Abstract
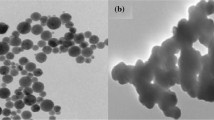
A molecularly imprinted polymer based on silica modified Fe3O4 microsphere and ionic liquid was prepared for the adsorption and specific recognition of DNA. Water-compatible imidazolium ionic liquids were introduced on the surface of silica-coated Fe3O4 microsphere, then used as the adsorbents, againsting DNA from salmon testes (stDNA) by combining immobilized template and surface imprinting techniques. The imprinted polymer layers were grafted onto ionic liquid functionalized microspheres through sol-gel approach using N-3-(3-triethoxysilylpropyl)-3-aminopropyl imidazolium chloride and N-3-(3-triethoxysilylpropyl)-3-mexyl imidazolium chloride as the functional monomers, and tetraethoxysilane as the cross-linker. Because both imidazolium ionic liquid and DNA are soluble in water, it is mandatory to implement an imprinted process in an aqueous medium to well maintain the integrity of the conformation. Fourier transform infrared spectrometry, thermogravimetric analysis, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction and vibrating sample magnetometry were employed to characterize the materials. The nanomaterials with multiple imprinting sites and biocompatible cavities exhibit high specific adsorption capacity of DNA (162 mg·g−1) and excellent rebinding selectivity (imprinting factor up to 6.6) against non-imprinted molecules at pH value of 5.10. Moreover, it is feasible to strip DNA from the highly cross-linked polymer network by using aqueous NaCl (1.0 M). The nanomaterials are cap able of capturing DNA from calf whole blood, which might provide a viable tool for DNA preconcentration, separation and recognition.

Molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) were grafted onto ionic liquid (IL) functionalized magnetic microspheres (Fe3O4@SiO2@IL) by using imidazolium ILs as the monomers and tetraethoxysilane (TEOS) as the cross-linker. Fe3O4@SiO2@MIPs show high adsorption capacity and satisfactory selectivity for DNA.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Polyakov MV, Khim ZF (1931) Adsorption properties of silica gel and its structure. Zh Fiz Khim Ser B 2:799–805
Chen LX, SF X, Li JH (2011) Recent advances in molecular imprinting technology: current status, challenges and highlighted applications. Chem Soc Rev. 40:2922–2942
Chen LX, Wang XY, WH L, XQ W, Li JH (2016) Molecular imprinting: perspectives and applications. Chem Soc Rev. 45:2137–2211
Li HF, Xie T, Ye LL, Wang YW, Xie CG (2017) Core-shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for the extraction of triazophos residues from cvegetables. Microchim Acta 184:1011–1019
Wackerlig J, Schirhagl R (2015) Applications of molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles and their advances toward industrial use: a review. Anal Chem 88:250–261
You M, Yang S, Jiao F, Yang LZ, Zhang F, He PG (2016) Label-free electrochemical multi-sites recognition of G-rich DNA using multi-walled carbon nanotubes–supported molecularly imprinted polymer with guanine sites of DNA. Electrochim Acta 199:133–141
Verheyen E, Schillemans JP, van Wijk M, Demeniex MA, Hennink WE, van Nostrum CF (2011) Challenges for the effective molecular imprinting of proteins. Biomaterials 32:3008–3020
Chen JX, Lei S, Xie YY, Wang MZ, Yang J, Ge XW (2015) Fabrication of high-performance magnetic lysozyme-imprinted microsphere and its NIR-responsive controlled release property. ACS Appl Mater Inter 7:28606–28615
Li SW, Yang KG, Deng N, Min Y, Liu LK, Zhang LH, Zhang YK (2016) Thermoresponsive epitope surface-imprinted nanoparticles for specific capture and release of target protein from human plasma. ACS Appl Mater Inter 8:5747–5751
Kubo T, Arimura S, Tominaga Y, Naito T, Hosoya K, Otsuka K (2015) Molecularly imprinted polymers for selective adsorption of lysozyme and cytochrome c using a PEG-based hydrogel: selective recognition for different conformations due to pH conditions. Macromolecules 48:4081–4087
Gao DM, Zhang ZP, MH W, Xie CG, Guan GJ, Wang DP (2007) A surface functional monomer-directing strategy for highly dense imprinting of TNT at surface of silica nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 129:7859–7866
Gao L, Chen LG, Li XW (2015) Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers based on carbon nanotubes for extraction of carbamates. Microchim Acta 182:781–787
Bhakta S, Seraji MSI, Suib SL, Rusling JF (2015) Antibody-like biorecognition sites for proteins from surface imprinting on nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Inter 7:28197–28206
Gao RX, Hao Y, Zhang LL, Cui XH, Liu DC, Zhang M, Tang YH, Zheng YS (2016) A facile method for protein imprinting on directly carboxyl-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles using non-covalent template immobilization strategy. Chem Eng J 284:139–148
Huang YH, Wang YZ, Wang Y, Pan Q, Ding XQ, KJ X, Li N, Wen Q (2016) Ionic liquid-coated Fe3O4/APTES/graphene oxide nanocomposites: synthesis, characterization and evaluation in protein extraction processes. RSC Adv 6:5718–5728
Wen Q, Wang YZ, KJ X, Li N, Zhang HM, Yang Q (2016) A novel polymeric ionic liquid-coated magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotubes for the solid-phase extraction of Cu, Zn-superoxide dismutase. Anal Chim Acta 939:54–63
Wang YY, Han M, Liu GS, Hou XD, Huang YN, KB W, Li CY (2015) Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensing interface based on in-situ-polymerization of amino-functionalized ionic liquid for specific recognition of bovine serum albumin. Biosens Bioelectron 74:792–798
Ding HY, Chen RF, Liu MM, Huang R, Du YM, Huang C, Yu XY, Feng XH, Liu F (2016) Preparation and characterization of biocompatible molecularly imprinted poly (ionic liquid) films on the surface of multi-walled carbon nanotubes. RSC Adv 6:43526–43538
CB D, XL H, Guan P, Gao XM, Song RY, Li J, Qian LW, Zhang N, Guo LX (2016) Preparation of surface-imprinted microspheres effectively controlled by orientated template immobilization using highly cross-linked raspberry-like microspheres for the selective recognition of an immunostimulating peptide. J Mater Chem B 4:1510–1519
Wu J, Kodzius R, Cao W, Wen W (2014) Extraction, amplification and detection of DNA in microfluidic chip-based assays. Microchimica Acta 181(13–14):1611–1631
Tang RH, Yang H, Choi JR, Gong Y, Hu J, Wen T, Li XJ, Xu B, Mei QB, Xu F (2017) Paper-based device with on-chip reagent storage for rapid extraction of DNA from biological samples. Microchimica Acta 184:2141–2150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2225-0
Clark KD, Nacham O, HL Y, Li TH, Yamsek MM, Ronning DR, Anderson JL (2015) Extraction of DNA by magnetic ionic liquids: tunable solvents for rapid and selective DNA analysis. Anal Chem 87:1552–1559
Li N, Wang YZ, Xu KJ, Wen Q, Ding XQ, Zhang HM, Yang Q (2016) High-performance of deep eutectic solvent based aqueous bi-phasic systems for the extraction of DNA. RSC Adv 6:84406–84414
Liu MM, Pi JY, Wang XJ, Huang R, YM D, XY Y, Tan WF, Liu F, Shea KJ (2016) A sol-gel derived pH-responsive bovine serum albumin molecularly imprinted poly (ionic liquids) on the surface of multiwall carbon nanotubes. Anal Chim Acta 932:29–40
Liu YJ, Wang YZ, Dai QZ, Zhou YG (2016) Magnetic deep eutectic solvents molecularly imprinted polymers for the selective recognition and separation of protein. Anal Chim Acta 936:168–178
KJ X, Wang YZ, Li YX, Lin YX, Zhang HB, Zhou YG (2016) A novel poly (deep eutectic solvent)-based magnetic silica composite for solid-phase extraction of trypsin. Anal Chim Acta 946:64–72
Zhou HC, Yang LR, Li W, Wang FC, Li WS, Zhao JM, Liang XF, Liu HZ (2012) Immobilizing penicillin g acylase using silica-supported ionic liquids: The effects of ionic liquid loadings. Ind Eng Chem Res 51:13173–13181
Li DY, Wang YZ, Zhao XL, He XW, Li WY, Zhang YK (2014) Facile synthesis of ionic liquid functionalized silica-capped CdTe quantum dots for selective recognition and detection of hemoproteins. J Mater Chem B 2:5659–5665
Chen XW, Mao QX, Liu JW, Wang JH (2012) Isolation/separation of plasmid DNA using hemoglobin modified magnetic nanocomposites as solid-phase adsorbent. Talanta 100:107–112
Li X, Zhang JX, HC G (2011) Adsorption and desorption behaviors of DNA with magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Langmuir 27:6099–6106
Wang Y, Ma XD, Ding C, Li J (2015) pH-responsive deoxyribonucleic acid capture/release by polydopamine functionalized magnetic nanoparticles[J]. Analytica chimica acta 862: 33–40
Ghaemi M, Absalan G (2014) Study on the adsorption of DNA on Fe3O4 nanoparticles and on ionic liquid-modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Microchimica Acta 181:45–53
LL H, Hu B, Shen LM, Zhang DD, Chen XW, Wang JH (2015) Polyethyleneimine-iron phosphate nanocomposite as a promising adsorbent for the isolation of DNA. Talanta 132:857–863
Spink CH, Chaires JB (1997) Thermodynamics of the binding of a cationic lipid to DNA. J Am Chem Soc 119:10920–10928
Vijayaraghavan R, Izgorodin A, Ganesh V, Surianarayanan M, MacFarlane DR (2010) Long-Term Structural and Chemical Stability of DNA in Hydrated Ionic Liquids. Angew Chem Int Edit 49:1631–1633
Acknowledgements
The authors greatly appreciate the financial supports by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.21375035; No.21675048) and the Foundation for Innovative Research Groups of NSFC (Grant 21,521,063).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 934 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, Q., Wang, Y., Xu, W. et al. Adsorption and specific recognition of DNA by using imprinted polymer layers grafted onto ionic liquid functionalized magnetic microspheres. Microchim Acta 184, 4433–4441 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2495-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2495-6