM with a detection limit of 0.074 µM (S/N = 3) and sensitivity of 220.59 µA mM−1 cm−2. The sensor also provides good selectivity and reproducibility (RSD = 1.91%, n = 5). Furthermore, the sensor exhibits long-term stability, retaining 91.4% of its original current after 4 weeks of storage at room temperature. Finally, assessing nitrite in tap and mineral water samples revealed that the Fe2O3@Cu-BDC/SPCE has a promising prospect in amperometric nitrite detection.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
He B, Yan D (2019) Au/ERGO nanoparticles supported on Cu-based metal-organic framework as a novel sensor for sensitive determination of nitrite. Food Control 103:70–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2019.04.001
Li X, Ping J, Ying Y (2019) Recent developments in carbon nanomaterial-enabled electrochemical sensors for nitrite detection. TrAC - Trends Anal Chem 113:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.01.008
Li G, Xia Y, Tian Y et al (2019) Review—recent developments on graphene-based electrochemical sensors toward nitrite. J Electrochem Soc 166:B881–B895. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0171912jes
Mao Y, Bao Y, Dx H, Zhao B (2018) Research progress on nitrite electrochemical sensor. Chinese J Anal Chem 46:147–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2040(17)61066-1
World Health Organization (2011) Guidelines for drinking-water quality, fourth edition. http://www.who.int. Accessed 7 Dec 2020
EFSA (2017) Nitrites and nitrates added to food. In: Efsa Explain. Risk Assess. https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/corporate/pub/nitritesandnitrates170614. Accessed 10 May 2022
Abou-Melha KS (2020) Analytical chemistry optical chemosensor for spectrophotometric determination of nitrite in wastewater. ChemistrySelect 5:6216–6223. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.202001366
El hani O, Karrat A, Digua K, Amine A (2022) Development of a simplified spectrophotometric method for nitrite determination in water samples. Spectrochim Acta - Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 267:120574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2021.120574
Hatta M, Ruzicka J (Jarda), Measures CI (2020) The performance of a new linear light path flow cell is compared with a liquid core waveguide and the linear cell is used for spectrophotometric determination of nitrite in sea water at nanomolar concentrations. Talanta 219:121240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121240
Huang KJ, Wang H, Guo YH et al (2006) Spectrofluorimetric determination of trace nitrite in food products with a new fluorescent probe 1,3,5,7-tetramethyl-2,6-dicarbethoxy-8-(3′,4′-diaminophenyl)-difluoroboradiaza-s-indacene. Talanta 69:73–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2005.08.062
Gan L, Su Q, Chen Z, Yang X (2020) Exploration of pH-responsive carbon dots for detecting nitrite and ascorbic acid. Appl Surf Sci 530:147269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.147269
Zhang J, Yang J, Chen J et al (2022) A novel propylene glycol alginate gel based colorimetric tube for rapid detection of nitrite in pickled vegetables. Food Chem 373:131678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131678
Kodamatani H, Iwaya Y, Saga M et al (2017) Ultra-sensitive HPLC-photochemical reaction-luminol chemiluminescence method for the measurement of secondary amines after nitrosation. Anal Chim Acta 952:50–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2016.11.045
Arul P, Gowthaman NSK, John SA et al (2020) Ultrasonic assisted synthesis of size-controlled Cu-metal-organic framework decorated graphene oxide composite: sustainable electrocatalyst for the trace-level determination of nitrite in environmental water samples. ACS Omega 5:14242–14253. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.9b03829
Wang YC, Chen YC, Chuang WS et al (2020) Pore-confined silver nanoparticles in a porphyrinic metal-organic framework for electrochemical nitrite detection. ACS Appl Nano Mater 3:9440–9448. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.0c02052
Lei H, Zhu H, Sun S et al (2021) Synergistic integration of Au nanoparticles, Co-MOF and MWCNT as biosensors for sensitive detection of low-concentration nitrite. Electrochim Acta 365:137375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2020.137375
Liu L, Ma Q, Liu Z et al (2014) Detection of trace nitrite in waters using a QDs-based chemiluminescence analysis system. Anal Bioanal Chem 406:879–886. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-7490-0
Tajik S, Orooji Y, Karimi F et al (2021) High performance of screen-printed graphite electrode modified with Ni–Mo-MOF for voltammetric determination of amaranth. J Food Meas Charact 15:4617–4622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-021-01027-0
Beitollahi H, Shahsavari M, Sheikhshoaie I et al (2022) Amplified electrochemical sensor employing screen-printed electrode modified with Ni-ZIF-67 nanocomposite for high sensitive analysis of Sudan I in present bisphenol A. Food Chem Toxicol 161:112824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2022.112824
Yang Z, Zhong Y, Zhou X et al (2022) Metal-organic framework-based sensors for nitrite detection: a short review. J Food Meas Charact. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11694-021-01270-5
Duan J, Li Y, Pan Y et al (2019) Metal-organic framework nanosheets: an emerging family of multifunctional 2D materials. Coord Chem Rev 395:25–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2019.05.018
Chuang CH, Kung CW (2020) Metal–organic frameworks toward electrochemical sensors: challenges and opportunities. Electroanalysis 32:1885–1895. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.202060111
Song Y, Yang Y, Mo S et al (2022) Fast construction of (Fe2O3)x@Ni-MOF heterostructure nanosheets as highly active catalyst for water oxidation. J Alloys Compd 892:162149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162149
Sun X, Gao G, Yan D, Feng C (2017) Synthesis and electrochemical properties of Fe3O4@MOF core-shell microspheres as an anode for lithium ion battery application. Appl Surf Sci 405:52–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.01.247
Radhakrishnan S, Krishnamoorthy K, Sekar C et al (2014) A highly sensitive electrochemical sensor for nitrite detection based on Fe2O3 nanoparticles decorated reduced graphene oxide nanosheets. Appl Catal B Environ 148–149:22–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.10.044
Wang S, Liu M, He S et al (2018) Protonated carbon nitride induced hierarchically ordered Fe2O3/H–C3N4/rGO architecture with enhanced electrochemical sensing of nitrite. Sens Actuators B Chem 260:490–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.01.073
Zhao Z, Xia Z, Liu C et al (2017) Green synthesis of Pd/Fe3O4 composite based on polyDOPA functionalized reduced graphene oxide for electrochemical detection of nitrite in cured food. Electrochim Acta 256:146–154. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.09.185
Zhan G, Fan L, Zhao F et al (2019) Fabrication of ultrathin 2D Cu-BDC nanosheets and the derived integrated MOF nanocomposites. Adv Funct Mater 29:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201806720
Amali RKA, Lim HN, Ibrahim I et al (2022) Silver nanoparticles-loaded copper (II)-terephthalate framework nanocomposite as a screen-printed carbon electrode modifier for amperometric nitrate detection. J Electroanal Chem 918:116440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2022.116440
Li X, Zhou H, Qi F et al (2018) Three hidden talents in one framework: a terephthalic acid-coordinated cupric metal-organic framework with cascade cysteine oxidase- and peroxidase-mimicking activities and stimulus-responsive fluorescence for cysteine sensing. J Mater Chem B 6:6207–6211. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TB02167H
Wang Y, Cao W, Wang L et al (2018) Electrochemical determination of 2,4,6-trinitrophenol using a hybrid film composed of a copper-based metal organic framework and electroreduced graphene oxide. Microchim Acta 185:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2857-8
Arul P, Huang ST, Mani V, Hu YC (2021) Ultrasonic synthesis of bismuth-organic framework intercalated carbon nanofibers: a dual electrocatalyst for trace-level monitoring of nitro hazards. Electrochim Acta 381:138280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2021.138280
Domenech A, Garcia H, Domenech-Carbo MT, Llabres-i-Xamena F (2007) Electrochemistry of metal-organic frameworks: a description from the voltammetry of microparticles approach. J Phys Chem C 111:13701–13711. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp073458x
Kornii A, Lisnyak VV, Grishchenko L, Tananaiko O (2022) Synthesis and characterization of hybrid silica/Fe2O3-carbon nanoparticles films electrodeposited onto planar electrodes. Electrochim Acta 409:139938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2022.139938
Suma BP, Pandurangappa M (2020) Graphene oxide/copper terephthalate composite as a sensing platform for nitrite quantification and its application to environmental samples. J Solid State Electrochem 24:69–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-019-04454-8
Cassani MC, Castagnoli R, Gambassi F et al (2021) A Cu(II)-MOF based on a propargyl carbamate-functionalized isophthalate ligand as nitrite electrochemical sensor. Sensors 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21144922
Chen H, Yang T, Liu F, Li W (2019) Electrodeposition of gold nanoparticles on Cu-based metal-organic framework for the electrochemical detection of nitrite. Sens Actuators B Chem 286:401–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.10.036
Yuan B, Zhang J, Zhang R et al (2016) Cu-based metal-organic framework as a novel sensing platform for the enhanced electro-oxidation of nitrite. Sens Actuators B Chem 222:632–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.08.100
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS) FRGS/1/2021/STG05/UPM/01/1 awarded by the Ministry of Higher Education of Malaysia (MOHE). R. K. A. Amali thanks the Sri Lanka Council for Agricultural Research Policy (SLCARP) for a Ph.D. scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R.K.A.A.: formal analysis, methodology, investigation, data curation, writing — original draft, writing — review and editing. H.N.L.: conceptualization, supervision, writing — review and editing. I.I.: visualization, writing — review and editing. Z.Z.: supervision. S.A.A.A.: supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Amali, R.K.A., Lim, H.N., Ibrahim, I. et al. A copper-based metal–organic framework decorated with electrodeposited Fe2O3 nanoparticles for electrochemical nitrite sensing. Microchim Acta 189, 356 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05450-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05450-y