Abstract
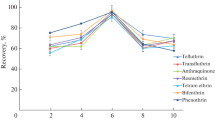
A sensitive and readily deployable analytical method has been reported for the simultaneous analysis of pirimicarb (PRM) and fenitrothion (FEN) pesticide residues in environmental water samples using fabric phase sorptive extraction (FPSE) followed by high-performance liquid chromatography combined with photodiode array (HPLC-PDA) detector. Both pesticides were successfully determined with a Luna omega C18 column under isocratic elution mode by means of acetonitrile and phosphate buffer (pH 3.0) as the mobile phase. The quantitative data for PRM and FEN were obtained at their maximum wavelengths of 310 nm and 268 nm, respectively. The calibration plots were linear in the range 10.00–750.00 ng mL−1 and 10.00–900.00 ng mL−1 with correlation coefficient of 0.9984 and 0.9992 for PRM and FEN, respectively. Major FPSE experimental variables were investigated in detail, such as contact time with the FPSE membrane, pH and electrolyte concentration, and the volume and type of desorption solvent. Under the optimized conditions, the developed method showed satisfactory reproducibility with relative standard deviations less than 2.5% and low limits of detection of 2.98 and 3.02 ng mL−1 for PRM and FEN, respectively. The combined procedure allows for enhancement factors ranging from 88 to 113, with pre-concentration values of 125 for both analytes. The chromatographic resolutions were approx. 12 for FEN (retention factor of 3.52) and PRM (retention factor of 6.09), respectively, with a selectivity factor of 1.73. Finally, the validated method was successfully applied to real environmental water samples for the determination of these pesticides.

Graphical abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yilmaz E, Soylak M (2016) Preparation and characterization of magnetic carboxylated nano diamonds for vortex-assisted magnetic solid-phase extraction of ziram in food and water samples. Talanta 158:152–158
Vazquez PP, Lozano A, Ucles S, Ramos MMG, Fernandez-Alba AR (2015) A sensitive and efficient method for routine pesticide multi residue analysis in bee pollen samples using gas and liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1426:161–173
Miao QC, Wang JM, Nie J, Wu HZ, Liu YP, Li ZG, Qian MR (2016) Magnetic dispersive solid-phase extraction based on a novel adsorbent for the detection of triazole pesticide residues in honey by HPLC-MS/MS. Anal Methods 8:5296–5303
Fukushima M, Katagi T (2006) Photodegradation of fenitrothion and parathion in tomato epicuticular waxes. J Agric Food Chem 54:474–479
Kandil MA, Abdallah IS, Abou-Yousef HM, Abdallah NA, Fouad EA (2017) Mechanism of resistance to pirimicarb in the cowpea aphid Aphis craccivora. Crop Prot 94:173–177
Bazmandegan-Shamili A, Dadfarnia S, Shabani AMH, Moghadam MR, Saeidi M (2018) MultiSimplex optimization of the dispersive solid-phase microextraction and determination of fenitrothion by magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer and high-performance liquid chromatography. J Iran Chem Soc 15:1181–1189
Larki A (2017) A novel application of carbon dots for colorimetric determination of fenitrothion insecticide based on the microextraction method. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 173:1–5
Canlı AG, Sürücü B, Ulusoy HI, Yılmaz HI, Kabir A, Locatelli M (2019) Analytical methodology for trace determination of propoxur and fenitrothion pesticide residues by decanoic acid modified magnetic nanoparticles. Molecules 24(24):4621
Locatelli M, Furton KG, Tartaglia A, Sperandio E, Ulusoy HI, Kabir A (2019) An FPSE-HPLC-PDA method for rapid determination of solar UV filters in human whole blood, plasma and urine. J Chromatogr B 1118-1119:40–50
Niessen WMA, Manini P, Andreoli R (2006) Matrix effects in quantitative pesticide analysis using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom Rev 25:881–899
Chen LN, Song FR, Liu ZQ, Zheng Z, Xing JP, Liu SY (2012) Multi-residue method for fast determination of pesticide residues in plants used in traditional Chinese medicine by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1225:132–140
Rousis NI, Bade R, Bijlsma L, Zuccato E, Sancho JV, Hernandez F, Castiglioni S (2017) Monitoring a large number of pesticides and transformation products in water samples from Spain and Italy. Environ Res 156:31–38
Gilbert-Lopez B, Garcia-Reyes JF, Molina-Diaz A (2009) Sample treatment and determination of pesticide residues in fatty vegetable matrices. Talanta 79:109–128
Szpyrka E, Kurdziel A, Matyaszek A, Podbielska M, Rupar J, Slowik-Borowiec M (2015) Evaluation of pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables from the region of south-eastern Poland. Food Control 48:137–142
Hegazy AM, Abdelfatah RM, Mahmoud HM, Elsayed MA (2020) Development and validation of two robust simple chromatographic methods for estimation of tomatoes specific pesticides’ residues for safety monitoring prior to food processing line and evaluation of local samples. Food Chem 306:125640
Yi LX, Fang R, Chen GH (2013) Molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction in the analysis of agrochemicals. J Chromatogr Sci 51:608–618
Galuszka A, Konieczka P, Migaszewski ZM, Namiesnik J (2012) Analytical Eco-Scale for assessing the greenness of analytical procedures. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 37:61–72
Samanidou V, Kaltzi I, Kabir A, Furton KG (2016) Simplifying sample preparation using fabric phase sorptive extraction technique for the determination of benzodiazepines in blood serum by high-performance liquid chromatography. Biomed Chromatogr 30:829–836
Kabir A, Furton KG, Tinari N, Grossi L, Innosa D, Macerola D, Tartaglia A, Di Donato V, D'Ovidio C, Locatelli M (2018) Fabric phase sorptive extraction-high performance liquid chromatography-photo diode array detection method for simultaneous monitoring of three inflammatory bowel disease treatment drugs in whole blood, plasma and urine. J Chromatogr B 1084:53–63
Celeiro M, Acerbi R, Kabir A, Furton KG, Llompart M (2020) Development of an analytical methodology based on fabric phase sorptive extraction followed by gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry to determine UV filters in environmental and recreational waters. Anal Chim Acta X 4:100038
Kaur R, Rani S, Malik AK, Kabir A, Furton KG (2019) Application of fabric phase sorptive extraction with gas chromatography and mass spectrometry for the determination of organophosphorus pesticides in selected vegetable samples. J Sep Sci 42:862–870
Pérez-Mayán L, Rodríguez I, Ramil M, Kabir A, Furton KG, Cela R (2018) Fabric phase sorptive extraction followed by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of fungicides and insecticides in wine. J Chromatogr A 1584:13–23
Mesa R, Kabir A, Samanidou V, Furton KG (2019) Simultaneous determination of selected estrogenic endocrine disrupting chemicals and bisphenol a residues in whole milk using fabric phase sorptive extraction coupled to HPLC-UV detection and LC-MS/MS. J Sep Sci 42:598–608
Kaur R, Kaur R, Rani S, Malik AK, Kabir A, Furton KG, Samanidou VF (2019) Rapid monitoring of organochlorine pesticide residues in various fruit juices and water samples using fabric phase sorptive extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Molecules 24:1013
Guedes-Alonso R, Ciofi L, Sosa-Ferrera Z, Juan Santana-Rodriguez J, del Bubba M, Kabir A, Furton KG (2016) Determination of androgens and progestogens in environmental and biological samples using fabric phase sorptive extraction coupled to ultra-high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1437:116–126
Alcudia-León MC, Lucena R, Cárdenas S, Valcárcel M, Kabir A, Furton KG (2017) Integrated sampling and analysis unit for the determination of sexual pheromones in environmental air using fabric phase sorptive extraction and headspace-gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1488:17–25
Samanidou V, Michaelidou K, Kabir A, Furton KG (2017) Fabric phase sorptive extraction of selected penicillin antibiotic residues from intact milk followed by high performance liquid chromatography with diode array detection. Food Chem 224:131–138
Aznar M, Úbeda S, Nerin C, Kabir A, Furton KG (2017) Fabric phase sorptive extraction as a reliable tool for rapid screening and detection of freshness markers in oranges. J Chromatogr A 1500:32–42
Kazantzi V, Anthemidis A (2017) Fabric sol–gel phase sorptive extraction technique: a review. Separations 4:20
Montesdeoca-Esponda S, Guedes-Alonso R, Santana-Viera S, Sosa-Ferrera Z, Santana-Rodríguez J (2018) Applications of fabric phase sorptive extraction to the determination of micropollutants in liquid samples. Separations 5:35
Tuzimski T, Rejczak T (2016) Application of HPLC-DAD after SPE/QuEChERS with ZrO2-based sorbent in d-SPE clean-up step for pesticide analysis in edible oils. Food Chem 190:71–79
Kabir A, Locatelli M, Ulusoy HI (2017) Recent trends in microextraction techniques employed in analytical and bioanalytical sample preparation. Separations 4:36
Kabir A, Mesa R, Jurmain J, Furton K (2017) Fabric phase sorptive extraction explained. Separations 4:21
Locatelli M, Kabir A, Innosa D, Lopatriello T, Furton KG (2017) A fabric phase sorptive extraction-high performance liquid chromatography-photo diode array detection method for the determination of twelve azole antimicrobial drug residues in human plasma and urine. J Chromatogr B 1040:192–198
Tankiewicz M, Biziuk M (2018) Fast, sensitive and reliable multi-residue method for routine determination of 34 pesticides from various chemical groups in water samples by using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction coupled with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 410:1533–1550
Locatelli M, Tinari N, Grassadonia A, Tartaglia A, Macerola D, Piccolantonio S, Sperandio E, D'Ovidio C, Carradori S, Ulusoy HI, Furton KG, Kabir A (2018) FPSE-HPLC-DAD method for the quantification of anticancer drugs in human whole blood, plasma, and urine. J Chromatogr B 1095:204–213
Taraboletti A, Goudarzi M, Kabir A, Moon BH, Laiakis E, Lacombe J, Ake P, Shoishiro S, Brenner D, Fornace A, Zenhausern F (2019) Fabric phase sorptive extraction-a metabolomic pre-processing approach for ionizing radiation exposure assessment. J Proteome Res 18(8):3020–3031
Kabir A, Furton KG, Malik A (2013) Innovations in sol-gel microextraction phases for solvent-free sample preparation in analytical chemistry. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 45:197–218
Lakade SS, Borrull F, Furton KG, Kabir A, Fontanals N, Maria Marcé R (2015) Comparative study of different fabric phase sorptive extraction sorbents to determine emerging contaminants from environmental water using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 144:1342–1351
Lakade SS, Borrull F, Furton KG, Kabir A, Marce RM, Fontanals N (2015) Dynamic fabric phase sorptive extraction for a group of pharmaceuticals and personal care products from environmental waters. J Chromatogr A 1456:19–26
Zhou S, Chen H, Wu B, Ma C, Ye Y (2012) Sensitive determination of carbamates in fruit and vegetables by a combination of solid-phase extraction and dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction prior to HPLC. Microchim Acta 176:419–427
Zhou J, Ma C, Zhou S, Ma P, Chen F, Qi Y, Chen H (2010) Preparation, evaluation and application 23 of molecularly imprinted solid-phase microextraction monolith for selective extraction of pirimicarb in tomato and pear. J Chromatogr A 1217:7478–7483
Selva TMG, de Araujo WR, Bacil RP, Paixão TRLC (2017) Study of electrochemical oxidation and quantification of the pesticide pirimicarb using a boron-doped diamond electrode. Electrochim Acta 246:588–596
Qi P, Wang J, Wang X, Wang X, Wang Z, Xu H, di S, Wang Q, Wang X (2018) Sensitive determination of fenitrothion in water samples based on an electrochemical sensor layered reduced graphene oxide, molybdenum sulfide (MoS 2 )-Au and zirconia films. Electrochim Acta 292:667–675
Maddah B, Javadi SS, Mirzaei A, Rahimi-Nasrabadi M (2015) Application of electrospun polystyrene nanofibers as solid phase extraction sorbent for the preconcentration of diazinon and fenitrothion in environmental waters. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 38(2):208–214
Malhat F, Boulangé J, Abdelraheem E, Abd Allah O, Abd el-Hamid R, Abd el-Salam S (2017) Validation of QuEChERS based method for determination of fenitrothion residues in tomatoes by gas chromatography–flame photometric detector: decline pattern and risk assessment. Food Chem 229:814–819
Funding
The present study was performed with partial contributions obtained from the other projects supported by Sivas Cumhuriyet University Scientific Research Projects Commission, Turkey. This article is based upon work from the Sample Preparation Task Force and Network, supported by the Division of Analytical Chemistry of the European Chemical Society.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 95 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ulusoy, H.İ., Köseoğlu, K., Kabir, A. et al. Fabric phase sorptive extraction followed by HPLC-PDA detection for the monitoring of pirimicarb and fenitrothion pesticide residues. Microchim Acta 187, 337 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04306-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04306-7