Abstract
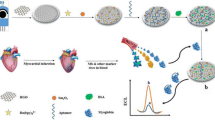
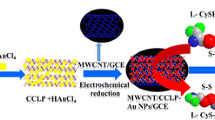
A composite was prepared from PtSn nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes (PtSnNP/CNTs) and applied to the electrochemical determination of myoglobin (Mb). An Mb-aptamer was immobilized on a glassy carbon electrode (GCE), and hexcyanoferrate was used as an electrochemical probe. The PtSnNP/CNTs were synthesized by a microwave-aided ethylene glycol reduction method. Detection is based on electron transfer inhibition that is caused by the folding and conformational change of the Mb-aptamer in the presence of Mb. The amperometric signal for hexacyanoferrate, best measured at 0.2 V vs. Ag/AgCl depends on the concentration of Mb that interacts with the aptamer on the GCE. This approach is selective and sensitive for Mb due to (a) the highly specific recognition ability of the aptamer for Mb, (b) the powerful electronic properties of carbon nanotubes, (c) the arranged decoration of CNTs with PtSnNPs, and (d), the superior electron transfer to hexacyanoferrate. The assay is highly selective, with linear relationships from 0.01–1 nM and 10 nM–200 nM, and a limit of detection as low as 2.2 ± 0.1 pM. The modified GCE was applied to the quantitation of Mb in spiked human serum samples.

Schematic illustration of the method for Mb detection.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu J, Zou N, Mao H, Wang P, Zhu D, Ji H, Cong H, Sun C, Wang H, Zhang F, Qian J, Jin Q, Zhao J (2013) Evaluation of a modified lateral flow immunoassay for detection of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I and myoglobin. Biosens Bioelectron 42:522–525
W H O World Health Statistics 2014, http://www.who.int/gho/publications/world-health-statistics/2014/en, (accessed May 12, 2016)
Nambi V, Liu X, Chambless LE, de Lemos JA, Virani SS, Agarwal S, Boerwinkle E, Hoogeveen RC, Aguilar D, Astor BC, Srinivas PR, Deswal A, Mosley TH, Coresh J, Folsom AR, Heiss G, Ballantyne CM (2013) Troponin T and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide: a biomarker approach to predict heart failure risk-the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Clin Chem 59:1802–1810
Aldous SJ (2013) Cardiac biomarkers in acute myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol 164:282–294
Pervaiz S, Anderson FP, Lohman TP, Lawson CJ, Feng YJ, Waskiewicz D (1997) Comparative analysis of cardiac troponin I and creatine kinase-MB as markers of acute myocardial infarction. Clin Cardiol 20:269–271
Janota T (2014) Biochemical markers in the diagnosis of myocardial infarction. Cor Vasa 56: e304–e310
Stone MJ, Waterman MR, Harimoto D, Murray G, Willson N, Platt MR, Blomqvist G, Willerson JT (1997) Serum myoglobin level as diagnostic test in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Br Heart J 39:375–380
Kumar V, Shorie M, Ganguli AK, Sabherwal P (2015) Graphene-CNT nanohybrid aptasensor for label free detection of cardiac biomarker myoglobin. Biosens Bioelectron 72:56–60
Li YC, Li YJ, Yang YY (2011) Direct electrochemistry and electrocatalysis of myoglobin-based nanocomposite membrane electrode. Bioelectrochemistry 82:112–116
Naveena BM, Faustman C, Tatiyaborworntham N, Yin S, Ramanathan R, Mancini RA (2010) Detection of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal adducts of turkey and chicken myoglobins using mass spectrometry. Food Chem 122:836–840
Giaretta N, Giuseppe AM, Lippert M, Parente A, Maro AD (2013) Myoglobin as marker in meat adulteration: A UPLC method for determining the presence of pork meat in raw beef burger. Food Chem 141:1814–1820
Yue Q, Song Z (2006) Assay of femtogram level nitrite in human urine using luminol–myoglobin chemiluminescence. Microchem J 84:10–13
Zhang X, Kong X, Fan W, Du X (2011) Iminodiacetic acid-functionalized gold nanoparticles for optical sensing of myoglobin via Cu2+ coordination. Langmuir 27:6504–6510
Gnedenko OV, Mezentsev YV, Molnar AA, Lisitsa AV, Ivanov AS, Archakov AI (2013) Highly sensitive detection of human cardiac myoglobin using a reverse sandwich immunoassay with a gold nanoparticle-enhanced surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Anal Chim Acta 759:105–109
Yang Z, Zhou DM (2006) Cardiac markers and their point-of-care testing for diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction. Clin Biochem 39:771–780
Ellington AD, Szostak JW (1990) In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 346:818–822
Famulok M, Mayer G (2011) Aptamer modules as sensors and detectors. Acc Chem Res 44:1349–1358
Sabherwal P, Mutreja R, Suri CR (2016) Biofunctionalized carbon composites: new-generation diagnostic tools. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 82:12–21
Holzinger M, Goff AL, Cosnier S (2014) Nanomaterials for biosensing applications: a review. Front Chem 2:1–10
Britz DA, Khlobystov AN (2006) Noncovalent interactions of molecules with single walled carbon nanotubes. Chem Soc Rev 35:637–659
Wang J, Liu G, Jan MR (2014) Ultrasensitive electrical biosensing of proteins and DNA: carbon-nanotube derived amplification of the recognition and transduction Eevents. J Am Chem Soc 126:3010–3011
Li H, Chen S, Li Q, Liu F (2016) Effect of the pH of the preparation medium on the microstructure and electrocatalytic activity of carbon nanotubes decorated with PtSn nanoparticles for use in methanol oxidation. New Carbon Mater 31:293–300
Christina B, Chantal P, Martin C (2004) Size-selected synthesis of PtRu nano-catalysts: reaction and size control mechanism. J Am Chem Soc 126:8028–8037
Wang Q, Liu W, Xing Y, Yang X, Wang K, Jiang R, Wang P, Zhao Q (2014) Screening of DNA aptamers against myoglobin using a positive and negative selection units integrated microfluidic chip and its biosensing application. Anal Chem 86:6572–6579
Kumar V, Brent JR, Shorie M, Kaur H, Chadha G, Thomas AG, Lewis EA, Rooney AP, Nguyen L, Zhong XL, Burke MG, Haigh SJ, Walton A, McNaughter PD, Tedstone AA, Savjani N, Muryn CA, Brien P, Ganguli AK, Lewis DJ, Sabherwal P (2016) Nanostructured aptamer-functionalized black phosphorus sensing platform for label-free detection of myoglobin, a cardiovascular disease biomarker. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:22860–22868
Abnous K, Danesh NM, Emrani AS, Ramezani M, Taghdisi SM (2016) A novel fluorescent aptasensor based on silica nanoparticles, PicoGreen and exonuclease III as a signal amplification method for ultrasensitive detection of myoglobin. Anal Chim Acta 917:71–78
Kumar V, Shorie M, Ganguli AK, Sabherwal P (2015) Graphene-CNT nanohybrid aptasensor for label free detection of car- diac biomarker myoglobin. Biosens Bioelectron 72:56–60
Taghdisi SM, Danesh NM, Ramezani M, Emrani AS, Abnous K (2016) A novel electrochemical aptasensor based on Y-shape structure of dual-aptamer-complementary strand conjugate for ultrasensitive detection of myoglobin. Biosens Bioelectron 80:532–537
Li C, Li J, Yang X, Gao L, Jing L, Ma X (2017) A label-free electrochemical aptasensor for sensitive myoglobin detection in meat. Sensors Actuators B Chem 242:1239–1245
Shumyantseva VV, Bulko TV, Sigolaeva LV, Kuzikov AV, Archakov AI (2016) Electrosynthesis and binding properties of molecularly imprinted poly-o-phenylenediamine for selective recognition and direct electrochemical detection of myoglobin. Biosens Bioelectron 86:330–336
Wang Q, Liu F, Yang X, Wang K, Wang H, Deng X (2015) Sensitive point-of-care monitoring of cardiac biomarker myoglobin using aptamer and ubiquitous personal glucose meter. Biosens Bioelectron 64:161–164
Shorie M, Kumar V, Kaur H, Singh K, Tomer VK, Sabherwal P (2018) Plasmonic DNA hotspots made from tungsten disulfide nanosheets and gold nanoparticles for ultrasensitive aptamer-based SERS detection of myoglobin. Microchim Acta 185:158
Karimi Pur MR, Hosseini M, Faridbod F, Ganjali MR (2017) Highly sensitive label-free electrochemiluminescence aptasensor for early detection of myoglobin, a biomarker for myocardial infarction. Microchim Acta 184:3529–3537
Wang Y, Han M, Ye X, Wu K, Wu T, Chunya Li C (2017) Voltammetric myoglobin sensor based on a glassy carbon electrode modified with a composite film consisting of carbon nanotubes and a molecularly imprinted polymerized ionic liquid. Microchim Acta 184:195–202
Singh S, Tuteja SK, Sillu D, Deep A, Suri CR (2016) Gold nanoparticles-reduced graphene oxide based electrochemical immunosensor for the cardiac biomarker myoglobin. Microchim Acta 183:1729–1738
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the support of this work by the Khorramabad Branch, Islamic Azad University and Iran National Science Foundation: INSF for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 596 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nia, N.G., Azadbakht, A. Nanostructured aptamer-based sensing platform for highly sensitive recognition of myoglobin. Microchim Acta 185, 333 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2860-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2860-0