Abstract
Two kinds of aptasensors for ampicillin (AMP) are described. The assay strategies include the use of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) that were modified with (a) a thiolated aptamer (T-Apt), and (b) a non-thiolated polyadenine aptamer (polyA Apt). The AuNPs and the aptamers were brought to interaction prior to addition of AMP. T-Apt and polyA Apt are adsorbed on the AuNPs by different mechanisms. The adsorbed aptamer was able to bind the target while preventing non-specific interactions. Remarkably different optical absorbances (measured at 520 and 680 nm) are produced the absence and presence of AMP. The assay can selectively recognize AMP even in the presence of species of similar chemical structure. The T-Apt based assay has a linear response in the 1–600 nM AMP concentration range and a 0.1 nM limit of detection. The respective data for the polyA Apt assay are 1–400 nM and 0.49 nM.

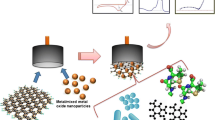
Schematic presentation of the colorimetric aptasensor for ampicillin detection using two kinds of anti-ampicillin aptamers and gold nanoparticles. Polydiallyldimethylammonium chloride (PDDA) acts as aggregation agent.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ang CYW, Luo W, Call VL, Righter HF (1997) Comparison of liquid chromatography with microbial inhibition assay for determination of incurred amoxicillin and ampicillin residues in milk. J Agric Food Chem 45:4351–4356. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf970307q
Riediker S, Diserens JM, Stadler RH (2001) Analysis of β-lactam antibiotics in incurred raw milk by rapid test methods and liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 49:4171–4176. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf010057k
Khan AAP, Mohd A, Bano S, Siddiqi KS, Asiri AM (2015) Spectrophotometric methods for the determination of ampicillin by potassium permanganate and 1-chloro-2,4-dinitrobenzene in pharmaceutical preparations. Arab J Chem 8:255–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2012.04.033
Xu LX, Wang HY, Xiao Y (2004) Spectrophotometric determination of ampicillin sodium in pharmaceutical products using sodium 1,2-naphthoquinone-4-sulfonic as the chromogentic reagent. Spectrochim Acta A 60:3007–3012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2004.02.018
Benito-pena E, Moreno-bondi M, Orellana G, Maquieira A, Amerongen AV (2005) Development of a novel and automated fluorescent immunoassay for the analysis of β-lactam antibiotics. J Agric Food Chem 53:6635–6642. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0511502
Li MJ, Jiao PC, Lin M, He WW, Chen GN, Chen X (2011) High electrochemiluminescence of a new water-soluble iridium(III) complex for determination of antibiotics. Analyst 136:205–210. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0AN00444H
Khalilzadeh MA, Khaleghi F, Gholami F, Karimi-Maleh H (2009) Electrocatalytic determination of ampicillin using carbon-paste electrode modified with ferrocendicarboxylic acid. Anal Lett 42:584–599. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032710802677126
Muhammad A, Yusof NA, Hajian R, Abdullah J (2009) Construction of an electrochemical sensor based on carbon nano tubes/gold nanoparticles for trace determination of amoxicillin in bovine milk. Sensors 16:56–61. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16010056
Deng BY, Lin W, Wang C, Li F, Wang ZX, Zhang HQ, Li XF, Le XC (2014) Aptamer binding assays for proteins: the thrombin example-a review. Anal Chim Acta 837:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2014.04.055
Phillips JA, Lopez-Colon D, Zhu Z, Xu Y, Tan WH (2008) Applications of aptamers in cancer cell biology. Anal Chim Acta 621:101–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2008.05.031
Strehlitz B, Reinemann C, Linkorn S, Stoltenburg R (2012) Aptamers for pharmaceuticals and their application in environmental analytics. Bioanal Rev 4:1–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12566-011-0026-1
Chen Ch, Zhou Sh, Cai Y, Tang F (2017) Nucleic acid aptamer application in diagnosis and therapy of colorectal cancer based on cell-SELEX technology. npj Precision Oncology 1: 37. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41698-017-0041-y
Lee KY, Kang H, Ryu SH, Lee DS, Lee JH, Kim S (2010) Bioimaging of nucleolin aptamer-containing 5-(N-benzylcarboxyamide)-2′-deoxyuridine more capable of specific binding to targets in cancer cells. J Biomed Biotechnol 2010:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/168306
Sara L, Ashwin H, Brian H, Dallas A, Kazakov SA, Jonathan AT, Sharman M, Kay J, Brendan BJ (2010) An RNA-aptamer-based assay for the detection and analysis of malachite green and leucomalachite green residues in fish tissue. Anal Chem 82:2652–2660. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac902226v
Malekzada H, Jouyban A, Hasanzadeh M, Shadjoude N, Guardiaf M (2017) Ensuring food safety using aptamer based assays: electroanalytical approach. Trends Anal Chem 94:77–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2017.07.001
Cunha I, Biltes R (2018) Aptamer-based biosensors to detect aquatic phycotoxins and cyanotoxins. Sensors 18:2367. https://doi.org/10.3390/s18072367
Hayat A, Marty JL (2014) Aptamer based electrochemical sensors for emerging environmental pollutants. Front Chem 41(2). https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2014.00041
Liu CW, Huang CC, Chang HT (2009) Highly selective DNA-based sensor for lead(II) and mercury(II) ions. Anal Chem 81:2383–2387. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac8022185
Feng CJ, Dai S, Wang L (2014) Optical aptasensors for quantitative detection of small biomolecules: a review. Biosens Bioelectron 59:64–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.03.014
Song S, Wang L, Li J, Fan C, Zhao J (2008) Aptamer-based biosensors. Trends Anal Chem 27:108–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2007.12.004
Yang Z, Qian J, Yang X, Jiang D, Du X, Wang K, Mao H, Wang K (2015) A facile label-free colorimetric aptasensor for acetamiprid based on the peroxidase-like activity of hemin-functionalized reduced graphene oxide. Biosens Bioelectron 65:39–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.10.004
Schoukroun-Barnes LR, Wagan S, White RJ (2014) Enhancing the analytical performance of electrochemical RNA aptamer-based sensors for sensitive detection of aminoglycoside antibiotics. Anal Chem 86:1131–1137. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac4029054
Walter J-G, Heilkenbrinker A, Austerjost J, Timur S, Stahl F, Scheper T (2012) Aptasensors for small molecule detection. Z Naturforsch 67b:976–986. https://doi.org/10.5560/ZNB.2012-0147
Song Y, Wei W, Qu X (2011) Colorimetric biosensing using smart materials. Adv Mater 23:4215–4236. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201101853
Doria G, Conde J, Veigas B, Giestas L, Almeida C, Assunção M, Rosa J, Baptista PV (2012) Noble metal nanoparticles for biosensing applications. Sensors 12:1657–1687. https://doi.org/10.3390/s120201657
He L, Smith EA, Natan MJ, Keating CD (2004) The distance-dependence of colloidal au-amplified surface plasmon resonance. J Phys Chem B 108:10973–10980. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp048536k
Bala R, Kumar M, Bansal K, Sharma RK, Wangoo N (2016) Ultrasensitive aptamer biosensor for malathion detection based on cationic polymer and gold nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 85:445–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.05.042
Wu Y, Liu L, Zhan S, Wang F, Zhou P (2012) Ultrasensitive aptamer biosensor for arsenic(III) detection in aqueous solution based on surfactant-induced aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Analyst 137:4171–4178. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2an35711a
Song K, Cho M, Jo H, Min K, Jeon SH, Kim T, Han MS Ku JK, Ban C (2011) Gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric detection of kanamycin using a DNA aptamer. Anal Biochem 415:175–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2011.04.007
Kim YS, Kim JH, Kim IA, Lee SJ, Jurng J, Gu MB (2010) A novel colorimetric aptasensor using gold nanoparticle for a highly sensitive and specific detection of oxytetracycline. Biosens Bioelectron 26:1644–1649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2010.08.046
Peng Y, Li L, Mu X, Guo L (2013) Aptamer-gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric assay for the sensitive detection of thrombin. Sens Actuators B Chem 177:818–825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2012.12.004
Storhoff JJ, Elghanian R, Mucic RC, Mirkin CA, Letsinger RL (1998) One-pot colorimetric differentiation of polynucleotides with single base imperfections using gold nanoparticle probes. J Am Chem Soc 120:1959–1964. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja972332i
Zhang X, Liu B, Servos MR, Liu J (2013) Polarity control for non-thiolated DNA adsorption onto gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 29:6091–6098. https://doi.org/10.1021/la400617u
Li H, Liang R, Turner DH, Rothberg LJ, Duan S (2007) Selective quenching of fluorescence from unbound oligonucleotides by gold nanoparticles as a probe of RNA structure. RNA 13:2034–2041. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.138807
Zhang J, Wang LH, Pan D, Song SP, Boey FYC, Zhang H, Fan CH (2008) Visual cocaine detection with gold nanoparticles and rationally engineered aptamer structures. Small 4:1196–1200. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.200800057
Wang Z, Lee JH, Lu Y (2008) Label-free colorimetric detection of lead ions with a nanomolar detection limit and tunable dynamic range by using gold nanoparticles and DNAzyme. Adv Mater 20:3263–3267. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200703181
Zheng X, Liu Q, Jing C, Li Y, Li D, Luo W, Wen Y, He Y, Huang Q, Long YT, Fan C (2011) Catalytic gold nanoparticles for nanoplasmonic detection of DNA hybridization. Angew Chem Int Ed 50:11994–11998. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201105121
Wang Z, Zhang J, Ekman JM, Kenis PJA, Lu Y (2010) DNA-mediated control of metal nanoparticle shape: one-pot synthesis and cellularuptake of highly stable and functional gold nanoflowers. Nano Lett 10:1886–1891. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl100675p
Rosi NL, Giljohann DA, Thaxton CS, Lytton-Jean AKR, Han MS, Mirkin CA (2006) Oligonucleotide-modified gold nanoparticles for intracellular gene regulation. Science 312:1027–1030. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1125559
Smith JE, Griffin DK, Leny JK, Hagen JA, Chávez JL, Loughnane NK (2014) Colorimetric detection with aptamer-gold nanoparticle conjugates coupled to an android-based color analysis application for use in the field. Talanta 121:247–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2013.12.062
Kim YS, Gu MB (2014) Advances in aptamer screening and small molecule aptasensors. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 140:29–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/10_2013_225
Song KM, Jeong E, Jeon W, Cho M, Ban C (2012) Aptasensor for ampicillin using gold nanoparticle based dual fluorescence–colorimetric methods. Anal Bioanal Chem 402:2153–2161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5662-3
Strong L, Whitesides GM (1988) Structures of self-assembled monolayer films of organosulfur compounds adsorbed on gold single crystals: electron diffraction studies. Langmuir 4:546–558. https://doi.org/10.1021/la00081a009
Pei H, Li F, Wan Y, Wei M, Liu H, Su Y, Chen N, Huang Q, Fan C (2012) Designed diblock oligonucleotide for the synthesis of spatially isolated and highly hybridizable functionalization of DNA-gold nanoparticle nanoconjugates. J Am Chem Soc 134:11876–11879. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja304118z
Wu Y, Zhan S, Wang F, He L, Zhia W, Zhou P (2012) Cationic polymers and aptamers mediated aggregation of gold nanoparticles for the colorimetric detection of arsenic(III) in aqueous solution. Chem Commun 48(37):4459–4461. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CC30384A
Bala R, Sharma RK, Wangoo N (2016) Development of gold nanoparticles-based aptasensor for the colorimetric detection of organophosphorus pesticide phorate. Anal Bioanal Chem 408:333–338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-9085-4
Yang Z, Dinga X, Guo Q, Wanga Y, Oub LZ, Luo Zh H, Lou X (2017) Second generation of signaling-probe displacement electrochemical aptasensor for detection of picomolar ampicillin and sulfadimethoxine. Sens Actuators B Chem 253:1129–1136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.07.119
Luo Z, Wang Y, Lu X, Chen J, Wei F, Huang Z, Zhou C, Duan Y (2017) Fluorescent aptasensor for antibiotic detection using magnetic bead composites coated with gold nanoparticles and a nicking enzyme. Anal Chim Acta 984:177–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.06.037
Zhou N, Zhang J, Tian Y (2014) Aptamer-based spectrophotometric detection of kanamycin in milk. Anal Methods 6:1569–1574. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3AY41816B
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 487 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shayesteh, O.H., Ghavami, R. Two colorimetric ampicillin sensing schemes based on the interaction of aptamers with gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 186, 485 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3524-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3524-4