Abstract
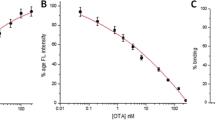
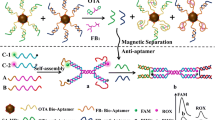
A fluorometric aptamer-based assay for ochratoxin A (OTA) is described. It is making use of magnetic separation and a cationic conjugated fluorescent polymer. Amino-tagged aptamer (Apt) against OTA is immobilized on magnetic beads (MBs) to form a conjugate of type Apt-MBs. The immobilized aptamer is partially complementary to carboxyfluorescein-labeled DNA which binds to the Apt-MBs via hybridization if OTA is absent. Only few FAM-DNA will remain in the supernatant after magnetic separation, and only weak fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) occurs on addition of the fluorescent polymer. If, however, OTA is present, it will bind to the aptamer and prevent the hybridization between Apt-DNA and FAM-DNA. This results in the presence of large amounts of FAM-DNA in the supernatant after magnetic separation. On addition of fluorescent polymer, efficient FRET occurs from the polymer to FAM-DNA. Fluorescence, best measured at excitation/emission peaks of 370/530 nm, increases with increasing concentrations of OTA. This assay is highly sensitive and selective. The detection limit is as low as 0.11 ng mL−1. This is 6 times lower than the aptamer assay without using the fluorescent polymer. Conceivably, this method has a wider scope in that it may be extended to other mycotoxins by simply changing the aptamer.

Schematic of a fluorometric aptamer assay for ochratoxin A (OTA). It is based on magnetic separation coupled with a cationic conjugated polymer (PFP).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pfohl-Leszkowicz A, Manderville RA (2007) Ochratoxin a: an overview on toxicity and carcinogenicity in animals and humans. Mol Nutr Food Res 51:61–99
Imperato R, Campone L, Piccinelli AL, Veneziano A, Rastrelli L (2011) Survey of aflatoxins and ochratoxin a contamination in food products imported in Italy. Food Control 22:1905–1910
Campone L, Piccinelli AL, Celano R, Pagano I, Russo M, Rastrelli L (2018) Rapid and automated on-line solid phase extraction HPLC-MS/MS with peak focusing for the determination of ochratoxin a in wine samples. Food Chem 244:128–135
Amézqueta S, González-Peñas E, Murillo-Arbizu M, López de Cerain A (2009) Ochratoxin a decontamination: a review. Food Control 20:326–333
Li F, Zhang H, Wang Z, Newbigging AM, Reid MS, Li XF, Le XC (2015) Aptamers facilitating amplified detection of biomolecules. Anal Chem 87:274–292
Wu S, Duan N, Ma X, Xia Y, Wang H, Wang Z, Zhang Q (2012) Multiplexed fluorescence resonance energy transfer aptamer assay between upconversion nanoparticles and graphene oxide for the simultaneous determination of mycotoxins. Anal Chem 84:6263–6270
Zhang J, Zhang X, Yang G, Chen J, Wang S (2013) A signal-on fluorescent aptamer assay based on Tb3+ and structure-switching aptamer for label-free detection of Ochratoxin a in wheat. Biosens Bioelectron 41:704–709
Bianco M, Sonato A, De Girolamo A, Pascale M, Romanato F, Rinaldi R, Arima V (2017) An aptamer-based SPR-polarization platform for high sensitive OTA detection. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 241:314–320
Lin C, Zheng H, Sun M, Guo Y, Luo F, Guo L, Qiu B, Lin Z, Chen G (2018) Highly sensitive colorimetric aptamer assay for ochratoxin a detection based on enzyme-encapsulated liposome. Anal Chim Acta 1002:90–96
Lu Z, Chen X, Hu W (2017) A fluorescence aptamer assay based on semiconductor quantum dots and MoS2 nanosheets for ochratoxin a detection. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 246:61–67
Wu H, Liu R, Kang X, Liang C, Lv L, Guo Z (2018) Fluorometric aptamer assay for ochratoxin a based on the use of single walled carbon nanohorns and exonuclease III-aided amplification. Microchim Acta 185:1–27
Mahdi M, Mansour B, Afshin M (2016) Competitive immunoassay for ochratoxin a based on FRET from quantum dot-labeled antibody to rhodamine-coated magnetic silica nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 183:3093–3099
Lv L, Cui C, Liang C, Quan W, Wang S, Guo Z (2016) Aptamer-based single-walled carbon nanohorn sensors for ochratoxin a detection. Food Control 60:296–301
Feng J, Li Y, Gao Z, Lv H, Zhang X, Fan D, Wei Q (2018) Visible-light driven label-free photoelectrochemical immunosensor based on TiO2/S-BiVO4@Ag2S nanocomposites for sensitive detection OTA. Biosens Bioelectron 99:14–20
Zhang C, Tang J, Huang L (2017) In-situ amplified voltammetric immunoassay for ochratoxin a by coupling a platinum nanocatalyst based enhancement to a redox cycling process promoted by an enzyme mimic. Microchim Acta 184:2445–2453
Zhao Y, Liu R, Sun W, Lv L, Guo Z (2018) Ochratoxin a detection platform based on signal amplification by exonuclease III and fluorescence quenching by gold nanoparticles. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 255:1640–1645
Yuan Y, Wei S, Liu G, Xie S, Chai Y, Yuan R (2014) Ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescent aptamer assay for ochratoxin a detection with the loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Anal Chim Acta 811:70–75
Lv L, Li D, Cui C, Zhao Y, Guo Z (2017) Nuclease-aided target recycling signal amplification strategy for ochratoxin a monitoring. Biosens Bioelectron 87:136–141
Huang L, Wu J, Zheng L, Qian H, Xue F, Wu Y, Pan D, Adeloju SB, Chen W (2013) Rolling chain amplification based signal-enhanced electrochemical aptamer assay for ultrasensitive detection of ochratoxin a. Anal Chem 85:10842–10849
Wang B, Wu Y, Chen Y, Weng B, Xu L, Li C (2016) A highly sensitive aptamer assay for OTA detection based on hybridization chain reaction and fluorescent perylene probe. Biosens Bioelectron 81:125–130
Wang C, Dong X, Liu Q, Wang K (2015) Label-free colorimetric aptamer assay for sensitive detection of ochratoxin a utilizing hybridization chain reaction. Anal Chim Acta 860:83–88
Zhang Z, Xia X, Xiang X, Huang F, Han L (2018) Quantum dots-Ru complex assembling dyads for cancer cell detection and cellular imaging based on hybridization chain reaction. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 257:1–8
Wang J, Xiong G, Ma L, Wang S, Zhou X, Wang L, Xiao L, Su X, Yu C (2017) A dynamic sandwich assay on magnetic beads for selective detection of single-nucleotide mutations at room temperature. Biosens Bioelectron 94:305–311
Zhang Y, Xue Q, Liu J, Wang H (2017) Magnetic bead-liposome hybrids enable sensitive and portable detection of DNA methyltransferase activity using personal glucose meter. Biosens Bioelectron 87:537–544
Luo M, Feng Y, Wang J, Guan J (2018) Micro-/Nanorobots at work in active drug delivery. Adv Funct Mater 1706100
Zhang Z, Xia X, Xiang X, Huang F, Han L (2017) Conjugated cationic polymer-assisted amplified fluorescent biosensor for protein detection via terminal protection of small molecule-linked DNA and graphene oxide. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 249:8–13
Xing XJ, Liu XG, He Y, Lin Y, Zhang CL, Tang HW, Pang DW (2013) Amplified fluorescent sensing of DNA using graphene oxide and a conjugated cationic polymer. Biomacromolecules 14:117–123
Liu YF, Gao LY, Yan HJ, Shangguan JF, Zhang Z, Xiang X (2018) A cationic conjugated polymer coupled with exonuclease I: application to the fluorometric determination of protein and cell imaging. Microchim Acta 185:118
Tian JY, Wei WQ, Wang JW, Ji SJ, Chen GC, Lu JS (2018) Fluorescence resonance energy transfer aptasensor between nanoceria and graphene quantum dots for the determination of ochratoxin a. Anal Chim Acta 1000:265–272
Liu RD, Huang YS, Ma YL, Jia SS, Gao MX, Li JX, Zhang HM, Xu DM, Wu M, Chen Y, Zhu Z, Yang CY (2015) Design and synthesis of target-responsive aptamer-cross-linked hydrogel for visual quantitative detection of ochratoxin a. ACS Appl Mater Inter 7:6982–6990
Rivas L, Mayorga-Martinez CC, Quesada-González D, Zamora-Gálvez A, Escosura-Muñiz A, Merkoçi A (2015) Label-free impedimetric aptasensor for ochratoxin-a detection using iridium oxide nanoparticles. Anal Chem 87:5167–5172
Zhao Q, Lv Q, Wang HL (2014) Identification of allosteric nucleotide sites of tetramethylrhodamine-labeled aptamer for noncompetitive aptamer-based fluorescence anisotropy detection of a small molecule, ochratoxin a. Anal Chem 86:1238–1245
Lu LH, Wang MD, Liu LJ, Leung CH, Ma DL (2015) Label-free luminescent switch-on probe for ochratoxin a detection using a G-quadruplex-selective iridium (III) complex. ACS Appl Mater Inter 7:8313–8318
Wang CK, Tan R, Chen D (2018) Fluorescence method for quickly detecting ochratoxin a in flour and beer using nitrogen doped carbon dots and silver nanoparticles. Talanta 182:363–370
Pei K, Xiong Y, Xu BL, Wu KS, Li XM, Jiang H, Xiong YH (2018) Colorimetric ELISA for ochratoxin a detection based on the urease-induced metallization of gold nanoflowers. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 226:102–109
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21505114) and Doctorial Starting Fund of Xinxiang Medical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author (s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 1059 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Yan, H., Shangguan, J. et al. A fluorometric aptamer-based assay for ochratoxin A using magnetic separation and a cationic conjugated fluorescent polymer. Microchim Acta 185, 427 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2962-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2962-8