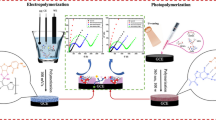
Abstract
The authors describe an immunosensor for the prostate specific antigen (PSA). It was obtained by modifying a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) first modified with gold nanoparticles and then with reduced graphene oxide that was decorated with gold nanoparticles. The AuNPs on reduced graphene oxide provide a suitable surface for attachment of antibodies. On binding of the antigen, the square wave voltammetric signal (measured by using hexacyanoferrate as a probe) reduced. This method has two logarithmically linear analytical ranges that extend from 25 to 55 fg.mL−1 and from 1 to 36 ng.mL−1, respectively. The lowest detection limit is 2 pg.mL−1. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy was also carried out for PSA determination. EIS works in the 0.0018 to 41 ng.mL−1 concentration range and has an LOD of 60 pg.mL−1. This method was applied to the determination of PSA in (spiked) human serum samples. In order to survey the selectivity of immunosensor, determination of PSA was performed in human serum samples, and finally sensitivity and reproducibility were examined.

Facile label free immunosensor based on reduced graphene oxide decorated with gold nanoparticles for early diagnosis prostate cancer via ultrasensitive detection of PSA biomarker: application in human serum.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bok RA, Small EJ (2002) Bloodborne biomolecular markers in prostate cancer development and progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2(12):918
Powers JL, Rippe KD, Imarhia K, Swift A, Scholten M, Islam N (2012) A direct, competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) as a quantitative technique for small molecules. J Chem Educ 89(12):1587–1590
Sonawane MD, Nimse SB, Song K-S, Kim T (2016) Detection, quantification, and profiling of PSA: current microarray technologies and future directions. RSC Adv 6(9):7599–7609
Tardivo M, Toffoli V, Fracasso G, Borin D, Dal Zilio S, Colusso A, Carrato S, Scoles G, Meneghetti M, Colombatti M (2015) Parallel optical read-out of micromechanical pillars applied to prostate specific membrane antigen detection. Biosens Bioelectron 72:393–399
Deng L, Chen H-Y, Xu J-J (2015) A novel electrochemiluminescence resonance energy transfer system for ultrasensitive detection of prostate-specific antigen. Electrochem Commun 59:56–59
He Z, Gao N, Jin W (2003) Determination of tumor marker CA125 by capillary electrophoretic enzyme immunoassay with electrochemical detection. Anal Chim Acta 497(1–2):75–81
Chuah K, Lai LM, Goon IY, Parker SG, Amal R, Gooding JJ (2012) Ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) using gold-coated magnetic nanoparticles as ‘dispersible electrodes’. Chem Commun 48(29):3503–3505
Damborska D, Bertok T, Dosekova E, Holazova A, Lorencova L, Kasak P, Tkac J (2017) Nanomaterial-based biosensors for detection of prostate specific antigen. Microchim Acta 184(9):3049–3067
Fan H, Guo Z, Gao L, Zhang Y, Fan D, Ji G, Du B, Wei Q (2015) Ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensor for carbohydrate antigen 72-4 based on dual signal amplification strategy of nanoporous gold and polyaniline–Au asymmetric multicomponent nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 64:51–56
Xu Z, Chen X, Dong S (2006) Electrochemical biosensors based on advanced bioimmobilization matrices. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 25(9):899–908
Choudhary M, Kumar V, Singh A, Singh M, Kaur S, Reddy G, Pasricha R, Singh S, Arora K (2013) Graphene oxide based label free ultrasensitive immunosensor for lung cancer biomarker, hTERT. Journal of Biosensors & Bioelectronics 4(4):1–9
Chu Y, Wang H, Ma H, Wu D, Du B, Wei Q (2016) Sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor for ultrasensitive detection of prostate-specific antigen using palladium-doped cuprous oxide nanoparticles. RSC Adv 6(88):84698–84704
Rafati AA, Afraz A, Hajian A, Assari P (2014) Simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid using a carbon paste electrode modified with multiwalled carbon nanotubes, ionic liquid, and palladium nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 181(15–16):1999–2008
Shoja Y, Rafati AA, Ghodsi J (2017) Enzymatic biosensor based on entrapment of D-amino acid oxidase on gold nanofilm/MWCNTs nanocomposite modified glassy carbon electrode by sol-gel network: analytical applications for D-alanine in human serum. Enzym Microb Technol 100:20–27
Afraz A, Rafati AA, Najafi M (2014) Optimization of modified carbon paste electrode with multiwalled carbon nanotube/ionic liquid/cauliflower-like gold nanostructures for simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Mater Sci Eng C 44:58–68
Lerf A, He H, Forster M, Klinowski J (1998) Structure of graphite oxide revisited. J Phys Chem B 102(23):4477–4482
Ma X, Qu Q, Zhao Y, Luo Z, Zhao Y, Ng KW, Zhao Y (2013) Graphene oxide wrapped gold nanoparticles for intracellular Raman imaging and drug delivery. J Mater Chem B 1(47):6495–6500
Turcheniuk K, Boukherroub R, Szunerits S (2015) Gold–graphene nanocomposites for sensing and biomedical applications. J Mater Chem B 3(21):4301–4324
Guex LG, Sacchi B, Peuvot KF, Andersson RL, Pourrahimi AM, Ström V, Farris S, Olsson RT (2017) Experimental review: chemical reduction of graphene oxide (GO) to reduced graphene oxide (rGO) by aqueous chemistry. Nanoscale 9(27):9562–9571
Chng ELK, Pumera M (2013) The toxicity of graphene oxides: dependence on the oxidative methods used. Chem Eur J 19(25):8227–8235
Hussain N, Gogoi A, Sarma RK, Sharma P, Barras A, Boukherroub R, Saikia R, Sengupta P, Das MR (2014) Reduced graphene oxide nanosheets decorated with au nanoparticles as an effective bactericide: investigation of biocompatibility and leakage of sugars and proteins. ChemPlusChem 79(12):1774–1784
Kim Y-K, Kim M-H, Min D-H (2011) Biocompatible reduced graphene oxide prepared by using dextran as a multifunctional reducing agent. Chem Commun 47(11):3195–3197
Wu L, Chu H, Koh W, Li E (2010) Highly sensitive graphene biosensors based on surface plasmon resonance. Opt Express 18(14):14395–14400
Hummers WS Jr, Offeman RE (1958) Preparation of graphitic oxide. J Am Chem Soc 80(6):1339–1339
Kim YJ, Kim JW, Lee JE, Ryu JH, Kim J, Chang IS, Suh KD (2004) Synthesis and adsorption properties of gold nanoparticles within pores of surface-functional porous polymer microspheres. J Polym Sci A Polym Chem 42(22):5627–5635
javad Assari M, Rezaee A, Rangkooy H (2015) Bone char surface modification by nano-gold coating for elemental mercury vapor removal. Appl Surf Sci 342:106–111
Shao Y, Wang J, Engelhard M, Wang C, Lin Y (2010) Facile and controllable electrochemical reduction of graphene oxide and its applications. J Mater Chem 20(4):743–748
Xiong Z, Zhang LL, Ma J, Zhao X (2010) Photocatalytic degradation of dyes over graphene–gold nanocomposites under visible light irradiation. Chem Commun 46(33):6099–6101
Zhang G, Liu Z, Fan L, Guo Y (2018) Electrochemical prostate specific antigen aptasensor based on hemin functionalized graphene-conjugated palladium nanocomposites. Microchim Acta 185(3):159
Zhao J, Guo Z, Feng D, Guo J, Wang J, Zhang Y (2015) Simultaneous electrochemical immunosensing of alpha-fetoprotein and prostate specific antigen using a glassy carbon electrode modified with gold nanoparticle-coated silica nanospheres and decorated with azure a or ferrocenecarboxylic acid. Microchim Acta 182(15–16):2435–2442
Çevik E, Bahar Ö, Şenel M, Abasıyanık MF (2016) Construction of novel electrochemical immunosensor for detection of prostate specific antigen using ferrocene-PAMAM dendrimers. Biosens Bioelectron 86:1074–1079
Oliveira N, Costa-Rama E, Viswanathan S, Delerue-Matos C, Pereira L, Morais S (2018) Label-free Voltammetric Immunosensor for prostate specific antigen detection. Electroanalysis 30(11):2604–2611. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201800417
Wang H, Zhang Y, Yu H, Wu D, Ma H, Li H, Du B, Wei Q (2013) Label-free electrochemical immunosensor for prostate-specific antigen based on silver hybridized mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Anal Biochem 434(1):123–127
Li L, Xu J, Zheng X, Ma C, Song X, Ge S, Yu J, Yan M (2014) Growth of gold-manganese oxide nanostructures on a 3D origami device for glucose-oxidase label based electrochemical immunosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 61:76–82
Akter R, Rahman MA, Rhee CK (2012) Amplified electrochemical detection of a cancer biomarker by enhanced precipitation using horseradish peroxidase attached on carbon nanotubes. Anal Chem 84(15):6407–6415
Ertürk G, Hedström M, Tümer MA, Denizli A, Mattiasson B (2015) Real-time prostate-specific antigen detection with prostate-specific antigen imprinted capacitive biosensors. Anal Chim Acta 891:120–129
Acknowledgements
The authors greatly acknowledge Bu-Ali Sina University for the financial support from the Grant Research Council.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Assari, P., Rafati, A.A., Feizollahi, A. et al. An electrochemical immunosensor for the prostate specific antigen based on the use of reduced graphene oxide decorated with gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 186, 484 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3565-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3565-8