Abstract
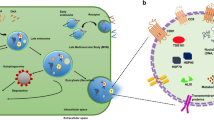
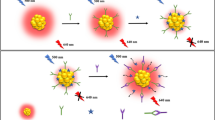
An improved enzyme-free immunosorbent assay is described for the simultaneous detection of the myocardial infarction biomarkers N-terminal pro B type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB), and cardiac muscle troponin T (cTnT). The assay integrates 3D gold nanovesicles (GNVs) and three allochroic agents (phenolphthalein, methyl red, bromothymol blue). The pH regulated allochroic agents were enwrapped in GNVs to acts as ultrasensitive nanoprobes. Loading can be controlled by adjusting the temperature to efficiently load and release the allochroic agents. This bare-eye multicolor assay has limits of detection of 70 pg·mL−1 for NT-proBNP, 910 pg·mL−1 for CK-MB, and 7.8 pg·mL−1 for cTnT. Other features include (a) a linear range that extends over a wide range and sometimes is better than conventional HRP-based immunoassays, and (b) a precision that is comparable to immunofluorescence assays as used in the clinical laboratory.

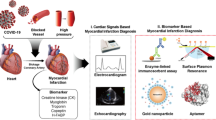
Schematic presentation of an improved enzyme-free immunosorbent assay (EFISA). It integrates 3D gold nano-vesicles (GNVs) and allochroic agents for the simultaneous detection of acute myocardial infarction (AMI) biomarkers (N-terminal prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), kinase-muscle/brain test (CK-MB), and cardiac muscle troponin (cTnT)).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auer J, Berent R, Lassnig E, Eber B (2003) C-reactive protein and coronary artery disease. Japan Heart J 43(6):607–619
Horvath AR, Lord SJ, Stjohn A, Sandberg S, Cobbaert CM, Lorenz S, Monaghan PJ, Verhagen-Kamerbeek WDJ, Ebert C, Bossuyt PMM (2014) From biomarkers to medical tests: the changing landscape of test evaluation. Clin Chim Acta 427(1):49–57
Jaruvongvanich V, Rattanadech W, Damkerngsuntorn W, Jaruvongvanich S, Vorasettakarnkij Y (2015) CK-MB activity, any additional benefit to negative troponin in evaluating patients with suspected acute myocardial infarction in the emergency department. J Med Assoc Thail 98(10):935–941
Gerhardt W, Ljungdahl L (1998) Troponin T: a sensitive and specific diagnostic and prognostic marker of myocardial damage. Clin Chim Acta 272(1):47–57
Hunt PJ, Richards AM, Nicholls MG, Yandle TG, Doughty RN, Espiner EA (2010) Immunoreactive amino-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-PROBNP): a new marker of cardiac impairment. Clin Endocrinol 47(3):287–296
Shao M, Huang C, Li Z, Yang H, Feng Q (2015) Effects of glutamine and valsartan on the brain natriuretic peptide and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide of patients with chronic heart failure. Pak J Med Sci 31(1):82
Li X, Chen C, Gan F, Wang Y, Ding L, Hua W (2014) Plasma NT pro-BNP, hs-CRP and big-ET levels at admission as prognostic markers of survival in hospitalized patients with dilated cardiomyopathy: a single-center cohort study. J Am Coll Cardiol 14(16):67–67
Fan J, Ma J, Xia N, Sun L, Li B, Liu H (2017) Clinical value of combined detection of CK-MB, MYO, cTnI and plasma NT-proBNP in diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. Clin Lab 63(3):427–433
Liang Y, Huang X, Chen X, Zhang W, Ping G, Xiong Y (2018) Plasmonic ELISA for naked-eye detection of ochratoxin a based on the tyramine-H2O2 amplification system. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 259:162–169
Zhang LZ, Wang YL, Hua-Mei LU, Jian-Liang LI, Feng HU, Fu-Jin LI, Xiao YQ, Huang B, Cui YS (2018) Development of an indirect ELISA for detecting antibodies against rabbit haemorrhagic disease virus. Chin J Prev Vet Med
Pestka JJ, Azconaolivera JI, Plattner RD, Minervini F, Doko MB, Visconti A (2016) Comparative assessment of fumonisin in grain-based foods by ELISA, GC-MS, and HPLC. J Food Prot 57(2):169–172(4)
Zhao LJ, Yu RJ, Ma W, Han HX, Tian H, Qian RC, Long YT (2017) Sensitive detection of protein biomarkers using silver nanoparticles enhanced immunofluorescence assay. Theranostics 7(4):876–883
Sheng W, Chang Q, Shi Y, Duan W, Zhang Y, Wang S (2018) Visual and fluorometric lateral flow immunoassay combined with a dual-functional test mode for rapid determination of tetracycline antibiotics. Microchim Acta 185(9):404
Ren S, Li Y, Guo Q, Peng Y, Bai J, Ning B, Gao Z (2018) Turn-on fluorometric immunosensor for diethylstilbestrol based on the use of air-stable polydopamine-functionalized black phosphorus and upconversion nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 185(9):429
Lv H, Li Y, Zhang X, Gao Z, Zhang C, Zhang S, Dong Y (2018) Enhanced peroxidase-like properties of au@Pt DNs/NG/cu 2+ and application of sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor for highly sensitive detection of CEA. Biosens Bioelectron 112:1–7
Suresh L, Brahman PK, Reddy KR, JS B (2018) Development of an electrochemical immunosensor based on gold nanoparticles incorporated chitosan biopolymer nanocomposite film for the detection of prostate cancer using PSA as biomarker. Enzyme Microb Tech 112:43–51
Liu N, Yi H, Lin Y, Zheng H, Zheng X, Lin D, Dai H (2018) Combined electrochemiluminescent and electrochemical immunoassay for interleukin 6 based on the use of TiO2 mesocrystal nanoarchitectures. Microchim Acta 185(5):277
Lequin RM (2005) Enzyme immunoassay (EIA)/enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Clin Chem 51(12):2415–2418
Liu Q, Aroonyadet N, Song Y, Wang X, Cao X, Liu Y, Cong S, Wu F, Thompson ME, Zhou C (2016) Highly sensitive and quick detection of acute myocardial infarction biomarkers using In2O3 nanoribbon biosensors fabricated using shadow masks. ACS Nano 10(11):10117–10125
Radha Shanmugam N, Muthukumar S, Chaudhry S, Anguiano J, Prasad S (2017) Ultrasensitive nanostructure sensor arrays on flexible substrates for multiplexed and simultaneous electrochemical detection of a panel of cardiac biomarkers. Biosens Bioelectron 89(Pt 2):764–772
Li Y, Wu J, Zhang C, Chen Y, Wang Y, Xie M (2017) Manganese dioxide nanoparticle-based colorimetric immunoassay for the detection of alpha-fetoprotein. Microchim Acta 184(8):1–8
Dehghani Z, Hosseini M, Mohammadnejad J, Bakhshi B, Rezayan AH (2018) Colorimetric aptasensor for campylobacter jejuni cells by exploiting the peroxidase like activity of au@Pd nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 185(10):448
Yigit MV, Nandu N, Hizir MS (2018) Masking the peroxidase-like activity of MoS2 nanozyme enables label-free lipase detection. ACS Central Sci 4(7):862–867
Liang H, Jingwen YE, Jiali LI, Chen C, Guo X, Liu X, Zhong S, Jiexing LI, Laiqing LI (2018) Development and effectiveness evaluation of double label time resolved immunofluorescence assay kit for detection of CEA and NMP22 for bladder cancer. J Mol Imaging
Pan LH, Pang ST, Fang PY, Chuang CK, Yang HW (2017) Label-free biochips for accurate detection of prostate Cancer in the clinic: dual biomarkers and circulating tumor cells. Theranostics 7(17):4289–4300
Ren X, Ma H, Zhang T, Zhang Y, Yan T, Du B, Wei Q (2017) Sulfur-doped graphene-based immunological biosensing platform for multianalysis of Cancer biomarkers. ACS Appl Mater Inte 9(43):37637–37644
Cheng Z, Choi N, Wang R, Lee S, Moon KC, Yoon SY, Chen L, Choo J (2017) Simultaneous detection of dual prostate specific antigens using surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based immunoassay for accurate diagnosis of prostate Cancer. ACS Nano 11(5):4926–4933
Li C, Yang Y, Wu D, Li T, Yin Y, Li G (2016) Improvement of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the multicolor detection of biomarkers. Chem Sci 7(5):3011–3016
Jin HJ, Lee SH, Kim TH, Park J, Song HS, Park TH, Hong S (2012) Nanovesicle-based bioelectronic nose platform mimicking human olfactory signal transduction. Biosens Bioelectron 35(1):335–341
Liu JM, Zhang DD, Fang GZ, Wang S (2018) Erythrocyte membrane bioinspired near-infrared persistent luminescence nanocarriers for in vivo long-circulating bioimaging and drug delivery. Biomaterials 165:39–47
George J, Hayashi N, Saito T, Ozaki K, Toshikuni N, Tsuchishima M, Tsutsumi M (2017) Nanovesicle mediated delivery of combination of anticancer agents effectively induced cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. J Hepatol 66(1):S462
Yi C, Zhang S, Webb KT, Nie Z (2017) Anisotropic self-assembly of hairy inorganic nanoparticles. Accounts Chem Res 50(1):12–21
Liu Y, He J, Yang K, Yi C, Liu Y, Nie L, Khashab NM, Chen X, Nie Z (2015) Folding up of gold nanoparticle strings into Plasmonic vesicles for enhanced photoacoustic imaging. Angew Chem Int Edit 54(52):15809–15812
Song J, Zhou J, Duan H (2012) Self-assembled plasmonic vesicles of SERS-encoded amphiphilic gold nanoparticles for cancer cell targeting and traceable intracellular drug delivery. J Am Chem Soc 134(32):13458–13469
Acknowledgements
This research work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81672112, 81702101), Chongqing Technology Innovation and Application Demonstration Project (cstc2018jscx-msybX0010) and Key Project of Education Department of Sichuan(No. 16ZA0181).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 1682 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pu, Q., Yang, X., Guo, Y. et al. Simultaneous colorimetric determination of acute myocardial infarction biomarkers by integrating self-assembled 3D gold nanovesicles into a multiple immunosorbent assay. Microchim Acta 186, 138 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3242-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3242-y