Abstract
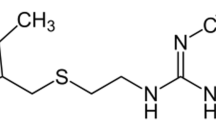
The authors describe a colorimetric assay for the quantitation of antibiotic kanamycin. It is based on hydrogen-bonding recognition capability of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) in a chitosan matrix. Hydrogen-bonding interaction between kanamycin and chitosan induces the aggregation of the AuNPs, and this result in a color change of the AuNPs from wine red to blue. The ratio of the absorbance at 650 nm and 520 nm increases linearly over the 0.01 to 40 μM kanamycin concentration range, and the detection limit is 8 nM (at an S/N ratio of 3). This low detection limit easily matches the maximum residue limits established by the European Union for milk (288 nM). Selectivity experiments revealed the assay to have a satisfactory specificity. It was applied to the determination of trace levels of kanamycin in (spiked) real samples. Results agreed well with those obtained by HPLC. The method does not require tedious detection procedure or sophisticated instrumentation.

Schematic of a colorimetric method for sensitive determination of kanamycin. It is based on chitosan-wrapped gold nanoparticles (chitosan-AuNPs) for hydrogen-bonding recognition. The method has a detection limit as low as 8 nM.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang C, Lai C, Zeng GM, Huang DL, Yang CP, Wang Y, Zhou YY, Cheng M (2016) Efficacy of carbonaceous nanocomposites for sorbing ionizable antibiotic sulfamethazine from aqueous solution. Water Res 95:103–112. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2016.03.014
Li R, Liu Y, Cheng L, Yang C, Zhang J (2014) Photoelectrochemical aptasensing of kanamycin using visible light-activated carbon nitride and graphene oxide nanocomposites. Anal Chem 86(19):9372–9375. doi:10.1021/ac502616n
Wang C, Liu C, Luo J, Tian Y, Zhou N (2016) Direct electrochemical detection of kanamycin based on peroxidase-like activity of gold nanoparticles. Anal Chim Acta 936:75–82. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2016.07.013
Zhu Y, Chandra P, Song KM, Ban C, Shim YB (2012) Label-free detection of kanamycin based on the aptamer-functionalized conducting polymer/gold nanocomposite. Biosens Bioelectron 36(1):29–34. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2012.03.034
Watanabe H, Satake A, Kido Y, Tsuji A (1999) Production of monoclonal antibody and development of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for kanamycin in biological matrices. Analyst 124(11):1611–1615
Loomans EE, van Wiltenburg J, Koets M, van Amerongen A (2003) Neamin as an immunogen for the development of a generic ELISA detecting gentamicin, kanamycin, and neomycin in milk. J Agric Food Chem 51(3):587–593
Yan JL (2008) Determinationation of kanamycin by square-wave cathodic adsorptive stripping voltammetry. Russ J Electrochem 44(12):1334–1338
Althaus R, Berruga MI, Montero A, Roca M, Molina MP (2009) Evaluation of a microbiological multi-residue system on the detection of antibacterial substances in ewe milk. Anal Chim Acta 632(1):156–162
Chen SH, Liang YC, Chou YW (2006) Analysis of kanamycin a in human plasma and in oral dosage form by derivatization with 1-naphthyl isothiocyanate and high-performance liquid chromatography. J Sep Sci 29(5):607–612
Megoulas N, Koupparis M (2005) Direct determination of kanamycin in raw materials, veterinary formulation and culture media using a novel liquid chromatography-evaporative light scattering method. Anal Chim Acta 547(1):64–72
Yu S, Wei Q, Du B, Wu D, Li H, Yan L, Ma H, Zhang Y (2013) Label-free immunosensor for the detection of kanamycin using ag@Fe(3)O(4) nanoparticles and thionine mixed graphene sheet. Biosens Bioelectron 48:224–229. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2013.04.025
Wang X, Zou M, Xu X, Lei R, Li K, Li N (2009) Determination of human urinary kanamycin in one step using urea-enhanced surface plasmon resonance light-scattering of gold nanoparticles. Anal Bioanal Chem 395(7):2397–2403. doi:10.1007/s00216-009-3134-9
Zhang C, Lai C, Zeng GM, Huang DL, Tang L, Yang CP, Zhou YY, Qin L, Cheng M (2016) Nanoporous au-based chronocoulometric aptasensor for amplified detection of Pb(2+) using DNAzyme modified with au nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 81:61–67. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2016.02.053
Zhang C, Liu L, Zeng GM, Huang DL, Lai C, Huang C, Wei Z, Li NJ, Xu P, Cheng M, Li FL, He XX, Lai MY, He YB (2014) Utilization of nano-gold tracing technique: study the adsorption and transmission of laccase in mediator-involved enzymatic degradation of lignin during solid-state fermentation. Biochem Eng J 91:149–156. doi:10.1016/j.bej.2014.08.009
Zhang X, Zhao H, Xue Y, Wu Z, Zhang Y, He Y, Li X, Yuan Z (2012) Colorimetric sensing of clenbuterol using gold nanoparticles in the presence of melamine. Biosens Bioelectron 34(1):112–117. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2012.01.026
Feng JJ, Guo H, Li YF, Wang YH, Chen WY, Wang AJ (2013) Single molecular functionalized gold nanoparticles for hydrogen-bonding recognition and colorimetric detection of dopamine with high sensitivity and selectivity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5(4):1226–1231. doi:10.1021/am400402c
Lai C, Qin L, Zeng GM, Liu Y, Huang DL, Zhang C, Xu P, Cheng M, Qin XB, Wang MM (2016) Sensitive and selective detection of mercury ions based on papain and 2,6-pyridinedicarboxylic acid functionalized gold nanoparticles. RSC Adv 6(4):3259–3266. doi:10.1039/c5ra23157d
Wei H, Li B, Li J, Wang E, Dong S (2007) Simple and sensitive aptamer-based colorimetric sensing of protein using unmodified gold nanoparticle probes. Chem Commun 36:3735–3737
Li F, Zhang J, Cao X, Wang L, Li D, Song S, Ye B, Fan C (2009) Adenosine detection by using gold nanoparticles and designed aptamer sequences. Analyst 134(7):1355–1360
Zhang X, Zhang Y, Zhao H, He Y, Li X, Yuan Z (2013) Highly sensitive and selective colorimetric sensing of antibiotics in milk. Anal Chim Acta 778:63–69. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2013.03.059
Song KM, Cho M, Jo H, Min K, Jeon SH, Kim T, Han MS, Ku JK, Ban C (2011) Gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric detection of kanamycin using a DNA aptamer. Anal Biochem 415(2):175–181. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2011.04.007
Leung KH, He HZ, Chan DSH, Fu WC, Leung CH, Ma DL (2013) An oligonucleotide-based switch-on luminescent probe for the detection of kanamycin in aqueous solution. Sensors Actuators B Chem 177:487–492. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2012.11.053
Arunan E, Desiraju GR, Klein RA, Sadlej J, Scheiner S, Alkorta I, Clary DC, Crabtree RH, Dannenberg JJ, Hobza P, Kjaergaard HG, Legon AC, Mennucci B, Nesbitt DJ (2011) Defining the hydrogen bond: an account (IUPAC technical report). Pure Appl Chem 83(8). doi:10.1351/pac-rep-10-01-01
Cao Q, Zhao H, He Y, Li X, Zeng L, Ding N, Wang J, Yang J, Wang G (2010) Hydrogen-bonding induced colorimetric detection of melamine by nonaggregation-based AuNPs as a probe. Biosens Bioelectron 25(12):2680–2685
Ai K, Liu Y, Lu L (2009) Hydrogen-bonding recognition-induced color change of gold nanoparticles for visual detection of melamine in raw milk and infant formula. J Am Chem Soc 131(27):9496–9497
Qin L, Zeng GM, Lai C, Huang DL, Zhang C, Xu P, Hu TJ, Liu XG, Cheng M, Liu Y, Hu L, Zhou YY (2017) A visual application of gold nanoparticles: simple, reliable and sensitive detection of kanamycin based on hydrogen-bonding recognition. Sensors Actuators B Chem 243:946–954. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2016.12.086
Chen Z, Zhang C, Tan Y, Zhou T, Ma H, Wan C, Lin Y, Li K (2014) Chitosan-functionalized gold nanoparticles for colorimetric detection of mercury ions based on chelation-induced aggregation. Microchim Acta 182(3–4):611–616. doi:10.1007/s00604-014-1365-8
Manna U, Bharani S, Patil S (2009) Layer-by-layer self-assembly of modified hyaluronic acid/chitosan based on hydrogen bonding. Biomacromolecules 10(9):2632–2639
Raveendran P, Fu J, Wallen SL (2003) Completely “green” synthesis and stabilization of metal nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 125(46):13940–13941
Lai C, Zeng GM, Huang DL, Zhao MH, Wei Z, Huang C, Xu P, Li NJ, Zhang C, Chen M (2014) Synthesis of gold–cellobiose nanocomposites for colorimetric measurement of cellobiase activity. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 132:369–374
Kalita M, Balivada S, Swarup VP, Mencio C, Raman K, Desai UR, Troyer D, Kuberan B (2014) A nanosensor for ultrasensitive detection of oversulfated chondroitin sulfate contaminant in heparin. J Am Chem Soc 136(2):554–557
Chen J, Li Z, Ge J, Yang R, Zhang L, Qu LB, Wang HQ, Zhang L (2015) An aptamer-based signal-on bio-assay for sensitive and selective detection of kanamycin a by using gold nanoparticles. Talanta 139:226–232. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2015.02.036
Chi H, Liu B, Guan G, Zhang Z, Han MY (2010) A simple, reliable and sensitive colorimetric visualization of melamine in milk by unmodified gold nanoparticles. Analyst 135(5):1070–1075
Chen Z, Wang Z, Chen X, Xu H, Liu J (2013) Chitosan-capped gold nanoparticles for selective and colorimetric sensing of heparin. Journal of Nanoparticle Research : an Interdisciplinary Forum for Nanoscale Science and Technology 15:1930. doi:10.1007/s11051-013-1930-9
Rinaudo M (2006) Chitin and chitosan: properties and applications. Prog Polym Sci 31(7):603–632
Agnihotri SA, Mallikarjuna NN, Aminabhavi TM (2004) Recent advances on chitosan-based micro-and nanoparticles in drug delivery. Journal of Controlled Release : Official Journal of the Controlled Release Society 100(1):5–28. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2004.08.010
Liao QG, Wei BH, Luo LG (2016) Aptamer based fluorometric determination of kanamycin using double-stranded DNA and carbon nanotubes. Microchim Acta 184(2):627–632. doi:10.1007/s00604-016-2050-x
Wang Y, Ma T, Ma S, Liu Y, Tian Y, Wang R, Jiang Y, Hou D, Wang J (2016) Fluorometric determination of the antibiotic kanamycin by aptamer-induced FRET quenching and recovery between MoS2 nanosheets and carbon dots. Microchim Acta 184(1):203–210. doi:10.1007/s00604-016-2011-4
De Jong WH, Hagens WI, Krystek P, Burger MC, Sips AJAM, Geertsma RE (2008) Particle size-dependent organ distribution of gold nanoparticles after intravenous administration. Biomaterials 29(12):1912–1919. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.12.037
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by the Program for the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51408206, 51378190, 51278176, 51579098, 51521006, 21507034), the National Program for Support of Top-Notch Young Professionals of China (2014), the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-13-0186), the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (IRT-13R17), Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department (No.521293050), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, China (2016A030310022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 489 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lai, C., Liu, X., Qin, L. et al. Chitosan-wrapped gold nanoparticles for hydrogen-bonding recognition and colorimetric determination of the antibiotic kanamycin. Microchim Acta 184, 2097–2105 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2218-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2218-z