Abstract
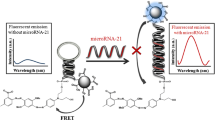
An efficient coreaction accelerator scheme is introduced in an electrochemiluminescence (ECL) based method for sensitive determination of microRNA-21. It is making use of a domino type hemin/G-wire supramolecular DNA nanostructure (where “G-wire” represents a guanine-rich DNA structure) without a base pairing dependence. A glassy carbon electrode was modified with carbon dots (prepared from fullerene) and TiO2 nanoneedles. In the first step, a first hairpin 1 (H1) binds to microRNA-21 to form the hybridized complex in solution. This is followed by a T7 exonuclease (T7 Exo)-assisted target recycling to obtain a simulated target which can unfold hairpin 2 (H2) to form a double-stranded structure. After cleavage by T7 Exo, the G-rich sequences in H2 re-fold into G-quadruplexes on the electrode to form hemin/G-wire supramolecular nanostructure with the strand 1 (S1, a custom-made G-rich sequence) and hemin. As a result, the hemin/G-wire catalyzes the reaction of peroxothiosulfate that generates ECL. Thus, the signal is strongly enhanced. The method allows for the determination of microRNA-21 with a detection limit as low as 0.1 fM. It is conceived to represent a valuable tool in cancer research.

The hemin/G-wire supramolecular nanostructures assembled on a carbon dot (CD)-based glassy carbon electrode (GCE), thereby achieving electrochemiluminescence (ECL) signal amplification of the CD/S2O82− system and sensitive detection of microRNA-21.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen W, Yao X, Zhou X, Zhao K, Deng A, Li J (2018) Electrochemiluminescence based competitive immunoassay for Sudan I by using gold-functionalized graphitic carbon nitride and au/cu alloy nanoflowers. Microchim Acta 185:275
Jian Y, Wang H, Lan F, Liang L, Ren N, Liu H, Ge S, Yu J (2018) Electrochemiluminescence based detection of microRNA by applying an amplification strategy and hg (II)-triggered disassembly of a metalorganic frameworks functionalized with ruthenium (II) tris (bipyridine). Microchim Acta 185:133
Kahn J, Trifonov A, Cecconello A, Guo W, Fan C, Willner I (2015) Integration of switchable DNA-based hydrogels with surfaces by the hybridization chain reaction. Nano Lett 15:7773–7778
Chen A, Gui G, Zhuo Y, Chai Y, Xiang Y, Yuan R (2015) Signal-off electrochemiluminescence biosensor based on phi29 DNA polymerase mediated strand displacement amplification for microRNA detection. Anal Chem 87:6328–6334
Wu L, Tan L, Zhao Y, Wang X (2015) Based electrochemiluminescence origami device for protein detection using assembled cascade DNA–carbon dots nanotags based on rolling circle amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 68:413–420
Xiao L, Chai Y, Yuan R, Cao Y, Wang H, Bai L (2013) Amplified electrochemiluminescence of luminol based on hybridization chain reaction and in situ generate co-reactant for highly sensitive immunoassay. Talanta 115:577–582
Chen A, Ma S, Zhuo Y, Chai Y, Yuan R (2016) In situ electrochemical generation of electrochemiluminescent silver naonoclusters on target-cycling synchronized rolling circle amplification platform for microRNA detection. Anal Chem 88:3203–3210
Zhu G, Hu R, Zhao Z, Chen Z, Zhang X, Tan W (2013) Noncanonical self-assembly of multifunctional DNA nanoflowers for biomedical applications. J Am Chem Soc 135:16438–16445
Wang H, Yuan Y, Zhuo Y, Chai Y, Yuan R (2016) Sensitive electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for detection of N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase based on a “light-switch” molecule combined with DNA dendrimer. Anal Chem 88:5797–5803
Xie S, Dong Y, Yuan Y, Chai Y, Yuan R (2016) Ultrasensitive lipopolysaccharides detection based on doxorubicin conjugated N-(Aminobutyl)-N-(ethylisoluminol) as electrochemiluminescence indicator and self-assembled tetrahedron DNA dendrimers as nanocarriers. Anal Chem 88:5218–5224
Zhang P, Wu X, Yuan R, Chai Y (2015) An “off–on” electrochemiluminescent biosensor based on DNAzyme-assisted target recycling and rolling circle amplifications for ultrasensitive detection of microRNA. Anal Chem 87:3202–3207
Jiang B, Yang M, Yang C, Xiang Y, Yuan R (2017) Methylation-induced inactivation of restriction enzyme for amplified and signal-on electrochemiluminescence detection of methyltransferase activity. Sensors Actuators B Chem 247:573–579
Lin J, Yan Y, Ou T, Tan J, Huang S, Li D, Huang Z, Gu L (2010) Effective detection and separation method for G-quadruplex DNA based on its specific precipitation with Mg2+. Biomacromolecules 11:3384–3389
Ye C, Wang M, Li L, Luo H, Li N (2017) Fabrication of Pt/Cu3(PO4)2 ultrathin nanosheet heterostructure for photoelectrochemical microRNA sensing using novel G-wire-enhanced strategy. Nanoscale 9:7526–7532
Das R, Debnath M, Gaurav A, Dash J (2014) Environment-sensitive probes containing a 2, 6-diethynylpyridine motif for fluorescence turn-on detection and induction of nanoarchitectures of human telomeric quadruplex. Chem Eur J 20:16688–16693
Shi Y, Luo H, Li N (2013) A highly sensitive resonance Rayleigh scattering method to discriminate a parallel-stranded G-quadruplex from DNA with other topologies and structures. Chem Commun 49:6209–6211
Baker S, Baker G (2010) Luminescent carbon nanodots: emergent nanolights. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:6726–6744
Dong Y, Pang H, Yang H, Guo C, Shao J, Chi Y, Li C, Yu T (2013) Carbon-based dots co-doped with nitrogen and sulfur for high quantum yield and excitation-independent emission. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:7800–7804
Zhai Q, Li J, Wang E (2017) Recent advances based on nanomaterials as electrochemiluminescence probes for the fabrication of sensors. ChemElectroChem 4:1639–1650
Qiu Y, Zhou B, Yang X, Long D, Hao Y, Yang P (2017) Novel single-cell analysis platform based on a solid-state zinc-coadsorbed carbon dots electrochemiluminescence probe for the evaluation of CD44 expression on breast cancer cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:16848–16856
Xing B, Zhu W, Zheng X, Zhu Y, Wei Q, Wu D (2018) Electrochemiluminescence immunosensor based on quenching effect of SiO2@PDA on SnO2/rGO/au NPs-luminol for insulin detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem 265:403–411
Han Q, Wang R, Xing B, Chi H, Wu D, Wei Q (2018) Label-free photoelectrochemical aptasensor for tetracycline detection based. Biosens Bioelectron 106:7–13
Xing B, Zhu W, Zheng X, Zhu Y, Wei Q, Wu D (2018) Electrochemiluminescence immunosensor based on quenching effect of SiO2@PDA on SnO2/rGO/au NPs-luminol for insulin detection. Biosens Bioelectron 99:493–499
Ren X, Ma H, Zhang T, Zhang Y, Yan T, Du B, Wei Q (2017) Sulfur-doped graphene-based immunological biosensing platform for multianalysis of cancer biomarkers. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:37637–37644
Shen J, Zhu Y, Chen C, Yang X, Li C (2011) Facile preparation and upconversion luminescence of graphene quantum dots. Chem Commun 47:2580–2582
Ma M, Zhang X, Zhuo Y, Chai Y, Yuan R (2015) An amplified electrochemiluminescent aptasensor using au nanoparticles capped by 3,4,9,10-perylene tetracar. Nanoscale 7:2085–2092
Zhao W, Han Y, Zhu Y, Zhang N, Xu J, Chen H (2015) DNA labeling generates a unique amplification probe for sensitive photoelectrochemical immunoassay of HIV-1 p24 antigen. Anal Chem 87:5496–5499
Ding Z, Quinn B, Haram S, Pell L, Korgel B (2002) Electrochemistry and electrogenerated chemiluminescence from silicon nanocrystal quantum dots. Science 296:1293–1297
Ma M, Zhuo Y, Yuan R, Chai Y (2015) New signal amplification strategy using semicarbazide as co-reaction accelerator for highly sensitive electrochemiluminescent aptasensor. Anal Chem 87:11389–11397
Zhao J, Lei Y, Chai Y, Yuan R, Zhuo Y (2016) Novel electrochemiluminescence of perylene derivative and its application to mercury ion detection based on a dual amplification strategy. Biosens Bioelectron 86:720–727
Azzouzi S, Wing C, Kor K, Turner A, Ali M, Beni V (2017) An integrated dual functional recognition/amplification bio-label for the one-step impedimetric detection of micro-RNA-21. Biosens Bioelectron 92:154–161
Liu L, Gao Y, Liu H, Xia N (2015) An ultrasensitive electrochemical microRNAs sensor based on microRNAs-initiated cleavage of DNA by duplex-specific nuclease and signal amplification of enzyme plus redox cycling reaction. Sensors Actuators B Chem 208:137–142
Liu H, Bei X, Xia Q, Fu Y, Zhang S, Liu M, Fan K, Zhang M, Yang Y (2016) Enzyme-free electrochemical detection of microRNA-21 using immobilized hairpin probes and a target-triggered hybridization chain reaction amplification strategy. Microchim Acta 183:297–304
Yuan R, Yu X, Zhang Y, Xu L, Cheng W, Tu Z, Ding S (2017) Target-triggered DNA nanoassembly on quantum dots and DNAzyme-modulated double quenching for ultrasensitive microRNA biosensing. Biosens Bioelectron 92:342–348
Liu W, Zhou X, Xing D (2014) Rapid and reliable microRNA detection by stacking hybridization on electrochemiluminescent chip system. Biosens Bioelectron 58:388–394
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the NNSF of China (21775124, 21575116, 21675129, 51473136,21675130), the Natural Science Foundation Project of CQ CSTC (cstc2018jcyjAX0546) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (XDJK2018AA003), China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 3947 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, R., Chen, A., Yu, Y. et al. Electrochemiluminescent carbon dot-based determination of microRNA-21 by using a hemin/G-wire supramolecular nanostructure as co-reaction accelerator. Microchim Acta 185, 432 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2959-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2959-3