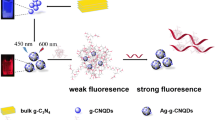
Abstract
A method is introduced for the fluorometric turn-on detection of cytochrome C (cyt c) by using a specific aptamer and nanosheets composed of fluorescent graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) nanosheets. Bulk g-C3N4 was obtained by pyrolysis of melamine at 550 °C. The nanosheets were characterized by scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. The material was then subjected to protonation and exfoliation to obtain blue fluorescent g-C3N4 nano-sheets. The adsorption of aptamers on the surface of the g-C3N4 nanosheets leads to quenching of its fluorescence (measured at excitation/emission wavelengths of 320/450 nm), but fluorescence is restored on addition of cyt c. Response is linear in the 16 to 140 nM cyt c concentration window, and the detection limit is as low as 2.6 nM. The assay is simple, inexpensive, and can be easily performed. It is selective for cyt c over a number of interfering species. The method was successfully applied to the determination of cyt c in spiked human serum samples.

The adsorption of aptamers on the surface of graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) nanosheets leads to quenching of its fluorescence, which is restored on addition of cytochrome C (cyt c). Response is linear in the 16 to 140 nM cyt c concentration window, and the detection limit is as low as 2.6 nM.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Raphael AL, Gray HB (1991) Semisynthesis of axial-ligand (position 80) mutants of cytochrome c. J Am Chem Soc 113:1038
Green DR, Kroemer G (2004) The pathophysiology of mitochondrial cell death. Science 305:626
Huttemann M, Pecina P, Rainbolt M, Sanderson TH, Kagan VE, Samavati L et al (2011) The multiple functions of cytochrome c and their regulation in life and death decisions of the mammalian cell: from respiration to apoptosis. Mitochondrion 11:369
Ow YP, Green DR, Hao Z, Mak TW (2008) Cytochrome c: functions beyond respiration. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:532
Gao LL, Li FR, Jiao P, Yang MF, Zhou XJ, Si YH et al (2011) Paris chinensis dioscin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells. World J Gastroenterol 17:4389
Shen Y, Yang XF, Wu Y, Li C (2008) Sensitive spectrofluorimetric determination of cytochrome C with spirocyclic rhodamine B hydrazide in micellar medium. J Fluoresc 18:163
Appaix F, Minatchy M-N, Riva-Lavieille C, Olivares J, Antonsson B, Saks VA (2000) Rapid spectrophotometric method for quantitation of cytochrome c release from isolated mitochondria or permeabilized cells revisited. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics 1457:175
Liu JM, Yan XP (2011) Ultrasensitive, selective and simultaneous detection of cytochrome c and insulin based on immunoassay and aptamer-based bioassay in combination with Au/Ag nanoparticle tagging and ICP-MS detection. J Anal At Spectrom 26:1191
Li X, Liu H, He X, Song Z (2010) Determination of cytochrome c in human serum and pharmaceutical injections using flow injection chemiluminescence. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 160:1065
Del Valle-Mondragon L, Ramirez-Ortega M, Zarco-Olvera G, Sanchez-Mendoza A, Pastelin-Hernandez G, Tenorio-Lopez FA (2008) Capillary zone electrophoretic determination of cytochrome c in mitochondrial extracts and cytosolic fractions: application to a digitalis intoxication study. Talanta 74:478–488
Crouser ED, Gadd ME, Julian MW, Huff JE, Broekemeier KM, Robbins KA et al (2003) Quantitation of cytochrome c release from rat liver mitochondria. Anal Biochem 317:67
Pandiaraj M, Madasamy T, Gollavilli PN, Balamurugan M, Kotamraju S, Rao VK et al (2013) Nanomaterial-based electrochemical biosensors for cytochrome c using cytochrome c reductase. Bioelectrochemistry 91:1
Luo D, Huang J (2009) Determination of cytochrome c and other heme proteins using the reduction wave of mercury protoporphyrin IX groups generated by a hydroxylamine induced replacement reaction. Anal Chem 81:2032
Chen TT, Tian X, Liu CL, Ge J, Chu X, Li Y (2015) Fluorescence activation imaging of cytochrome c released from mitochondria using aptameric nanosensor. J Am Chem Soc 137:982
Xi X, Li J, Wang H, Zhao Q, Li H (2015) Non-enzymatic photoelectrochemical sensing of hydrogen peroxide using hierarchically structured zinc oxide hybridized with graphite-like carbon nitride. Microchim Acta 182:1273
Lee EZ, Jun YS, Hong WH, Thomas A, Jin MM (2010) Cubic mesoporous graphitic carbon (IV) nitride: an all-in-one chemosensor for selective optical sensing of metal ions. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 49:9706
Rong M, Lin L, Song X, Wang Y, Zhong Y, Yan J et al (2015) Fluorescence sensing of chromium (VI) and ascorbic acid using graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets as a fluorescent "switch". Biosens Bioelectron 68:210
Lin LS, Cong ZX, Li J, Ke KM, Guo SS, Yang HH et al (2014) Graphitic-phase C3N4 nanosheets as efficient photosensitizers and pH-responsive drug nanocarriers for cancer imaging and therapy. J Mater Chem B 2:1031
Lin T, Zhong L, Wang J, Guo L, Wu H, Guo Q et al (2014) Graphite-like carbon nitrides as peroxidase mimetics and their applications to glucose detection. Biosens Bioelectron 59:89
Li Y, Zhang H, Liu P, Wang D, Li Y, Zhao H (2013) Cross-linked g-C3 N4/rGO nanocomposites with tunable band structure and enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity. Small 9:3336
Wang Q, Wang W, Lei J, Xu N, Gao F, Ju H (2013) Fluorescence quenching of carbon nitride nanosheet through its interaction with DNA for versatile fluorescence sensing. Anal Chem 85:12182
Lau IP, Ngan EK, Loo JF, Suen YK, Ho HP, Kong SK (2010) Aptamer-based bio-barcode assay for the detection of cytochrome-c released from apoptotic cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 395:560
Choi J, Shin J, Lee J, Cha M (2012) Magnetic response of mitochondria-targeted cancer cells with bacterial magnetic nanoparticles. Chem Commun (Camb) 48:7474
Zheng Y, Liu J, Liang J, Jaroniec M, Qiao SZ (2012) Graphitic carbon nitride materials: controllable synthesis and applications in fuel cells and photocatalysis. Energy Environ Sci 5:6717
Zhang X, Xie X, Wang H, Zhang J, Pan B, Xie Y (2013) Enhanced photoresponsive ultrathin graphitic-phase C3N4 nanosheets for bioimaging. J Am Chem Soc 135:18
Ge L, Han C, Liu J (2012) In situ synthesis and enhanced visible light photocatalytic activities of novel PANI-g-C3N4 composite photocatalysts. J Mater Chem 22:11843
Liu Z, Xiao J, Wu X, Lin L, Weng S, Chen M et al (2016) Switch-on fluorescent strategy based on N and S co-doped graphene quantum dots (N-S/GQDs) for monitoring pyrophosphate ions in synovial fluid of arthritis patients. Sens Actuators, B Chem 229:217
Hu K, Zhong T, Huang Y, Chen Z, Zhao S (2015) Graphitic carbon nitride nanosheet-based multicolour fluorescent nanoprobe for multiplexed analysis of DNA. Microchim Acta 182:949
Wang T, Zhang S, Mao C, Song J, Niu H, Jin B et al (2012) Enhanced electrochemiluminescence of CdSe quantum dots composited with graphene oxide and chitosan for sensitive sensor. Biosens Bioelectron 31:369
Zhang W, He XW, Chen Y, Li WY, Zhang YK (2011) Composite of CdTe quantum dots and molecularly imprinted polymer as a sensing material for cytochrome c. Biosens Bioelectron 26:2553
Ocaña C, Lukic S, Del Valle M (2015) Aptamer-antibody sandwich assay for cytochrome c employing an MWCNT platform and electrochemical impedance. Microchim Acta 182:2045
Shamsipur M, Molaabasi F, Hosseinkhani S, Rahmati F (2016) Detection of early stage apoptotic cells based on label-free cytochrome c assay using Bioconjugated metal nanoclusters as fluorescent probes. Anal Chem 88:2188
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Research Council of University of Tehran for the financial support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 524 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salehnia, F., Hosseini, M. & Ganjali, M.R. A fluorometric aptamer based assay for cytochrome C using fluorescent graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets. Microchim Acta 184, 2157–2163 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2130-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2130-6