Abstract
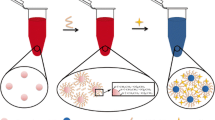
The preparation and application of casein-capped gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) as a specific probe for ferric ions Fe(III) is reported. The functionalized AuNPs exhibit narrow size distribution and form stable dispersions in water of different ionic strengths and basicity. The presence of diverse functional groups from the side chain of peptides warrants colloidal stability of AuNPs and also assists recognition of Fe(III) in versatile conditions. Fe(III) ion reportedly causes the aggregation of AuNPs and a red-shift in absorbance toward longer wavelength (660 nm). A spectrophotometric method is appropriate for selective detection of Fe(III) and the spectral shift is also accompanied by a color change from red to blue. The aggregation of AuNPs is not suppressed after the addition of NaOH or at moderate ionic strength. The resulting spectrophotometric method works for Fe(III) in the concentration range of 0.1 to 0.9 μM and has a detection limit of 450 nM. The AuNP probe can also detect Fe(III) ion content in real samples at the same detection limit, which is much lower than the maximum contaminant level allowed for Fe(III) in drinking water (5.37 μM) by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.

Casein peptide functionalized gold nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and their application to the visual detection of Fe(III).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sheikh N, Dudas J, Ramadori G (2007) Changes of gene expression of iron regulatory proteins during turpentine oil-induced acute-phase response in the rat. Lab Investig 87(7):713–725. https://doi.org/10.1038/labinvest.3700553
Miller JL (2013) Iron deficiency anemia: a common and curable disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 3(7):a011866. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a011866
Lipinski B, Pretorius E (2013) The role of iron-induced fibrin in the pathogenesis of alzheimer’s disease and the protective role of magnesium. Front Hum Neurosci 7:735. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2013.00735
Shamspur T, Sheikhshoaie I, Mashhadizadeh MH (2005) Flame atomic absorption spectroscopy (FAAS) determination of iron(iii) after preconcentration on to modified analcime zeolite with 5-((4-nitrophenylazo)-N-(2[prime or minute],4[prime or minute]-dimethoxyphenyl))salicylaldimine by column method. J Anal At Spectrom 20(5):476–478. https://doi.org/10.1039/B416097E
Spolaor A, Vallelonga P, Gabrieli J, Cozzi G, Boutron C, Barbante C (2012) Determination of Fe2+ and Fe3+ species by FIA-CRC-ICP-MS in Antarctic ice samples. J Anal At Spectrom 27(2):310–317. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1JA10276A
Sooriyaarachchi M, Gailer J (2010) Removal of Fe3+ and Zn2+ from plasma metalloproteins by iron chelating therapeutics depicted with SEC-ICP-AES. Dalton Trans 39(32):7466–7473. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0DT00229A
Lopez V, Peña MJ (1981) Electrochemical kinetic study of the Fe3+ and Fe2+ system in oxalate medium. Electrochim Acta 26(7):857–863. https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-4686(81)85046-3
Resch-Genger U, Grabolle M, Cavaliere-Jaricot S, Nitschke R, Nann T (2008) Quantum dots versus organic dyes as fluorescent labels. Nat Methods 5(9):763–775. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1248
Zarlaida F, Adlim M (2017) Gold and silver nanoparticles and indicator dyes as active agents in colorimetric spot and strip tests for mercury(II) ions: a review. Microchim Acta 184(1):45–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1967-4
Liu Y, Yu J (2016) Oriented immobilization of proteins on solid supports for use in biosensors and biochips: a review. Microchim Acta 183(1):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1623-4
Jo TG, Bok KH, Han J, Lim MH, Kim C (2017) Colorimetric detection of Fe3+ and Fe2+ and sequential fluorescent detection of Al3+ and pyrophosphate by an imidazole-based chemosensor in a near-perfect aqueous solution. Dyes Pigments 139:136–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dyepig.2016.11.052
Ghodake G, Lim S-R, Lee DS (2013) Casein hydrolytic peptides mediated green synthesis of antibacterial silver nanoparticles. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 108:147–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.02.044
Dahl JA, Maddux BLS, Hutchison JE (2007) Toward greener nanosynthesis. Chem Rev 107(6):2228–2269. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr050943k
Saha K, Agasti SS, Kim C, Li X, Rotello VM (2012) Gold nanoparticles in chemical and biological sensing. Chem Rev 112(5):2739–2779. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr2001178
Leng W, Pati P, Vikesland PJ (2015) Room temperature seed mediated growth of gold nanoparticles: mechanistic investigations and life cycle assessment. Environ Sci: Nano 2(5):440–453. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5EN00026B
Ghodake G, Kim D-Y, Jo JH, Jang J, Lee DS (2016) One-step green synthesis of gold nanoparticles using casein hydrolytic peptides and their anti-cancer assessment using the DU145 cell line. J Ind Eng Chem 33:185–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2015.10.001
Pedireddy S, Lee HK, Tjiu WW, Phang IY, Tan HR, Chua SQ, Troadec C, Ling XY (2014) One-step synthesis of zero-dimensional hollow nanoporous gold nanoparticles with enhanced methanol electrooxidation performance. Nat Commun 5:4947. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms5947 http://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms5947#supplementary-information
Ruan C-Y, Murooka Y, Raman RK, Murdick RA (2007) Dynamics of size-selected gold nanoparticles studied by ultrafast electron nanocrystallography. Nano Lett 7(5):1290–1296. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl070269h
Yang Q, Wei L, Zheng X, Xiao L (2015) Single particle dynamic imaging and Fe3+ sensing with bright carbon dots derived from bovine serum albumin proteins. Sci Rep 5:17727. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep17727
J-a AH, Chang H-C, Su W-T (2012) DOPA-mediated reduction allows the facile synthesis of fluorescent gold nanoclusters for use as sensing probes for ferric ions. Anal Chem 84(7):3246–3253. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac203362g
Li L, Li L, Wang C, Liu K, Zhu R, Qiang H, Lin Y (2015) Synthesis of nitrogen-doped and amino acid-functionalized graphene quantum dots from glycine, and their application to the fluorometric determination of ferric ion. Microchim Acta 182(3):763–770. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-014-1383-6
Wang F, Hao Q, Zhang Y, Xu Y, Lei W (2016) Fluorescence quenchometric method for determination of ferric ion using boron-doped carbon dots. Microchim Acta 183(1):273–279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1650-1
Yu J, Xu C, Tian Z, Lin Y, Shi Z (2016) Facilely synthesized N-doped carbon quantum dots with high fluorescent yield for sensing Fe3+. New J Chem 40(3):2083–2088. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NJ03252K
Xia J, Zhuang Y-T, Yu Y-L, Wang J-H (2017) Highly fluorescent carbon polymer dots prepared at room temperature, and their application as a fluorescent probe for determination and intracellular imaging of ferric ion. Microchim Acta 184(4):1109–1116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2104-8
Ananthanarayanan A, Wang X, Routh P, Sana B, Lim S, Kim D-H, Lim K-H, Li J, Chen P (2014) Facile synthesis of graphene quantum dots from 3D graphene and their application for Fe3+ sensing. Adv Funct Mater 24(20):3021–3026. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201303441
Sener G, Uzun L, Denizli A (2014) Colorimetric sensor array based on gold nanoparticles and amino acids for identification of toxic metal ions in water. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(21):18395–18400. https://doi.org/10.1021/am5071283
Wu S-P, Chen Y-P, Sung Y-M (2011) Colorimetric detection of Fe3+ ions using pyrophosphate functionalized gold nanoparticles. Analyst 136(9):1887–1891. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1AN15028F
Li J-J, Wang X-F, Huo D-Q, Hou C-J, Fa H-B, Yang M, Zhang L (2017) Colorimetric measurement of Fe3+ using a functional paper-based sensor based on catalytic oxidation of gold nanoparticles. Sensors Actuators B Chem 242:1265–1271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.09.039
Chaud MV, Izumi C, Nahaal Z, Shuhama T, Bianchi MLP, Od F (2002) Iron derivatives from casein hydrolysates as a potential source in the treatment of iron deficiency. J Agric Food Chem 50(4):871–877. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0111312
Wang B, Xie N, Li B (2016) Charge properties of peptides derived from casein affect their bioavailability and cytoprotection against H2O2-induced oxidative stress. J Dairy Sci 99(4):2468–2479. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2015-10029
Argyri K, Miller DD, Glahn RP, Zhu L, Kapsokefalou M (2007) Peptides isolated from in vitro digests of milk enhance iron uptake by caco-2 cells. J Agric Food Chem 55(25):10221–10225. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0727387
Kapsokefalou M, Miller DD (1991) Effects of meat and selected food components on the valence of nonheme iron during in vitro digestion. J Food Sci 56(2):352–355. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2621.1991.tb05278.x
Lv Y, Liu Q, Bao X, Tang W, Yang B, Guo S (2009) Identification and characteristics of iron-chelating peptides from soybean protein hydrolysates using IMAC-Fe3+. J Agric Food Chem 57(11):4593–4597. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf9000204
Guan J, Jiang L, Li J, Yang W (2008) pH-dependent aggregation of histidine-functionalized au nanoparticles induced by Fe3+ ions. J Phys Chem C 112(9):3267–3271. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp7097763
Li J, Wang Q, Guo Z, Ma H, Zhang Y, Wang B, Bin D, Wei Q (2016) Highly selective fluorescent chemosensor for detection of Fe3+ based on Fe3O4@ZnO. Sci Rep 6:23558. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep23558
Slocik JM, Zabinski JS, Phillips DM, Naik RR (2008) Colorimetric response of peptide-functionalized gold nanoparticles to metal ions. Small 4(5):548–551. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.200700920
Fu X-C, Wu J, Li J, Xie C-G, Liu Y-S, Zhong Y, Liu J-H (2013) Electrochemical determination of trace copper(II) with enhanced sensitivity and selectivity by gold nanoparticle/single-wall carbon nanotube hybrids containing three-dimensional l-cysteine molecular adapters. Sensors Actuators B Chem 182:382–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2013.02.074
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by National Research Foundation South Korea under the project number 2017R1C1B-5017360. This research was also supported by Dongguk University-Seoul research fund 2016-2017. The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for partly funding this work under research group No (RG-1438-078).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no financial and competing interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 1.15 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, DY., Shinde, S., Saratale, R. et al. Spectrophotometric determination of Fe(III) by using casein-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 184, 4695–4704 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2520-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2520-9