Abstract
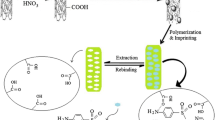
A cellulose paper was modified with an aptamer against methamphetamine on either carbon dots (CDs) or on multichannel carbon nanotubes (CNTs). The resulting sorbent was applied to the extraction of METH from blood or saliva. The METH-loaded paper than also was directly applied as a paper spray ionization source in ion mobility spectrometry. The carbon nanomaterial enhances sensitivity, and the aptamer enhances selectivity. The materials were covalently bound to the paper on one side, while the aptamer was immobilized on the other. After optimization of the extraction process and instrumental parameters, the limits of detection when using the aptamer-CNT modified paper are 0.6 ng·mL−1 for saliva, and 0.45 ng·mL−1 for plasma. The respective values when using aptamer-CD modified paper are 1.5 ng·mL−1 for saliva and 0.9 ng·mL−1 for plasma. Calibration plots are linear in the 2 to 150 ng·mL−1 METH concentration range for saliva, and in the 1.5 to 200 ng·mL−1 concentration ranges for blood when using the aptamer-CNT based method. When using the aptamer-CDs, the dynamic ranges extend from 5 to 200 ng·mL−1 and from 3 to 250 ng·mL−1, respectively. The method was applied to the determination of METH in real samples of saliva and blood, and the accuracy of the method was confirmed by comparison of the results with data analyzed by GC-MS.

ᅟ





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rothman RB, Baumann MH, Dersch CM, Romero DV, Rice KC, Carroll FI, Partilla JS (2001) Amphetamine-type central nervous system stimulants release norepinephrine more potently than they release dopamine and serotonin. Synapse 39:32–41
Stephans SE, Whittingham TS, Douglas AJ, Lust WD, Yamamoto BK (1998) Substrates of energy metabolism attenuate methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity in striatum. J Neurochem 71:613–621
Weinmann W, Bohnert M (1998) Lethal monointoxication by overdosage of MDEA. Forensic Sci Int 91:91–101
Huang Z, Zhang S (2003) Confirmation of amphetamine, methamphetamine, MDA and MDMA in urine samples using disk solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry after immunoassay screening. J Chromatogr B 792:241–247
Koide I, Noguchi O, Okada K, Yokoyama A, Oda H, Yamamoto S, Kataoka H (1998) Determination of amphetamine and methamphetamine in human hair by headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography with nitrogen–phosphorus detection. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 707:99–104
Okajima K, Namera A, Yashiki M, Tsukue I, Kojima T (2001) Highly sensitive analysis of methamphetamine and amphetamine in human whole blood using headspace solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Forensic Sci Int 116:15–22
Du P, Li K, Li J, Xu Z, Fu X, Yang J, Zhang H, Li X (2015) Methamphetamine and ketamine use in major Chinese cities, a nationwide reconnaissance through sewage-based epidemiology. Water Res 84:76–84
Subedi B, Kannan K (2014) Mass loading and removal of select illicit drugs in two wastewater treatment plants in New York state and estimation of illicit drug usage in communities through wastewater analysis. Environ Sci Technol 48:6661–6670
Boatto G, Faedda MV, Pau A, Asproni B, Menconi S, Cerri R (2002) Determination of amphetamines in human whole blood by capillary electrophoresis with photodiode array detection. J Pharm Biomed Anal 29:1073–1080
Iwata YT, Inoue H, Kuwayama K, Kanamori T, Tsujikawa K, Miyaguchi H, Kishi T (2006) Forensic application of chiral separation of amphetamine-type stimulants to impurity analysis of seized methamphetamine by capillary electrophoresis. Forensic Sci Int 161:92–96
Ochoa ML, Harrington PB (2004) Detection of methamphetamine in the presence of nicotine using in situ chemical derivatization and ion mobility spectrometry. Anal Chem 76:985–991
Miki A, Keller T, Regenscheit P, Dirnhofer R, Tatsuno M, Katagi M, Nishikawa M, Tsuchihashi H (1997) Application of ion mobility spectrometry to the rapid screening of methamphetamine incorporated in hair. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 692:319–328
Alizadeh N, Mohammadi A, Tabrizchi M (2008) Rapid screening of methamphetamines in human serum by headspace solid-phase microextraction using a dodecylsulfate-doped polypyrrole film coupled to ion mobility spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 1183:21–28
Wang H, Liu J, Cooks RG, Ouyang Z (2010) Paper spray for direct analysis of complex mixtures using mass spectrometry. Angew Chem Int Ed 122:889–892
Wang H, Manicke NE, Yang Q, Zheng L, Shi R, Cooks RG, Ouyang Z (2011) Direct analysis of biological tissue by paper spray mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 83:1197–1201
Zhang Z, Cooks RG, Ouyang Z (2012) Paper spray: a simple and efficient means of analysis of different contaminants in foodstuffs. Analyst 137:2556–2558
Liu J, Wang H, Manicke NE, Lin JM, Cooks RG, Ouyang Z (2010) Development, characterization, and application of paper spray ionization. Anal Chem 82:2463–2471
Manicke NE, Belford M (2015) Separation of opiate isomers using electrospray ionization and paper spray coupled to high-field asymmetric waveform ion mobility spectrometry. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 26:701–705
Li M, Zhang J, Jiang J, Zhang J, Gao J, Qiao X (2014) Rapid, in situ detection of cocaine residues based on paper spray ionization coupled with ion mobility spectrometry. Analyst 139:1687–1691
Lai PH, Chen PC, Liao YW, Liu JT, Chen CC, Lin CH (2015) Comparison of gampi paper and nanofibers to chromatography paper used in paper spray-mass spectrometry. Int J mass. Spectrum 375:14–17
Wang Q, Zheng Y, Zhang X, Han X, Wang T, Zhang Z (2015) A silica coated paper substrate: development and its application in paper spray mass spectrometry for rapid analysis of pesticides in milk. Analyst 140:8048–8056
Sherma J, Fried B (1984) Thin-layer and paper chromatography. Anal Chem 56:48–63
Zargar T, Khayamian T, Jafari MT (2017) Immobilized aptamer paper spray ionization source for ion mobility spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed Anal 132:232–237
Shi Q, Shi Y, Pan Y, Yue Z, Zhang H, Yi C (2015) Colorimetric and bare eye determination of urinary methylamphetamine based on the use of aptamers and the salt-induced aggregation of unmodified gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 182:505–511
Khayamian T, Jafari MT (2007) Design for electrospray ionization-ion mobility spectrometry. Anal Chem 79:3199–3205
Li H, He X, Liu Y, Huang H, Lian S, Lee ST, Kang Z (2011) One-step ultrasonic synthesis of water-soluble carbon nanoparticles with excellent photoluminescent properties. Carbon 49:605–609
Reese ES, de B Harrington P (1999) The analysis of methamphetamine hydrochloride by thermal desorption ion mobility spectrometry and SIMPLISMA. J Forensic Sci 44:68–76
Gentili S, Mortali C, Mastrobattista L, Berretta P, Zaami S (2016) Determination of different recreational drugs in sweat by headspace solid-phase microextraction gas chromatography mass spectrometry (HS-SPME GC-MS): application to drugged drivers. J Pharm Biomed Anal 129:282–287
Sergi M, Compagnone D, Curini R, D’Ascenzo G, Del Carlo M, Napoletano S, Risoluti R (2010) Micro-solid phase extraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of stimulants, hallucinogens, ketamine and phencyclidine in oral fluids. Anal Chim Acta 675:132–137
Hasegawa C, Kumazawa T, Lee XP, Marumo A, Shinmen N, Seno H, Sato K (2007) Pipette tip solid-phase extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for the determination of methamphetamine and amphetamine in human whole blood. Anal Bioanal Chem 389:563–570
Souza DZ, Boehl PO, Comiran E, Mariotti KC, Pechansky F, Duarte PC, De Boni R, Froehlich PE, Limberger RP (2011) Determination of amphetamine-type stimulants in oral fluid by solid-phase microextraction and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 696:67–76
Rezazadeh M, Yamini Y, Seidi S (2015) Application of a new nanocarbonaceous sorbent in electromembrane surrounded solid phase microextraction for analysis of amphetamine and methamphetamine in human urine and whole blood. J Chromatogr A 1396:1–6
Kumazawa T, Hasegawa C, Hara K, Uchigasaki S, Lee XP, Seno H, Suzuki O, Sato K (2012) Molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction for the selective determination of methamphetamine, amphetamine, and methylenedioxyphenylalkylamine designer drugs in human whole blood by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci 35:726–733
Taghvimi A, Hamishehkar H (2017) Carbon coated magnetic nanoparticles as a novel magnetic solid phase extraction adsorbent for simultaneous extraction of methamphetamine and ephedrine from urine samples. J Chromatogr B 1041:113–119
Domingos E, de Carvalho TC, Pereira I, Vasconcelos GA, Thompson CJ, Augusti R, Rodrigues RRT, Tose LV, Santos H, Araujo JR, Vaz BG, Romão W (2017) Paper spray ionization mass spectrometry applied to forensic chemistry – drugs of abuse, inks and questioned documents. Anal Methods 9:4400–4409
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 80.6 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zargar, T., Khayamian, T. & Jafari, M.T. Aptamer-modified carbon nanomaterial based sorption coupled to paper spray ion mobility spectrometry for highly sensitive and selective determination of methamphetamine. Microchim Acta 185, 103 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2623-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2623-3