Abstract
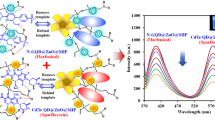
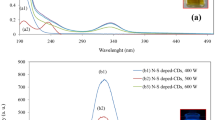
A hybrid molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP)-coated quantum dot (QD) nanocomposite was synthesized and applied as a fluorescence probe for the highly sensitive and selective determination of salbutamol. The hybrid MIP-coated QD nanocomposite was synthesized via a copolymerization process in the presence of thioglycolic acid capped CdTe QDs with salbutamol as a template, 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane as the functional monomer, and tetraethyl orthosilicate as a cross-linker. The optimum molar ratio of template, monomer, and cross-linker was 1:6:20. The fluorescence intensity of the hybrid MIP-coated QDs was efficiently quenched after salbutamol rebound to the recognition sites, as a result of charge transfer from QDs to salbutamol. The synthesized hybrid MIP-coated QD nanocomposite showed high sensitivity and good selectivity toward salbutamol. Under the optimal recognition conditions, the fluorescence intensity was quenched linearly with increasing concentration of salbutamol in the range from 0.10 to 25.0 μg L-1, with a detection limit of 0.034 μg L-1. The hybrid optosensor developed was successfully applied in the determination of salbutamol in animal feeds and meat samples. Satisfactory recoveries were obtained in the range from 85% to 98%, with a standard deviation of less than 8%. Furthermore, the accuracy of the hybrid MIP-coated QD nanocomposite was investigated by comparison with a conventional high-performance liquid chromatography method, with the results obtained with two methods agreeing well with each other. The advantages of this sensing method are simplicity, rapidity, cost-effectiveness, high sensitivity, and good selectivity.

The synthesis of hybrid MIP-coated QDs nanocomposite







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sheu SY, Lei YC, Tai YT, Chang TH, Kuo TF. Screening of salbutamol residues in swine meat and animal feed by an enzyme immunoassay in Taiwan. Anal Chim Acta. 2009;654:148–53.
Li C, Wu YL, Yang T, Zhang Y, Huang-Fu WG. Simultaneous determination of clenbuterol, salbutamol and ractopamine in milk by reversed-phase liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry with isotope dilution. J Chromatogr A. 2010;1217:7873–7.
Cai F, Wang N, Dong T, Deng A, Li J. Dual-signal amplified electrochemiluminescence immunoassay for salbutamol based on quantum dots and gold nanoparticle-labeled horseradish peroxidase. Analyst. 2015;140:5885–90.
Chu L, Zheng S, Qu B, Geng S, Kang X. Detection of β-agonists in pork tissue with novel electrospun nanofibers-based solid-phase extraction followed ultra-high performance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2017;227:315–21.
Brambilla G, Cenci T, Franconi F, Galarini R, Macrì A, Rondoni F, et al. Clinical and pharmacological profile in a clenbuterol epidemic poisoning of contaminated beef meat in Italy. Toxicol Lett. 2000;114:47–53.
Noosang S, Bunkoed O, Thavarungkul P, Kanatharana P. New sulfonate composite functionalized with multiwalled carbon nanotubes with cryogel solid-phase extraction sorbent for the determination of β-agonists in animal feeds. J Sep Sci. 2015;38:1951–58.
Chan SH, Lee W, Asmawi MZ, Tan SC. Chiral liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method development for the detection of salbutamol in urine samples. J Chromatogr B. 2016;1025:83–91.
Kulikovskii AV, Lisitsyn AB, Gorlov IF, Slozhenkina MI, Savchuk SA. Determination of growth hormones (β-agonists) in muscle tissue by HPLC with mass spectrometric detection. J Anal Chem. 2016;71:1052–6.
Liu H, Gan N, Chen Y, Ding Q, Huang J, Lin S, et al. Novel method for the rapid and specific extraction of multiple β-agonist residues in food by tailor-made monolith-MIPs extraction disks and detection by gas chromatography with mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci. 2016;39:3578–85.
Li J, Xu Z, Liu M, Deng P, Tang S, Jiang J, et al. Ag/N-doped reduced graphene oxide incorporated with molecularly imprinted polymer: an advanced electrochemical sensing platform for salbutamol determination. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;90:210–6.
Wang H, Zhang Y, Li H, Du B, Ma H, Wu D, et al. A silver-palladium alloy nanoparticle-based electrochemical biosensor for simultaneous detection of ractopamine, clenbuterol and salbutamol. Biosens Bioelectron. 2013;49:14–9.
Chen D, Yang M, Zheng N, Xie N, Liu D, Xie C, et al. A novel aptasensor for electrochemical detection of ractopamine, clenbuterol, salbutamol, phenylethanolamine and procaterol. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016;80:525–31.
Nguyen TA, Pham TN, Doan TT, Ta TT, Saiz J, Nguyen TQ, et al. Simple semi-automated portable capillary electrophoresis instrument with contactless conductivity detection for the determination of beta-agonists in pharmaceutical and pig-feed samples. J Chromatogr A. 2014;1360:305–11.
Lodén H, Pettersson C, Arvidsson T, Amini A. Quantitative determination of salbutamol in tablets by multiple-injection capillary zone electrophoresis. J Chromatogr A. 2008;1207:181–5.
Chen Q, Fan LY, Zhang W, Cao CX. Separation and determination of abused drugs clenbuterol and salbutamol from complex extractants in swine feed by capillary zone electrophoresis with simple pretreatment. Talanta. 2008;76:282–7.
Wei JR, Ni YL, Zhang W, Zhang ZQ, Zhang J. Detection of glycoprotein through fluorescent boronic acid-based molecularly imprinted polymer. Anal Chim Acta. 2017;960:110–6.
Urano Y, Kamiya M, Kanda K, Ueno T, Hirose K, Nagano T. Evolution of fluorescein as a platform for finely tunable fluorescence probes. J Am Chem Soc. 2005;127:4888–94.
Lu Z, Chen X, Hu W. A fluorescence aptasensor based on semiconductor quantum dots and MoS2 nanosheets for ochratoxin A detection. Sens Actuators B. 2017;246:61–7.
Doughan S, Uddayasankar U, Peri A, Krull UJ. A paper-based multiplexed resonance energy transfer nucleic acid hybridization assay using a single form of upconversion nanoparticle as donor and three quantum dots as acceptors. Anal Chim Acta. 2017;962:88–96.
Madrakian T, Maleki S, Afkhami A. Surface decoration of cadmium-sulfide quantum dots with 3-mercaptopropionic acid as a fluorescence probe for determination of ciprofloxacin in real samples. Sens Actuators B. 2017;243:14–21.
Zhou Z, Li T, Xu W, Huang W, Wang N, Yang W. Synthesis and characterization of fluorescence molecularly imprinted polymers as sensor for highly sensitive detection of dibutyl phthalate from tap water samples. Sens Actuators B. 2017;240:1114–22.
Zhou Z, Ying H, Liu Y, Xu W, Yang Y, Luan Y, et al. Synthesis of surface molecular imprinting polymer on SiO2-coated CdTe quantum dots as sensor for selective detection of sulfadimidine. Appl Surf Sci. 2017;404:188–96.
Bali Prasad B, Kumar A, Singh R. Synthesis of novel monomeric graphene quantum dots and corresponding nanocomposite with molecularly imprinted polymer for electrochemical detection of an anticancerous ifosfamide drug. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;94:1–9.
Luo J, Huang J, Wu Y, Sun J, Wei W, Liu X. Synthesis of hydrophilic and conductive molecularly imprinted polyaniline particles for the sensitive and selective protein detection. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;94:39–46.
Nandy Chatterjee T, Banerjee Roy R, Tudu B, Pramanik P, Deka H, Tamuly P, et al. Detection of theaflavins in black tea using a molecular imprinted polyacrylamide-graphite nanocomposite electrode. Sens Actuators B. 2017;246:840–7.
Yáñez-Sedeño P, Campuzano S, Pingarrón JM. Electrochemical sensors based on magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal Chim Acta. 2017;960:1–17.
Ashley J, Shahbazi MA, Kant K, Chidambara VA, Wolff A, Bang DD, et al. Molecularly imprinted polymers for sample preparation and biosensing in food analysis: progress and perspectives. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;91:606–15.
Barciela-Alonso MC, Otero-Lavandeira N, Bermejo-Barrera P. Solid phase extraction using molecular imprinted polymers for phthalate determination in water and wine samples by HPLC-ESI-MS. Microchem J. 2017;132:233–7.
Guo XC, Xia ZY, Wang HH, Kang WY, Lin LM, Cao WQ, et al. Molecularly imprinted solid phase extraction method for simultaneous determination of seven nitroimidazoles from honey by HPLC-MS/MS. Talanta. 2017;166:101–8.
González-Vila Á, Debliquy M, Lahem D, Zhang C, Mégret P, Caucheteur C. Molecularly imprinted electropolymerization on a metal-coated optical fiber for gas sensing applications. Sens Actuators B. 2017;244:1145–51.
Lopes F, Pacheco JG, Rebelo P, Delerue-Matos C. Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor prepared on a screen printed carbon electrode for naloxone detection. Sens Actuators B. 2017;243:745–52.
Xiao L, Zhang Z, Wu C, Han L, Zhang H. Molecularly imprinted polymer grafted paper-based method for the detection of 17β-estradiol. Food Chem. 2017;221:82–6.
Nurerk P, Kanatharana P, Bunkoed O. A selective determination of copper ions in water samples based on the fluorescence quenching of thiol-capped CdTe quantum dots. Luminescence. 2016;31:515–22.
Bunkoed O, Kanatharana P. Mercaptopropionic acid-capped CdTe quantum dots as fluorescence probe for the determination of salicylic acid in pharmaceutical products. Luminescence. 2015;30:1083–9.
Liu B, Yan H, Qiao F, Geng Y. Determination of clenbuterol in porcine tissues using solid-phase extraction combined with ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and HPLC-UV detection. J Chromatogr B. 2011;879:90–4.
Nath B, Nath LK, Mazumder B, Kumar P, Sharma N, Sahu BP. Preparation and characterization of salbutamol sulphate loaded ethyl cellulose microspheres using water-in-oil-oil emulsion technique. Iran J Pharm Res. 2010;9:97–105.
Xiu-Juan W, Feng Z, Fei D, Wei-Qing L, Qing-Yu C, Xiao-Gang C, et al. Simultaneous determination of 12 β-agonists in feeds by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2013;1278:82–8.
Xu M, Qian X, Zhao K, Deng A, Li J. Flow injection chemiluminescent competitive immunoassay for the β-adrenergic agonist salbutamol using carboxylic resin beads and enzymatic amplification. Sens Actuators B. 2015;215:323–9.
Tang J, Liu Z, Kang J, Zhang Y. Determination of salbutamol using R-phycoerythrin immobilized on eggshell membrane surface as a fluorescence probe. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010;397:3015–22.
Gao H, Han J, Yang S, Wang Z, Wang L, Fu Z. Highly sensitive multianalyte immunochromatographic test strip for rapid chemiluminescent detection of ractopamine and salbutamol. Anal Chim Acta. 2014;839:91–6.
Zhang G, Tang Y, Shang J, Wang Z, Yu H, Du W, et al. Flow-injection chemiluminescence method to detect a β2 adrenergic agonist. Luminescence. 2015;30:102–9.
Chen Z, Zhang L, Lu Q, Ye Q, Zhang L. On-line concentration and pressurized capillary electrochromatography analysis of five β-agonists in human urine using a methacrylate monolithic column. Electrophoresis. 2015;36:2720–6.
Sirichai S, Khanatharana P. Rapid analysis of clenbuterol, salbutamol, procaterol, and fenoterol in pharmaceuticals and human urine by capillary electrophoresis. Talanta. 2008;76:1194–8.
Guo XC, Wang HH, Chen XJ, Xia ZY, Kang WY, Zhou WH. One step electrodeposition of graphene-au nanocomposites for highly sensitive electrochemical detection of salbutamol. Int J Electrochem Sci. 2017;12:861–75.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the budget revenue of Prince of Songkla University (SCI600559S), the Thailand Research Fund, Office of the Higher Education Commission, Center for Innovation in Chemistry (PERCH–CIC), Science Achievement Scholarship of Thailand (SAST), and Trace Analysis and Biosensor Research Center, Faculty of Science, Prince of Songkla University, Hat Yai, Thailand. K.C. was supported by Scholarship Awards Thai Ph.D. students under Thailand’s Education Hub for Southern Region of ASEAN Countries.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 606 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raksawong, P., Chullasat, K., Nurerk, P. et al. A hybrid molecularly imprinted polymer coated quantum dot nanocomposite optosensor for highly sensitive and selective determination of salbutamol in animal feeds and meat samples. Anal Bioanal Chem 409, 4697–4707 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0466-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0466-8