Abstract
A fluorometric method is described for the detection of ampicillin. A polypyrrole containing fluorescent CdTe quantum dots was incorporated into a silica-based molecularly imprinted polymer. The composite MIP displays good fluorescence (with excitation/emission maxima at 355/548 nm), and high selectivity and affinity for ampicillin due to the use of polypyrrole. Ampicillin is found to quench the fluorescence of composite much more strongly than the emission of a non-imprinted polymer. The imprinting factor of 7.5 implies that the nanocomposite probe contains specific binding sites. The MIP probe has two linear response ranges, one from 0.10 to 25 μg L−1 of ampicillin, and one from 25 to 100 μg L−1. The limit of detection is 0.05 μg L−1. The method was applied to the determination of ampicillin in (spiked) milk and meat samples and gave recoveries between 81.7 and 98.7%. The results agreed well with HPLC techniques.

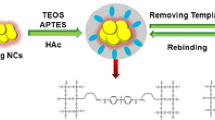
Schematic presentation of nanocomposite fluorescence probe of polypyrrole and quantum dots incorporated in a molecularly imprinted polymer. Integrating of QDs, high specificity of MIPs and high affinity of polypyrrole, the method exhibited highly sensitive and selective for ampicillin detection.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shrivas K, Sahu J, Maji P, Sinha D (2017) Label-free selective detection of ampicillin drug in human urine samples using silver nanoparticles as a colorimetric sensing probe. New J Chem 41:6685–6692. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NJ00448F
Sun L, Jia L, Xie X, Xie K, Wang J, Liu J, Cui L, Zhang G, Dai G, Wang J (2016) Quantitative analysis of amoxicillin, its major metabolites and ampicillin in eggs by liquid chromatography combined with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem 192:313–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.07.028
Paul P, Sänger-van de Griend C, Adams E, Van Schepdael A (2018) A simple, low-cost and robust capillary zone electrophoresis method with capacitively coupled contactless conductivity detection for the routine determination of four selected penicillins in money-constrained laboratories. Electrophoresis 39:2521–2529. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201800033
Wang J, Ma K, Yin H, Zhou Y, Ai S (2018) Aptamer based voltammetric determination of ampicillin using a single-stranded DNA binding protein and DNA functionalized gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 185:68–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2566-8
Yu ZG, Sutlief AL, Lai RY (2018) Towards the development of a sensitive and selective electrochemical aptamer-based ampicillin sensor. Sens Actuators B Chem 258:722–729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.11.193
Liu Y, Wang Q, Guo S, Jia P, Shui Y, Yao S, Huang C, Zhang M, Wang L (2018) Highly selective and sensitive fluorescence detection of hydroquinone using novel silicon quantum dots. Sens Actuators B Chem 275:415–421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.08.073
Zhang W, He XW, Chen Y, Li WY, Zhang YK (2011) Composite of CdTe quantum dots and molecularly imprinted polymer as a sensing material for cytochrome c. Biosens Bioelectron 26:2553–2558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2010.11.004
Canfarotta F, Czulak J, Guerreiro A, Cruz AG, Piletsky S, Bergdahl GE, Hedström M, Mattiasson B (2018) A novel capacitive sensor based on molecularly imprinted nanoparticles as recognition elements. Biosens Bioelectron 120:108–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.07.070
Carrasco S, Benito-Pena E, Navarro-Villoslada F, Langer J, Sanz-Ortiz MN, Reguera J, Liz-Marzan LM, Moreno-Bondi MC (2016) Multibranched gold-mesoporous silica nanoparticles coated with a molecularly imprinted polymer for label-free antibiotic surface-enhanced raman scattering analysis. Chem Mater 28:7947–7954. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.6b03613
Panjan P, Monasterio RP, Carrasco-Pancorbo A, Fernandez-Gutierrez A, Sesay AM, Fernandez-Sanchez JF (2018) Development of a folic acid molecularly imprinted polymer and its evaluation as a sorbent for dispersive solid-phase extraction by liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1576:26–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.09.037
Sunayama H, Ohta T, Kuwahara A, Takeuchi T (2016) Fluorescence signaling molecularly imprinted polymers for antibiotics prepared via site-directed post-imprinting introduction of plural fluorescent reporters within the recognition cavity. J Mater Chem B 4:7138–7145. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TB02000C
Urraca JL, Moreno-Bondi MC, Orellana G, Sellergren B, Hall AJ (2007) Molecularly imprinted polymers as antibody mimics in automated on-line fluorescent competitive assays. Anal Chem 79:4915–4923. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac070277i
Panahi Y, Motaharian A, Hosseini MRM, Mehrpour O (2018) High sensitive and selective nano-molecularly imprinted polymer based electrochemical sensor for midazolam drug detection in pharmaceutical formulation and human urine samples. Sens Actuators B Chem 273:1579–1586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.07.069
Gao D, Zhang Z, Wu M, Xie C, Guan G, Wang D (2007) A surface functional monomer-directing strategy for highly dense imprinting of TNT at surface of silica nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 129:7859–7866. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja070975k
Dabrowski M, Lach P, Cieplak M, Kutner W (2018) Nanostructured molecularly imprinted polymers for protein chemosensing. Biosens Bioelectron 102:17–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.10.045
Sorribes-Soriano A, Esteve-Turrillas FA, Armenta S, Montoya A, Herrero-Martínez JM, De la Guardia M (2018) Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for the selective determination of cocaine by ion mobility spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1545:22–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.02.055
Ekomo VM, Branger C, Bikanga R, Florea AM, Istamboulie G, Calas-Blanchard C, Noguer T, Sarbu A, Brisset H (2018) Detection of bisphenol a in aqueous medium by screen printed carbon electrodes incorporating electrochemical molecularly imprinted polymers. Biosens Bioelectron 112:156–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.04.022
Chullasat K, Nurerk P, Kanatharana P, Davis F, Bunkoed O (2018) A facile optosensing protocol based on molecularly imprinted polymer coated on CdTe quantum dots for highly sensitive and selective amoxicillin detection. Sens Actuators B Chem 254:255–263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.07.062
Amjadi M, Jalili R, Manzoori JL (2016) A sensitive fluorescent nanosensor for chloramphenicol based on molecularly imprinted polymer-capped CdTe quantum dots. Luminescence 31:633–639. https://doi.org/10.1002/bio.3003
Raksawong P, Chullasat K, Nurerk P, Kanatharana P, Davis F, Bunkoed O (2017) A hybrid molecularly imprinted polymer coated quantum dot nanocomposite optosensor for highly sensitive and selective determination of salbutamol in animal feeds and meat samples. Anal Bioanal Chem 409:4697–4707. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0466-8
Nezhadali A, Mehri L, Shadmehri R (2018) Determination of methimazole based on electropolymerized-molecularly imprinted polypyrrole modified pencil graphite sensor. Mater Sci Eng C 85:225–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2017.05.099
Meng J, Bu J, Deng C, Zhang X (2011) Preparation of polypyrrole-coated magnetic particles for micro solid-phase extraction of phthalates in water by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis. J Chromatogr A 1218:1585–1591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2011.01.057
Bunkoed O, Kanatharana P (2015) Mercaptopropionic acid-capped CdTe quantum dots as fluorescence probe for the determination of salicylic acid in pharmaceutical products. Luminescence 30:1083–1089. https://doi.org/10.1002/bio.2862
Wu N, Luo Z, Ge Y, Guo P, Du K, Tang W, Du W, Zeng A, Chang C, Fu Q (2016) A novel surface molecularly imprinted polymer as the solid-phase extraction adsorbent for the selective determination of ampicillin sodium in milk and blood samples. J Pharm Anal 6:157–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2016.01.004
Luo W, Ang CYW, Thompson HC Jr (1997) Rapid method for the determination of ampicillin residues in animal muscle tissues by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr B 694:401–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-4347(97)00171-0
Nurerk P, Kanatharana P, Bunkoed O (2016) A selective determination of copper ions in water samples based on the fluorescence quenching of thiol-capped CdTe quantum dots. Luminescence 31:515–522. https://doi.org/10.1002/bio.2990
Liu H, Wu D, Zhou K, Wang J, Sun B (2016) Development and applications of molecularly imprinted polymers based on hydrophobic CdSe/ZnS quantum dots for optosensing of Nϵ-carboxymethyllysine in foods. Food Chem 211:34–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.05.038
Ortiz SNC, Ospino EM, Cabanzo R (2016) Spectroscopy characterization and quantum yield determination of quantum dots. J Phys Conf Ser 687 http://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1742-6596/687/1/012097
Wang HF, He Y, Ji TR, Yan XP (2009) Surface molecular imprinting on Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots for room-temperature phosphorescence optosensing of pentachlorophenol in water. Anal Chem 81:1615–1621. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac802375a
Xie K, Jia L, Xu D, Guo H, Xie X, Huang Y, Chen X, Bao W, Dai G, Wang J (2012) Simultaneous determination of amoxicillin and ampicillin in eggs by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection using pre-column derivatization. J Chromatogr Sci 50:620–624. https://doi.org/10.1093/chromsci/bms052
Luo W, Hansen EB Jr, Ang CYW, Deck J, Freeman JP, Thompson HC Jr (1997) Simultaneous determination of amoxicillin and ampicillin in bovine Milk by HPLC with fluorescence detection. J Agri Food Chem 45:1264–1268. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf960739l
Soledad-Rodríguez B, Fernández-Hernando P, Garcinuño-Martínez RM, Durand-Alegría JS (2017) Effective determination of ampicillin in cow milk using a molecularly imprinted polymer as sorbent for sample preconcentration. Food Chem 224:432–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.11.097
Khalilzadeh MA, Khaleghi F, Gholami F, Karimi-Maleh H (2009) Electrocatalytic determination of ampicillin using carbon-paste electrode modified with ferrocendicarboxylic acid. Anal Lett 42:584–599. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032710802677126
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the government budget of Prince of Songkla University (SCI6301030S-0) and (SCI6202115N), the Thailand research fund, Office of the Higher Education Commission, Science Achievement Scholarship of Thailand (SAST) and Center of Excellence for Innovation in Chemistry (PERCH-CIC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1010 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raksawong, P., Nurerk, P., Chullasat, K. et al. A polypyrrole doped with fluorescent CdTe quantum dots and incorporated into molecularly imprinted silica for fluorometric determination of ampicillin. Microchim Acta 186, 338 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3447-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3447-0