Abstract
A bimetallic nanostructure of Co/Cu for the non-enzymatic determination of glucose is presented. The heterostructure includes cobalt thin film on a porous array of Cu nanocolumns. Glancing angle deposition (GLAD) method was used to grow Cu nanocolumns directly on a fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) substrate. Then a thin film of cobalt was electrodeposited on the Cu nanostructures. Various characterization studies were performed in order to define the optimum nanostructure for the determination of glucose. The results showed remarkable boosting of the electrocatalytic activity of Co/Cu bimetallic structure compare to the responses achieved by the monometallic structures of Co or Cu. The sensor showed two linear response ranges for the determination of glucose at 0.55 V in 0.1 M NaOH, from 5 μM–1 mM and 2–9 mM. The sensitivity was 1741 (μA mM−1 cm−2) and 626 (μA mM−1 cm−2), respectively, while the detection limit for a signal-to-noise ratio of 3 was found to be 0.4 μM. The sensor exhibited excellent selectivity and was successfully applied to the determination of glucose in real human blood serum samples.

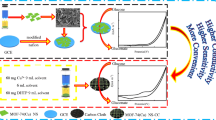
Schematic representation of fabrication process of the glucose sensor of Co (Cobalt)/Cu (Copper) on Fluorine doped Tin Oxide (FTO). The current voltage plots show higher electrooxidation activity of the bimetallic nanostructure of Co/Cu/FTO relative to the bare Co/FTO.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dhara K, Mahapatra DR (2017) Electrochemical nonenzymatic sensing of glucose using advanced nanomaterials. Microchim Acta 185(1):49. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2609-1
Gao Y, Yang F, Yu Q, Fan R, Yang M, Rao S, Lan Q, Yang M, Rao S, Lan Q, Yang Z, Yahng Z (2019) Three-dimensional porous cu@Cu2O aerogels for direct voltammetric sensing of glucose. Microchim Acta 186(3):192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3263-6
Lang XY, Fu HY, Hou C, Han GF, Yang P, Liu YB, Jiang Q (2013) Nanoporous gold supported cobalt oxide microelectrodes as high-performance electrochemical biosensors. Nat Commun 4:2169. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms3169
Sajadpour M, Siampour H, Abbasian S, Amiri M, Rameshan R, Rameshan C, Hajian A, Bagheri H, Moshaii A (2019) A non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on the hybrid thin films of cu on acetanilide/ITO. J Electrochem Soc 166(13):B1116–B1125. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0231913jes
Wu Y, Wang L, Chen M, Jin Z, Zhang W, Cao R (2017) Preparation of cobalt-based electrodes by physical vapor deposition on various nonconductive substrates for ELECTROCATALYTIC water oxidation. ChemSusChem 10(23):4699–4703. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201701576
Vivekananth R, Babu RS, Prasanna K, Lee CW, Kalaivani RA (2018) Non-enzymatic glucose sensing platform using self assembled cobalt oxide/graphene nanocomposites immobilized graphite modified electrode. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 29(8):6763–6770. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-8662-7
Wang L, Zheng Y, Lu X, Li Z, Sun L, Song Y (2014) Dendritic copper-cobalt nanostructures/reduced graphene oxide-chitosan modified glassy carbon electrode for glucose sensing. Sensors Actuators B Chem 195:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.01.007
Lin KC, Lin YC, Chen SM (2013) A highly sensitive nonenzymatic glucose sensor based on multi-walled carbon nanotubes decorated with nickel and copper nanoparticles. Electrochim Acta 96:164–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.02.098
Wang L, Lu X, Ye Y, Ye Y, Sun L, Song Y (2013) Nickel-cobalt nanostructures coated reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite electrode for nonenzymatic glucose biosensing. Electrochim Acta 114:484–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.10.125
Cao X, Wang N, Jia S, Shao Y (2013) Detection of glucose based on bimetallic PtCu nanochains modified electrodes. Anal Chem 85(10):5040–5046. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac400292n
Si P, Huang Y, Wang T, Ma J (2013) Nanomaterials for electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose biosensors. RSC Adv 3(11):3487–3502. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2RA22360K
Hwang DW, Lee S, Seo M, Chung TD (2018) Recent advances in electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensors – a review. Anal Chim Acta 1033:1–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.05.051
Zhang Y, Su L, Manuzzi D, Monteros HVE, Jia W, Huo D, Hou C, Lei Y (2012) Ultrasensitive and selective non-enzymatic glucose detection using copper nanowires. Biosens Bioelectron 31(1):426–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2011.11.006
Yang J, Zhang WD, Gunasekaran S (2010) An amperometric non-enzymatic glucose sensor by electrodepositing copper nanocubes onto vertically well-aligned multi-walled carbon nanotube arrays. Biosens Bioelectron 26(1):279–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2010.06.014
Wu HX, Cao W, Li Y, Liu G, Wen Y, Yang HF, Yang SP (2010) In situ growth of copper nanoparticles on multiwalled carbon nanotubes and their application as non-enzymatic glucose sensor materials. Electrochim Acta 55(11):3734–3740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2010.02.017
Chowdhury M, Ossinga C, Cummings F, Chamier J, Kebede M (2017) Novel Sn Doped Co3O4 Thin Film for Nonenzymatic Glucose Bio-Sensor and Fuel Cell. 29(8):1876–1886. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201700184
Stromberg LR, Hondred JA, Sanborn D, Mendivelso-Perez D, Ramesh S, Rivero IV, Kogot J, Smith E, Gomes C, Claussen JC (2019) Stamped multilayer graphene laminates for disposable in-field electrodes: application to electrochemical sensing of hydrogen peroxide and glucose. Microchim Acta 186(8):533. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3639-7
Yang H, Wang Z, Zhou Q, Xu C, Hou J (2019) Nanoporous platinum-copper flowers for non-enzymatic sensitive detection of hydrogen peroxide and glucose at near-neutral pH values. Microchim Acta 186(9):631. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3728-7
Batool R, Akhtar MA, Hayat A, Han D, Niu L, Ahmad MA, Nawaz MH (2019) A nanocomposite prepared from magnetite nanoparticles, polyaniline and carboxy-modified graphene oxide for non-enzymatic sensing of glucose. Microchim Acta. 186(5):267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3364-2
Wang R, Liang X, Liu H, Cui L, Zhang X, Liu C (2018) Non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor based on monodispersed stone-like PtNi alloy nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 185(7):339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2866-7
Chinnadayyala SR, Park I, Cho S (2018) Nonenzymatic determination of glucose at near neutral pH values based on the use of nafion and platinum black coated microneedle electrode array. Microchim Acta 185(5):250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2770-1
Luo J, Zhao D, Yang M, Qu F (2018) Porous Ni3N nanosheet array as a catalyst for nonenzymatic amperometric determination of glucose. Microchim Acta 185(4):229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2764-z
Ahmad R, Wolfbeis O, Hahn YB, Alshareef HN, Torsi L, Salama KN (2018) Deposition of nanomaterials: a crucial step in biosensor fabrication. Mater Today Commun 17:289–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2018.09.024
Abbasian S, Moshaii A, Vayghan NS, Nikkhah M (2018) Fabrication of Ag nanostructures with remarkable narrow plasmonic resonances by glancing angle deposition. Appl Surf Sci 441:613–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.02.072
Sobhkhiz N, Moshaii A (2015) Broadband improvement of light absorption properties of α-Fe2O3 thin-film by silver helical nanostructures. Plasmonics. 10(5):1243–1253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-9918-1
Salazar P, Rico V, Rodriguez-Amaro R (2015) New copper wide range nanosensor electrode prepared by physical vapor deposition at oblique angles for the non-enzimatic determination of glucose. Electrochim Acta 169:195–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.04.092
Salazar P, Rico V, Gonzalez-Elipe AR (2016) Non-enzymatic glucose sensors based on nickel nanoporous thin films prepared by physical vapor deposition at oblique angles for beverage industry applications. J Electrochem Soc 163(14):B704–B709. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.1241614jes
Sobhkhiz N, Moshaii A (2014) Silver conical helix broadband plasmonic nanoantenna. J Nanophotonics 8(1):083078. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JNP.8.083078
Zheng JY, Quan Z, Song G, Kim CW, Cha HG, Kim TW, Shin W, Lee KJ, Jung MH, Kang YS (2012) Vertical cobalt dendrite array films: electrochemical deposition and characterization, glucose oxidation and magnetic properties. J Mater Chem 22(24):12296–12304. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2JM30300K
Wang T, Yu Y, Tian H (2014) Hu J (2014) a novel non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on cobalt nanoparticles implantation-modified indium tin oxide electrode. Electroanalysis 26(12):2693–2700. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201400347
Bard AJ, Faulkner LR (2000) Electrochemical methods: fundamentals and applications. Wiley ISBN: 978-0-471-04372-0
Li SJ, Hou LL, Yuan BQ, Chang MZ, Ma Y, Du JM (2016) Enzyme-free glucose sensor using a glassy carbon electrode modified with reduced graphene oxide decorated with mixed copper and cobalt oxides. Microchim Acta 183(6):1813–1821. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1817-4
Justice Babu K, Sheet S, Lee YS, Gnana KG (2018) Three-dimensional dendrite Cu–Co/reduced graphene oxide architectures on a disposable pencil graphite electrode as an electrochemical sensor for nonenzymatic glucose detection. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6(2):1909–1918. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b03314
Gong X, Gu Y, Zhang F, Liu Z, Li Y, Chen G, Wang B (2019) High-performance non-enzymatic glucose sensors based on CoNiCu alloy nanotubes arrays prepared by electrodeposition. Front Mater 6(3). https://doi.org/10.3389/fmats.2019.00003
Li W, Qi H, Wang B, Wang Q, Wei S, Zhang X, Wang Y, Zhang L, Cui X (2018) Ultrathin NiCo2O4 nanowalls supported on a 3D nanoporous gold coated needle for non-enzymatic amperometric sensing of glucose. Microchim Acta 185(2):124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2663-8
Funding
This work has been supported by Tarbiat Modares University (TMU). M. P., A. M., and H. S. acknowledge the TMU support under the grant number IG-39708.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All procedures performed in studies involving human serums were in accordance with the ethical standards of Tarbiat Modares University and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1.25 mb).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pak, M., Moshaii, A., Siampour, H. et al. Cobalt-copper bimetallic nanostructures prepared by glancing angle deposition for non-enzymatic voltammetric determination of glucose. Microchim Acta 187, 276 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04246-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04246-2