Abstract
Molybdenum oxide quantum dots (MoOx QDs) were synthesized by a one-pot method and used as a versatile probe in an electrochemiluminescent (ECL) immunoassay of the non-small cell lung cancer biomarker cytokeratin 19 fragment 21–1 (CYFRA21-1) as a model analyte. The MoOx QDs exhibited stable and strong cathodic green ECL, with an emission peak at 535 nm, in the presence of K2S2O8 within the potential range of −2.0 to 0 V. On exposure to CYFRA21-1, the ECL decreases because of the immunoreaction between CYFRA21-1 and its antibody which generates a barrier for electron transfer. The determination of CYFRA21-1 with favorable analytical performances was successfully realized under the optimal conditions. ECL decreases linearly in the 1 pg mL−1 to 350 ng mL−1 CYFRA21-1 concentration range, and the detection is as low as 0.3 pg mL−1. Excellent recoveries from CYFRA21-1-spiked human serum indicate that the assay can be operated under physiological conditions.

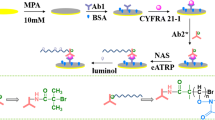
Schematic representation of the fabrication of molybdenum oxide quantum dots (MoOx QDs) and the electrochemiluminescent (ECL) immunoassay based on the use of the MoOx QDs ECL probe for cytokeratin 19 fragment 21–1 (CYFRA21-1).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lv XH, Pang XH, Li YY, Yan T, Cao W, Du B, Wei Q (2015) Electrochemiluminescent immune-modified electrodes based on Ag2Se@CdSe Nanoneedles loaded with Polypyrrole intercalated Graphene for detection of CA72-4. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:867–872
Yao X, Yan PP, Tang QH, Deng AP, Li JG (2013) Quantum dots based electrochemiluminescent immunosensor by coupling enzymatic amplification for ultrasensitive detection of clenbuterol. Anal Chim Acta 798:82–88
Yan PP, Zhang J, Tang QH, Deng AP, Li JG (2014) A quantum dot based electrochemiluminescent immunosensor for the detection of pg level phenylethanolamine a using gold nanoparticles as substrates and electron transfer accelerators. Analyst 139:4365–4372
Liu X, Jiang H, Fang Y, Zhao W, Wang NY, Zang GZ (2015) Quantum dots based potential-resolution dual-targets Electrochemiluminescent Immunosensor for subtype of tumor marker and its serological evaluation. Anal Chem 87:9163–9169
Pang XH, Li JX, Zhao YB, Wu D, Zhang Y, Du B, Ma HM, Wei Q (2015) Label-free Electrochemiluminescent Immunosensor for detection of Carcinoembryonic antigen based on Nanocomposites of GO/MWCNTs-COOH/au@CeO2. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:19260–19267
Geng J, Jia XD, Zhu JJ (2011) Sonochemical selective synthesis of ZnO/CdS core/shell nanostructures and their optical properties. CrystEngComm 13:193–198
Zhou J, Han TQ, Ma HM, Yan T, Pang XH, Li YY, Wei Q (2015) A novel electrochemiluminescent immunosensor based on the quenching effect of aminated graphene on nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots. Anal Chim Acta 889:82–89
Hu LY, Zheng J, Zhao K, Deng AP, Li JG (2018) An ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescent immunosensor based on graphene oxide coupled graphite-like carbon nitride and multiwalled carbon nanotubes-gold for the detection of diclofenac. Biosens Bioelectron 101:260–267
Peng HP, Jian ML, Deng HH, Wang WJ, Huang ZN, Huang KY, Liu AL, Chen W (2017) Valence states effect on Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence of gold Nanocluster. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:14929–14934
Zhang L, Hong MF, Chu ZJ, Xu H, Wang SP, Zhao XJ, Xiao SJ (2018) A new copper mediated on-off assay for alkaline phosphatase detection based on MoOx quantum dots. Microchem J 141:170–175
Xiao SJ, Zhao XJ, Zuo J, Huang HQ, Zhang L (2016) Highly photoluminescent MoOx quantum dots: facile synthesis and application in off-on pi sensing in lake water samples. Anal Chim Acta 906:148–155
Xiao SJ, Chu ZJ, Zhao XJ, Zhang ZB, Liu YH (2017) Off-on-off detection of the activity of acetylcholine esterase and its inhibitors using MoOx quantum dots as a photoluminescent probe. Microchim Acta 184:4853–4860
Yuan LL, Niu YS, Li RG, Zheng LH, Wang Y, Liu ML, Xu GF, Huang L, Xu YH (2018) Molybdenum oxide quantum dots prepared via a one-step stirring strategy and their application as fluorescent probes for pyrophosphate sensing and efficient antibacterial materials. J Mater Chem B 6:3240–3245
Wang N, Tang DY, Zou HY, Jia SY, Sun ZJ, Yang X, Peng J (2018) Synthesis of molybdenum oxide quantum dots with better dispersity and bio-imaging ability by reduction method. Opt Mater 83:19–27
Xiao SJ, Zhao XJ, Hu PP, Chu ZJ, Huang CZ, Zhang L (2016) Highly Photoluminescent molybdenum oxide quantum dots: one-pot synthesis and application in 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene determination. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:8184–8191
Ding DD, Guo W, Guo CS, Sun JZ, Zheng NN, Wang F, Yan M, Liu SQ (2017) MoO3-x quantum dots for photoacoustic imaging guided photothermal/photodynamic cancer treatment. Nanoscale 9:2020–2029
Ding DD, Huang WC, Song CQ, Yan M, Guo CS, Liu SQ (2017) Non-stoichiometric MoO3-x quantum dots as a light-harvesting material for interfacial water evaporation. Chem Commun 53:6744–6747
Qiu JD, Peng HZ, Liang RP, Li J, Xia XH (2007) Synthesis, characterization, and immobilization of Prussian blue-modified au nanoparticles: application to Electrocatalytic reduction of H2O2. Langmuir 23:2133–2137
Sui LL, Xu YM, Zhang XF, Cheng XL, Gao S, Zhao H, Cai Z, Huo LH (2015) Construction of three-dimensional flower-like α-MoO3 with hierarchical structure for highly selective triethylamine sensor. Sensors Actuators B Chem 208:406–414
Peng HP, Deng HH, Jian ML, Liu AL, Bai FQ, Lin XH, Chen W (2017) Electrochemiluminescence sensor based on methionine-modified gold nanoclusters for highly sensitive determination of dopamine released by cells. Microchim Acta 184:735–743
Ding Z, Quinn BM, Haram SK, Pell LE, Korgel BA, Bard AJ (2002) Electrochemistry and electrogenerated chemiluminescence from silicon nanocrystal quantum dots. Science 296:1293–1297
Myung N, Ding Z, Bard AJ (2002) Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence of CdSe Nanocrystals. Nano Lett 2:1315–1319
Zhang XL, Tang ZR, Dong YP, Wang CM (2018) Electrogenerated chemiluminescence of ZnO nanorods and its sensitive detection of cytochrome C. Talanta 179:139–144
Wu D, Liu Y, Wang Y, Hu L, Ma H, Wang G, Wei Q (2016) Label-free Electrochemiluminescent Immunosensor for detection of prostate specific antigen based on Aminated Graphene quantum dots and carboxyl Graphene quantum dots. Sci Rep 6:20511
Lu Q, Wei W, Zhou ZX, Zhou ZX, Zhang YJ, Liu SQ (2014) Electrochemiluminescence resonance energy transfer between graphene quantum dots and gold nanoparticles for DNA damage detection. Analyst 139:2404–2410
Dennany L, Hogan CF, Keyes TE, Forster RJ (2006) Effect of surface immobilization on the Electrochemiluminescence of ruthenium-containing Metallopolymers. Anal Chem 78:1412–1417
Van Houten J, Watts RJ (1976) Temperature dependence of the photophysical and photochemical properties of the tris(2,2′-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II) ion in aqueous solution. J Am Chem Soc 98:4853–4858
Tang M, Zhou ZX, Li SG, Zhao F, Liu SQ (2018) Electrochemiluminescent detection of cardiac troponin I by using soybean peroxidase labeled-antibody as signal amplifier. Talanta 180:47–53
Zhou Y, Zhuo Y, Liao N, Chai YQ, Yuan R (2014) Ultrasensitive immunoassay based on a pseudobienzyme amplifying system of choline oxidase and luminol-reduced Pt@au hybrid nanoflowers. Chem Commun 50:14627–14630
Zeng Y, Bao J, Zhao YN, Huo DQ, Chen M, Qi YL, Yang M, Fa HB, Hou CJ (2018) A sandwich-type electrochemical immunoassay for ultrasensitive detection of non-small cell lung cancer biomarker CYFRA21-1. Bioelectrochemistry 120:183–189
Wang HQ, Ma ZF (2019) “Off-on” signal amplification strategy amperometric immunosensor for ultrasensitive detection of tumour marker. Biosens Bioelectron 132:265–270
Zeng Y, Bao J, Zhao YN, Huo DQ, Chen M, Yang M, Fa HB, Hou CJ (2018) A sensitive label-free electrochemical immunosensor for detection of cytokeratin 19 fragment antigen 21-1 based on 3D graphene with gold nanopaticle modified electrode. Talanta 178:122–128
Kumar S, Sharma JG, Maji S, Malhotra BD (2016) Nanostructured zirconia decorated reduced graphene oxide based efficient biosensing platform for non-invasive oral cancer detection. Biosens Bioelectron 78:497–504
Shan J, Ma ZF (2016) Simultaneous detection of five biomarkers of lung cancer by electrochemical immunoassay. Microchim Acta 183:2889–2897
Han L, Wang D, Yan L, Petrenko VA, Liu AH (2019) Specific phages-based electrochemical impedimetric immunosensors for label-free and ultrasensitive detection of dual prostate-specific antigens. Sensors Actuators B Chem 297:126727
Acknowledgments
We sincerely acknowledge the financial support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21874020, 21405015), Fujian Province Health Commission Young and Middle-Aged Talent training project (2018-ZQN-62), Fujian Province Young Talent Supporting Project (2019B016), Joint Funds for the Innovation of Science and Technology, Fujian Province (2016Y9056, 2016Y9054), the Science and Technology Project of Fujian Province (2018 L3008), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2016BL19), and Program for Fujian Top-notch Innovative Personnel.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 245 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, X., Chen, X., Wu, W. et al. Electrochemiluminescent immunoassay for the lung cancer biomarker CYFRA21-1 using MoOx quantum dots. Microchim Acta 186, 855 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3917-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3917-4