Abstract
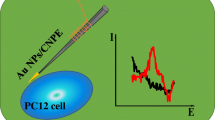
The electrogenerated chemiluminescence (ECL) of methionine stabilized gold nanoclusters (Met-AuNCs) is presented. The Met-AuNCs were used to modify a glassy carbon electrode (Met-AuNC/GCE) which is shown to exhibit a stable and strong cathodic ECL signal (at −1.86 V) when using potassium peroxodisulfate (K2S2O8) as the coreactant in aqueous solution of pH 7.4. Compared to a GCE modified with BSA-AuNCs, the ECL intensity of Met-AuNCs is 5-fold enhanced. The possible ECL reaction mechanism of the ECL system was studied, and a method for the determination of dopamine (DA) was worked out. The modified GCE has a linear response in the 0.1 to 4 μM DA concentration range, with a detection limit of 32 nM (at an S/N ratio of 3). The method was applied to the determination of DA released by PC12 cells. In our perception, the Met-AuNC/GCE provides a viable new tool in ECL based bioanalysis that also paves new routes to the design and application of new sensors.

The electrochemiluminescence (ECL) sensor based on methionine stabilized gold nanocluster modified glassy carbon electrode (Met-AuNC/GCE) using potassium peroxodisulfate (K2S2O8) as the coreactant in aqueous solution was fabricated for the highly sensitive detection of dopamine (DA) released by cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yin XB, Dong SS, Wang EK (2004) Analytical applications of the electrochemiluminescence of tris (2, 2′-bipyridyl) ruthenium and its derivatives. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 23(6):432–441
Bertoncello P, Forster RJ (2009) Nanostructured materials for electrochemiluminescence (ECL)-based detection methods: recent advances and future perspectives. Biosens Bioelectron 24:3191–3200
Muzyka K (2014) Current trends in the development of the electrochemiluminescent immunosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 54:393–407
Vashist SK, Luong JHT (2015) Recent advances in electrochemical biosensing schemes using graphene and graphene-based nanocomposites. Carbon 84:519–550
Liu LL, Wang XY, Ma Q, Lin ZH, Chen SF, Li Y, LH L, HP Q, XG S (2016) Multiplex electrochemiluminescence DNA sensor for determination of hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus based on multicolor quantum dots and Au nanoparticles. Anal Chim Acta 916:92–101
Bertoncello P, Stewart AJ, Dennany L (2014) Analytical applications of nanomaterials in electrogenerated chemiluminescence. Anal Bioanal Chem 406(23):5573–5587
Cui R, YP G, Bao L, Zhao JY, Qi BP, Zhang ZL, Xie ZX, Pang DW (2012) Near-infrared electrogenerated chemiluminescence of ultrasmall Ag2Se quantum dots for the detection of dopamine. Anal Chem 84(21):8932–8935
Han TQ, Yan T, Li YY, Cao W, Pang XH, Huang QJ, Wei Q (2015) Eco-friendly synthesis of electrochemiluminescent nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots from diethylene triamine pentacetate and their application for protein detection. Carbon 91:144–152
Wang ZX, Zheng CL, Li QL, Ding SN (2014) Electrochemiluminescence of a nano Ag–carbon nanodot composite and its application to detect sulfide ions. Analyst 139(7):1751–1755
Dong YQ, Tian WR, Ren SY, Dai RP, Chi YW, Chen GN (2014) Graphene quantum dots/l-cysteine coreactant electrochemiluminescence system and its application in sensing lead (II) ions. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(3):1646–1651
Antonello S, Perera NV, Ruzzi M, Gascon JA, Maran F (2013) Interplay of charge state, lability, and magnetism in the molecule-like Au25 (SR) 18 cluster. J Am Chem Soc 135(41):15585–15594
Feng JJ, Huang H, Zhou DL, Cai LY, QQ T, Wang AJ (2013) Peptide-templated synthesis of wavelength-tunable fluorescent gold nanoparticles. J Mater Chem C 31(1):4720–4725
Cao XL, Li HW, Lian LL, Xu N, Lou DW, YQ W (2015) A dual-responsive fluorescence method for the detection of clenbuterol based on BSA-protected gold nanoclusters. Anal Chim Acta 871:43–50
Negishi Y, Nobusada K, Tsukuda T (2005) Glutathione-protected gold clusters revisited: bridging the gap between gold (I)-thiolate complexes and thiolate-protected gold nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc 127(14):5261–5270
ZK W, Jin RC (2010) On the ligand’s role in the fluorescence of gold nanoclusters. Nano Lett 10(7):2568–2573
Xie J, Zheng Y, Ying JY (2009) Protein-directed synthesis of highly fluorescent gold nanoclusters. J Am Chem Soc 131(3):888–889
WW X, Li YD, Gao Y, Zeng XC (2016) Unraveling a generic growth pattern in structure evolution of thiolate-protected gold nanoclusters. Nanoscale 8:7396–7401
Wen F, Dong YH, Feng L, Wang S, Zhang S, Zhang XR (2011) Horseradish peroxidase functionalized fluorescent gold nanoclusters for hydrogen peroxide sensing. Anal Chem 83(4):1193–1196
Liu CL, HT W, Hsiao YH, Lai CW, Shih CW, Peng YK, Tang KC, Chang HW, Chien YC, Hsiao JK, Cheng JT, Chou PT (2011) Insulin-directed synthesis of fluorescent gold nanoclusters: preservation of insulin bioactivity and versatility in cell imaging. Angew Chem Int Ed 50(31):7056–7060
Nair LV, Philips DS, Jayasree RS, Ajayaghosh AA (2013) A near-infrared fluorescent nanosensor (AuC@urease) for the selective detection of blood urea. Small 9(16):2673–2677
XY M, Li Q, Dong P, Qiao J, Hou J, Nie ZX, Ma HM (2013) Facile one-pot synthesis of L-proline-stabilized fluorescent gold nanoclusters and its application as sensing probes for serum iron. Biosens Bioelectron 49:249–255
Deng HH, GW W, Zou ZQ, Peng HP, Liu AL, Lin XH, Xia XH, Chen W (2015) pH-sensitive gold nanoclusters: preparation and analytical applications for urea, urease, and urease inhibitor detection. Chem Commun 51:7847–7850
Wang CX, Wang Y, Xu L, Shi XD, Li XW, XW X, Sun HC, Yang B, Lin Q (2013) A galvanic replacement route to prepare strongly fluorescent and highly stable gold nanodots for cellular imaging. Small 9(3):413–420
Li LL, Liu HY, Shen YY, Zhang JR, Zhu JJ (2011) Electrogenerated chemiluminescence of Au nanoclusters for the detection of dopamine. Anal Chem 83(3):661–665
Fang YM, Song J, Li J, Wang YW, Yang HH, Sun JJ, Chen GN (2011) Electrogenerated chemiluminescence from Au nanoclusters. Chem Commun 47:2369–2371
Deng HH, Zhang LN, He SB, Liu AL, Li GW, Lin XH, Xia XH, Chen W (2015) Methionine-directed fabrication of gold nanoclusters with yellow fluorescent emission for Cu2+ sensing. Biosens Bioelectron 65:397–403
Tsai HY, Lin ZH, Chang HT (2012) Tellurium-nanowire-coated glassy carbon electrodes for selective and sensitive detection of dopamine. Biosens Bioelectron 35:479–483
Wang C, Hu YJ, Lieber CM, Sun SH (2008) Ultrathin Au nanowires and their transport properties. J Am Chem Soc 130(28):8902–8903
Jie GF, Zhang JJ, Wang DC, Cheng C, Chen HY, Zhu JJ (2008) Electrochemiluminescence immunosensor based on CdSe nanocomposites. Anal Chem 80(11):4033–4039
Myung N, Ding ZF, Bard AJ (2002) Electrogenerated chemiluminescence of CdSe nanocrystals. Nano Lett 2(11):1315–1319
Ding ZF, Quinn BM, Haram SK, Pell LE, Korgel BA, Bard AJ (2002) Electrochemistry and electrogenerated chemiluminescence from silicon nanocrystal quantum dots. Science 296(5571):1293–1297
Huang CX, Chen X, YL L, Yang H, Yang WS (2015) Electrogenerated chemiluminescence behavior of peptide nanovesicle and its application in sensing dopamine. Biosens Bioelectron 63:478–482
O’Reilly EJ, Keyes TE, Forster RJ, Dennany L (2012) Insights into electrochemiluminescent enhancement through electrode surface modification. Analyst 138:677–682
Dennany L, Hogan C, Keyes T, Forster RJ (2006) Effect of surface immobilization on the electrochemiluminescence of ruthenium-containing metallopolymers. Anal Chem 78(5):1412–1417
Wallace WL, Bard AJ (1979) Electrogenerated chemiluminescence. 35. Temperature dependence of the ECL efficiency of tris(2,2′-bipyridine)rubidium(2+) in acetonitrile and evidence for very high excited state yields from electron transfer reactions. J Phys Chem 83(10):1350–1357
Molapo KM, Venkatanarayanan A, Dolan CM, Prendergast U, Baker PG, Iwuoha EI, Keyes TE, Forster R (2014) High efficiency electrochemiluminescence from polyaniline: ruthenium metal complex films. Electrochem Commun 48:95–98
Clarke SJ, Hollmann CA, Zhang Z, Suffern D, Bradforth SE, Dimitrijevic NM, Minarik WG, Nadeau JL (2006) Photophysics of dopamine-modified quantum dots and effects on biological systems. Nat Mater 5:409–417
Yusoff N, Pandikumar A, Ramaraj R, Ngee LH, Huang NM (2015) Gold nanoparticle based optical and electrochemical sensing of dopamine. Microchim Acta 182:2091–2114
Sanghavi BJ, Wolfbeis OS, Hirsch T, Swami NS (2015) Nanomaterial-based electrochemical sensing of neurological drugs and neurotransmitters. Microchim Acta 182:1–41
Ming L, Peng T, Tu Y (2016) Multiple enhancement of luminol electrochemiluminescence using electrodes functionalized with titania nanotubes and platinum black: ultrasensitive determination of hydrogen peroxide, resveratrol, and dopamine. Microchim Acta 183:305–310
Liu X, Jiang H, Lei JP, HX J (2007) Anodic electrochemiluminescence of CdTe quantum dots and its energy transfer for detection of catechol derivatives. Anal Chem 79:8055–8060
Yuan DH, Chen SH, Yuan R, Zhang JJ, Liu XF (2014) An ECL sensor for dopamine using reduced graphene oxide/multiwall carbon nanotubes/gold nanoparticles. Sensors Actuators B Chem 191:415–420
Liu X, Cheng L, Lei J, Ju H (2008) Dopamine detection based on its quenching effect on the anodic electrochemiluminescence of CdSe quantum dots. Analyst 133(9):1161–1163
Gao WW, Ye SY, Shao MW (2011) Solution-combusting preparation of mono-dispersed Mn3O4 nanoparticles for electrochemical applications. J Phys Chem Solids 72(9):1027–1031
Wu F, Huang T, Hu Y, Yang X, Ouyang Y, Xie Q (2016) Differential pulse voltammetric simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid on a glassy carbon electrode modified with electroreduced graphene oxide and imidazolium groups. Microchim Acta 183(9):2539–2546
SJ Y, Luo CH, Wang LW, Peng H, Zhu ZQ (2013) Poly(3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-modified Ni/silicon microchannel plate electrode for the simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Analyst 138(4):1149–1155
Kwak K, Kumar SS, Lee D (2012) Selective determination of dopamine using quantum-sized gold nanoparticles protected with charge selective ligands. Nanoscale 4(14):4240–4246
Xing L, Ma Z (2016) A glassy carbon electrode modified with a nanocomposite consisting of MoS2 and reduced graphene oxide for electrochemical simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid. Microchim Acta 183(1):257–263
Hsieh YS, Hong BD, Lee CL (2016) Non-enzymatic sensing of dopamine using a glassy carbon electrode modified with a nanocomposite consisting of palladium nanocubes supported on reduced graphene oxide in a nafion matrix. Microchim Acta 183(2):905–910
Chen JL, Yan XP, Meng K, Wang SF (2011) Graphene oxide based photoinduced charge transfer label-free near-infrared fluorescent biosensor for dopamine. Anal Chem 83(22):8787–8793
Liu S, Shi F, Zhao X, Chen L, Su X (2013) 3-Aminophenyl boronic acid-functionalized CuInS2 quantum dots as a near-infrared fluorescence probe for the determination of dopamine. Biosens Bioelectron 47:379–384
Wang T, Zhang SY, Mao CJ, Song JM, Niu HL, Jin BK, Tian YP (2012) Enhanced electrochemiluminescence of CdSe quantum dots composited with graphene oxide and chitosan for sensitive sensor. Biosens Bioelectron 31:369–375
Jin L, Gao X, Wang L, Wu Q, Chen Z, Lin X (2013) Electrochemical activation of polyethyleneimine-wrapped carbon nanotubes/in situ formed gold nanoparticles functionalised nanocomposite sensor for high sensitive and selective determination of dopamine. J Electroanal Chem 692:1–8
Liu SF, Zhang X, YM Y, Zou GZ (2014) A monochromatic electrochemiluminescence sensing strategy for dopamine with dual-stabilizers-capped CdSe quantum dots as emitters. Anal Chem 86:2784–2788
Li JX, Li XJ, Zhang YH, Li RX, Wu D, Du B, Zhang Y, Ma HM, Wei Q (2015) Electrochemiluminescence sensor based on cationic polythiophene derivative and NH2–graphene for dopamine detection. RSC Adv 5:5432–5437
Rao D, Zhang X, Sheng Q, Zheng J (2016) Highly improved sensing of dopamine by using glassy carbon electrode modified with MnO2, graphene oxide, carbon nanotubes and gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 83(9):2597–2604
Mei LP, Feng JJ, Wu L, Chen JR, Shen L, Xie Y, Wang AJ (2016) A glassy carbon electrode modified with porous Cu2O nanospheres on reduced graphene oxide support for simultaneous sensing of uric acid and dopamine with high selectivity over ascorbic acid. Microchim Acta 183(6):2039–2046
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21175023, 21405015), the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-12-0618), the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (2014 J05092, 2016Y9054), and the Medical Elite Cultivation Program of Fujian (2013-ZQN-ZD-25).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Huaping Peng and Haohua Deng contributed equally to this work
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 4.11 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, H., Deng, H., Jian, M. et al. Electrochemiluminescence sensor based on methionine-modified gold nanoclusters for highly sensitive determination of dopamine released by cells. Microchim Acta 184, 735–743 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-2058-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-2058-2