Abstract
The paper describes a colorimetric sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for the determination of human IgG. It is based on the use of an Fe(II) coordination complex as a signal amplifier and of mesoporous silica nanoparticles modified with glucose oxidase (GOx) and secondary antibodies (Ab2). After formation of the immuno sandwich complex, the quantity of GOx is proportional to the quantity of IgG. On addition of Fe(II) and glucose, GOx catalyzes the oxidation of glucose to produce hydrogen peroxide which oxidizes Fe(II) to Fe(III). After adding a stop solution containing the complexing ligand 1,10-phenanthroline (Phen), un-reacted Fe(II) forms an orange-red complex with Phen which can be detected by plate reader and even seen with bare eyes. This sandwich ELISA has a linear response in the 1 pg.mL−1 to 100 ng.mL−1 human IgG concentration range and a 860 fg.mL−1 detection limit. This is 20 times lower than the commercial ELISA for human IgG. The assay also is selective, stable, highly sensitive and cost-effective.

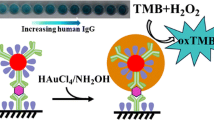
Schematic of a colorimetric enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) based on Fe(II) coordination complex as signal amplification strategy for human IgG detection. Glucose oxidase (GOx, green) and detection antibodies (Ab2, brown) functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSN) were prepared as probe.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhimji A, Zaragoza AA, Live LS, Kelley SO (2013) Electrochemical enzyme-linked Immunosorbent assay featuring proximal Reagent generation: detection of human immunodeficiency virus antibodies in clinical samples. Anal Chem 85(14):6813–6819
de la Rica R, Stevens MM (2012) Plasmonic ELISA for the ultrasensitive detection of disease biomarkers with the naked eye. Nat Nanotechnol 7(12):821–824
Zhou Y, Tian XL, Li YS, Pan FG, Zhang YY, Zhang JH, Yang L, Wang XR, Ren HL, Lu SY, Li ZH, Chen QJ, Liu ZS, Liu JQ (2011) An enhanced ELISA based on modified colloidal gold nanoparticles for the detection of Pb(II). Biosens Bioelectron 26(8):3700–3704
Szakal C, Roberts SM, Westerhoff P, Bartholomaeus A, Buck N, Illuminato I, Canady R, Rogers M (2014) Measurement of Nanomaterials in foods: integrative consideration of challenges and future prospects. ACS Nano 8(4):3128–3135
Asensio L, González I, García T, Martín R (2008) Determination of food authenticity by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Food Control 19(1):1–8
Yang M, Yi X, Wang J, Zhou F (2014) Electroanalytical and surface plasmon resonance sensors for detection of breast cancer and Alzheimer's disease biomarkers in cells and body fluids. Analyst 139(8):1814–1825
Zhang S, Huang N, Lu Q, Liu M, Li H, Zhang Y, Yao S (2016) A double signal electrochemical human immunoglobulin G immunosensor based on gold nanoparticles-polydopamine functionalized reduced graphene oxide as a sensor platform and AgNPs/carbon nanocomposite as signal probe and catalytic substrate. Biosens Bioelectron 77:1078–1085
Balzerova A, Fargasova A, Markova Z, Ranc V, Zboril R (2014) Magnetically-assisted surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (MA-SERS) for label-free determination of human immunoglobulin G (IgG) in blood using Fe3O4@Ag Nanocomposite. Anal Chem 86(22):11107–11114
Hu R, Liu T, Zhang X-B, Yang Y, Chen T, Wu C, Liu Y, Zhu G, Huan S, Fu T, Tan W (2015) DLISA: a DNAzyme-based ELISA for protein enzyme-free immunoassay of multiple Analytes. Anal Chem 87(15):7746–7753
Huang X, Chen R, Xu H, Lai W, Xiong Y (2016) Nanospherical brush as catalase container for enhancing the detection sensitivity of competitive Plasmonic ELISA. Anal Chem 88(3):1951–1958
Xie Q, Weng X, Lu L, Lin Z, Xu X, Fu C (2016) A sensitive fluorescent sensor for quantification of alpha-fetoprotein based on immunosorbent assay and click chemistry. Biosens Bioelectron 77:46–50
Sammes PG, Yahioglu G (1994) 1,10-Phenanthroline: a versatile ligand. Chem Soc Rev 23(5):327–334
Carter MT, Rodriguez M, Bard AJ (1989) Voltammetric studies of the interaction of metal chelates with DNA. 2. Tris-chelated complexes of cobalt(III) and iron(II) with 1,10-phenanthroline and 2,2′-bipyridine. J. Am. Chem. Soc 111(24):8901–8911
Chen L, Zhang Z, Zhang P, Zhang X, Fu A (2011) An ultra-sensitive chemiluminescence immunosensor of carcinoembryonic antigen using HRP-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles as labels. Sensor Actuator B Chem 155(2):557–561
Liang JJ, Yao CZ, Li XQ, Wu Z, Huang CH, Fu QQ, Lan CF, Cao DL, Tang Y (2015) Silver nanoprism etching-based plasmonic ELISA for the high sensitive detection of prostate-specific antigen. Biosens Bioelectron 69:128–134
Li YY, Ma XM, Xu ZM, Liu MH, Lin ZY, Qiu B, Guo LH, Chen GN (2016) Multicolor ELISA based on alkaline phosphatase-triggered growth of au nanorods. Analyst 141(10):2970–2976
Nie XM, Huang R, Dong CX, Tang LJ, Gui R, Jiang JH (2014) Plasmonic ELISA for the ultrasensitive detection of Treponema pallidum. Biosens Bioelectron 58:314–319
Radu DR, Lai C-Y, Wiench JW, Pruski M, Lin VSY (2004) Gatekeeping layer effect: a poly(lactic acid)-coated Mesoporous silica Nanosphere-based fluorescence probe for detection of amino-containing neurotransmitters. J Am Chem Soc 126(6):1640–1641
Slowing II, Trewyn BG, Lin VSY (2007) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for intracellular delivery of membrane-impermeable proteins. J Am Chem Soc 129(28):8845–8849
Yang M, Li H, Javadi A, Gong S (2010) Multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles as labels for the preparation of ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensors. Biomaterials 31(12):3281–3286
Zhao Y, Trewyn BG, Slowing II, Lin VSY (2009) Mesoporous silica nanoparticle-based double drug delivery system for glucose-responsive controlled release of insulin and cyclic AMP. J Am Chem Soc 131(24):8398–8400
Matsuzaki C, Hayakawa A, Matsumoto K, Katoh T, Yamamoto K, Hisa K (2015) Exopolysaccharides produced by Leuconostoc mesenteroides strain NTM048 as an Immunostimulant to enhance the mucosal barrier and influence the systemic immune response. J Agr Food Chem 63(31):7009–7015
Shen C, Xu H, Liu D, Veazey RS, Wang X (2014) Development of serum antibodies during early infancy in rhesus macaques: implications for humoral immune responses to vaccination at birth. Vaccine 32(41):5337–5342
Shore A, Mazzochette Z, Mugweru A (2016) Mixed valence Mn,La,Sr-oxide based magnetic nanoparticles coated with silica nanoparticles for use in an electrochemical immunosensor for IgG. Microchim Acta 183(1):475–483
Wu Q, Song D, Zhang D, Sun Y (2016) An enhanced SPR immunosensing platform for human IgG based on the use of silver nanocubes and carboxy-functionalized graphene oxide. Microchim Acta 183(7):2177–2184
Qian J, Zhang C, Cao X, Liu S (2010) Versatile immunosensor using a quantum dot coated silica nanosphere as a label for signal amplification. Anal Chem 82(15):6422–6429
Chen Y, Cheng H, Tram K, Zhang S, Zhao Y, Han L, Chen Z, Huan S (2013) A paper-based surface-enhanced resonance Raman spectroscopic (SERRS) immunoassay using magnetic separation and enzyme-catalyzed reaction. Analyst 138(9):2624–2631
Xu Q, Yan F, Lei J, Leng C, Ju H (2012) Disposable electrochemical immunosensor by using carbon sphere/gold nanoparticle composites as labels for signal amplification. Chem Eur J 18(16):4994–4998
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the support of this work by the National Key Basic Research Program of China (2014CB744502), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21575165) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan province (No. 2015JJ1019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 632 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, K., Tian, S., Wang, Z. et al. An ELISA for the determination of human IgG based on the formation of a colored iron(II) complex and photometric or visual read-out. Microchim Acta 184, 2791–2796 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2304-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2304-2